GRW Ball Bearings from a Leading UK Supplier
As a trusted UK distributor of GRW bearings, we deliver precision-engineered solutions to meet both technical and commercial requirements. Whether you need bespoke designs for ultra-high precision projects or readily available components, rely on our expertise honed since 1938.

Uncompromising Quality in GRW Bearings
We provide an extensive range of GRW ball bearings, engineered to handle complex applications without sacrificing affordability or performance. With over 80 years of refined quality standards, we ensure dependable results in the most demanding industries.
- Precision grades: ABEC-1 through ABEC-9
- Standard configurations available
- Carbon chrome and exotic materials
- Full customisation for unique requirements
- Specialist coatings and lubricants
- Immediate stock or built-to-order options
Bearing product range
A complete range of ball bearings from GRW and configurations designed to carry load, reduce friction and support rotating and oscillating systems in any application.
See the full catalogue of GRW bearings by IEC
Utilise our customised Bearing Selector tool here.


Markets
IEC have a range of mechanical solutions to suit a broad spectrum of markets and applications, from aerospace to skateboards.
Markets
IEC have a range of mechanical solutions to suit a broad spectrum of markets and applications, from aerospace to skateboards.
Markets
Molestie nunc non blandit massa. Iaculis nunc sed augue lacus. Malesuada nunc vel risus commodo. Dui id ornare arcu odio ut sem nulla pharetra.
Case Studies
We act as partners, making our customers’ engineering challenges ours to solve, removing stress and freeing up time to turn ideas in to innovation.

Product:
Application:
Challenge:
Solution:

Product:
Application:
Challenge:
Solution:

Product:
Application:
Challenge:
Solution:

Download technical documents and brochures.
Keep up to date with the latest product and technical information from IEC and its international supply partners.
Related products
Fey Laminar Seal Rings
Fuji Bearing Lock Nuts
Schnorr Load Washers
GRW Bearings Catalogue
HIGH PRECISION BALL BEARINGS by GRW
GRW manufactures high precision ball bearings with bores of up to 30mm and inch series from 0.040″ to 0.500″. These bearings are available in plain and flanged executions and can be supplied open, or with shields or seals, ensuring versatility for various applications.
High precision ball bearings from GRW are produced to the highest quality standards, with grades up to ISO P4A or ABEC 9, making them exceptionally suitable for demanding precision requirements. Typical applications include missile guidance systems, electric motor parts, encoders, and precision instrumentation of all types. These bearings are designed to provide reliable performance in critical applications where accuracy and durability are paramount.

The exclusive SV material used in GRW high precision ball bearings offers exceptional corrosion resistance, making it ideal for hybrid bearings (ceramic balls) and high-speed spindle bearings. These specialised bearings are available in bore sizes ranging from 3mm to 17mm, catering to specific high-speed and high-precision applications.
GRW also offers standard sizes with special features, special sizes, duplex, and super duplex configurations. In addition, customised ball bearing assemblies are available to meet unique application needs. This ISO9001:2008-approved company ensures that all bearings meet stringent quality standards, providing peace of mind and reliability for engineers and designers.
Benefits of GRW High Precision Ball Bearings:
- Exceptional Accuracy: Manufactured to ISO P4A or ABEC 9 standards, ensuring precise performance.
- Versatile Configurations: Available in plain and flanged executions, with options for shields or seals.
- Corrosion Resistance: The exclusive SV material provides outstanding resistance to corrosion, enhancing longevity.
- High-Speed Performance: Ideal for high-speed applications with hybrid bearings (ceramic balls) and spindle bearings.
- Custom Solutions: GRW offers customised ball bearing assemblies to meet specific application requirements.
- Reliability: Produced by an ISO9001:2008-approved company, guaranteeing high quality and dependable performance.
Whether you need bearings for aerospace parts, precision medical components, robotics, or precision instruments, GRW’s high precision ball bearings are engineered to meet the most demanding specifications. The combination of high accuracy, versatile configurations, and robust materials ensures that these bearings can handle the toughest applications with ease.
For more information on GRW’s high precision ball bearings and to discuss your specific application needs, please contact us. Our team of experts is ready to provide the guidance and support necessary to find the perfect bearing solution for your project.
Deep Groove Ball Bearings Index
| Click on tick to open page | Standard Open Ball Bearings | 2Z & 2RZ Shield Ball Bearings | ||||||
| Bearing Series | Open | Open with Flange | Open with Extended Inner Ring | Open Flange with Extended Inner Ring | Shield | Shield with Flange | Shield with Extended Inner Ring | Flange Shield with Extended Inner Ring |
| Metric | ||||||||
| Inch | ||||||||
| Click on tick to open page | Sealed Ball Bearings | |||||||
| Bearing Series | 2TS Seal | 2TS Seal with Flange | 2TS Seal with Extended Inner Ring | 2TS Seal with Flange & Extended Inner Ring | 2RS Seal | 2RS Seal with Flange | 2RS Seal with Extended Inner Ring | 2RS Seal with Flange & Extended Inner Ring |
| Metric | ||||||||
| Inch | ||||||||
| Dimensions (mm) | Used for | |||||
| Shims | Spring Washers | |||||
| d x D | S1 | d x D | H | S | Shaft Types | Housing Types |
| AS2.25X3.20 | 0.08 0.10 | WF2.15X3.10 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 682; 692; 5/64 | 1016 |
| AS2.80X3.90 | 0.08 0.10 | WF2.70X3.80 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 60/2.2; 68/2.5; 69/2.5; 3/32 | 68/1.5; 691; 1191 |
| AS3.30X4.40 | 0.08 0.10 0.12 | WF3.20X4.30 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 623; 683; 693; 1/8A; 1/8B; 3173; 1/8A/6; 1/8B/083 | |
| AS3.80X4.90 | 0.08 0.10 0.12 | WF3.70X4.80 | 0.55 | 0.10 | 682; 69/1.5 | |
| AS4.30X5.85 | 0.10 0.12 0.15 | WF4.20X5.75 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 604; 624; 634; 684; 694 | 68/2.5; 692; 3967 |
| AS4.90X6.20 | 0.10 0.12 0.15 | WF4.80X6.10 | 0.60 | 0.12 | 3/16; 4763A; 4763B | 5/64; 3175 |
| AS5.30X6.85 | 0.10 0.12 0.15 | WF5.20X6.75 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 625; 635; 685; 695 | 683; 69/2.5 |
| AS6.30X7.85 | 0.12 0.15 0.18 | WF6.20X7.75 | 0.70 | 0.15 | 626; 686; 696 | 60/25; 693; 3/32; 1/BA; 3967; 4763A |
| AS7.30X8.80 | 0.12 0.15 0.18 | WF7.20X8.70 | 0.90 | 0.15 | 607; 627; 687; 697 | 684 |
| WF7.20X12.00* | 1.40 | 0.125 | 607; 627 | 63508; 7938; 1/88/083 | ||
| AS8.30X9.80 | 0.15 0.18 0.20 | WF8.20X9.70 | 0.85 | 0.18 | 608; 688; 698; 7938 | 623 |
| AS9.30X10.80 | 0.15 0.18 0.20 | WF9.20X10.70 | 1.15 | 0.18 | 609; 629; 689; 699 | 685; 694 |
| AS10.30X11.80 | 0.18 0.20 0.22 | WF10.20X11.70 | 1.05 | 0.20 | 6000; 6800; 6900; 3/8 | 604 |
| WF10.50X15.80* | 1.70 | 0.20 | 6000 | 625; 634 | ||
| AS11.30X12.80 | 0.18 0.20 0.22 | WF11.20X12.70 | 1.30 | 0.20 | 624; 686; 695 | |
| AS12.30X13.80 | 0.20 0.22 0.25 | WF12.20X13.70 | 1.30 | 0.22 | 687 | |
| AS 13.30 X 14.80 | 0.20 0.22 0.25 | WF13.20X14.70 | 1.30 | 0.22 | 696 | |
| WF13.20X18.80* | 1.60 | 0.20 | 607; 626; 635; ¼ | |||
| AS14.35X15.80 | 0.22 0.25 0.30 | WF14.20X15.65 | 1.55 | 0.25 | 625; 634; 688; 1/4A | |
| AS15.35X16.80 | 0.22 0.25 0.30 | WF15.20X16.65 | 1.55 | 0.25 | 689; 697 | |
| WF15.80X21.80* | 1.60 | 0.20 | ||||
| AS 16.40 X 18.80 | 0.25 0.30 0.35 | WF16.20X18.55 | 2.15 | 0.30 | 607; 626; 635; 6800; 698; ¼ | |
| WF17.30X23.80* | 1.50 | 0.25 0.30 | 609 | |||
| WF19.30X25.80* | 1.90 1.80 | 0.35 0.30 | 6000; 629 | |||
GRW ACCESSORIES - Shims & Spring Washers
GRW Bearing Accessories
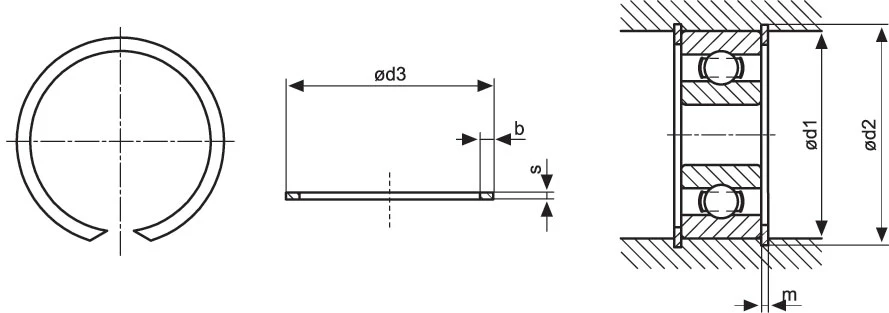
Shaft retaining rings
| Type | Dimensions (mm) | |||||
| Bore | Retaining Ring | Groove | ||||
| d1 Ø | d3 max. | b + 0.10 | s + 0.02 | d2 + 0.05 | m + 0.03 | |
| WSR3 | 3 | 2.60 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 2.70 | 0.33 |
| WSR4 | 4 | 3.60 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 3.70 | 0.33 |
| WSR5 | 5 | 4.50 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 4.60 | 0.44 |
| WSR6 | 6 | 5.45 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 5.60 | 0.44 |
| WSR7 | 7 | 6.45 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 6.60 | 0.44 |
| WSR8 | 8 | 7.35 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 7.50 | 0.55 |
| WSR9 | 9 | 8.30 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 8.50 | 0.55 |
| WSR10 | 10 | 9.25 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 9.50 | 0.55 |
ACCESSORIES
Bore retaining rings
| Type | Dimensions (mm) | |||||
| Bore | Retaining Ring | Groove | ||||
| d1 Ø | d3 max. | b + 0.10 | s + 0.02 | d2 + 0.05 | m + 0.03 | |
| BSR4 | 4 | 4.40 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 4.30 | 0.33 |
| BSR5 | 5 | 5.45 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 5.30 | 0.33 |
| BSR6 | 6 | 6.45 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 6.30 | 0.33 |
| BSR7 | 7 | 7.50 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 7.30 | 0.33 |
| BSR8 | 8 | 8.60 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 8.40 | 0.44 |
| BSR9 | 9 | 9.60 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 9.40 | 0.44 |
| BSR10 | 10 | 10.65 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 10.40 | 0.44 |
| BSR11 | 11 | 11.65 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 11.40 | 0.44 |
| BSR12 | 12 | 12.75 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 12.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR13 | 13 | 13.75 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 13.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR14 | 14 | 14.80 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 14.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR15 | 15 | 15.80 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 15.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR16 | 16 | 16.85 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 16.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR17 | 17 | 17.85 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 17.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR19 | 19 | 20.00 | 1.10 | 0.60 | 19.60 | 0.66 |
GRW SPECIAL BEARINGS
Thanks to its flexible manufacturing facilities GRW can provide a wide range of special ball bearings in addition to standard and high precision ball bearings made of chrome and stainless steel.
The special characteristics are:
- Special shapes
- Special lubricants
- Special treatments
Furthermore they also manufacture rotationally symmetrical turned parts.
Special shapes
Superduplex bearings
Double-row deep groove radial bearing or angular contact ball bearing with divided inner or outer ring are called Superduplex bearings. The raceways are on the one-piece ring. This reliably prevents any radial displacement during installation and ensures optimum running characteristics. The divided rings (inner or outer rings) are paired in accordance with customer’s wishes. This ensures that GRW bearings have the desired axial preload.
Extraduplex bearings
Extraduplex bearings are double-row deep groove radial bearings or angular contact ball bearings with divided inner or outer ring. The ring is laser-welded under a defined preload. The advantages of this bearing variant are also evident during installation: any radial displacement or variation of the axial preload is reliably excluded.
Tandem duplex bearings
In a Tandem Duplex bearing, which is a double-row deep groove radial bearing, the raceways are accurately aligned to each other. These bearings are suitable for taking radial loads and axial loads on one side only.
Bearings with modified external design
At customer’s request, GRW manufactures single- or double-row bearings with spherical outer ring or groove in the outer ring. Optionally, bearings are available with overmolded synthetic or rubber, or with displaced pitched circle diameter (to optimize the stiffness of the bearings rings in their fit on the shaft or in the housing).
Bearings with integrated shaft
Bearing and shaft do not necessarily have to be considered separately. The GRW product range comprises bearings with integrated shaft. The raceway is ground on the shaft. The shaft is delivered fully mounted with ball set, retainer, and outer ring.
Bearings with housing
For these types, the raceway of the outer ring is ground in the housing.
Complex housings with flange and thread keep the tolerances during installation to a minimum.
SPINDLE/ANGULAR CONTACT BALL BEARINGS
Spindle ball bearings are angular contact ball bearings which, depending on the type, have a relieved land on the inner ring (AC2) or the outer ring (AC1). Axial forces can thus only be accepted in one direction. Spindle ball bearings can be used as single ball bearings or as ball bearing pairs in back to back, face to face or tandem arrangement.

GRW spindle ball bearings have the following characteristics:
- Production in high precision quality (grade PS, P4, P2 or ABEC5, ABEC 7, ABEC9)
- One part solid phenolic retainer (TA, TB, see ‘Retainers for Miniature Ball Bearings’) [NOTE – PUT A LINK TO THE RELEVANT PAGE]
- Larger number of balls than a standard ball bearing
- Contact angle 15o (other angles available upon request)
- Available with steel balls or ceramic balls
- The preload for ball bearing pairs is selected according to the applied load (light, medium or heavy preload)
- Spindle ball bearings are generally lubricated with oil
These characteristics allow the ball bearings to run very accurately at high speeds. At the same time these ball bearings are very rigid and have minimum vibration levels:
The standard type is:
AC1 TA
Relieved on outer ring shoulder, ball bearing cannot be disassembled, solid phenolic retainer guided on outer ring.
Other types including ball bearings with removable inner rings are available upon request.
GRW DUPLEX BEARINGS
Duplex bearings are two matched bearings which, depending on the requirements, provide the following characteristics:
- Accurate bearing positioning in radial and axial directions, which can vary from defined clearance to controlled rigidity
- Limitation of the system’s yield
- High load capacity compared to single bearings
The matching of the bearings is achieved by loading each single bearing with the desired preload and then grinding the inner or outer rings until the surfaces of both rings are flush with each other.
Two of the bearings treated in this manner are assembled according to the instructions on the package and loaded axially until the ground faces meet, this repeats the preload previously set in manufacture. Depending on the matching used either the inner rings or the outer rings or possibly both are preloaded against each other.

The ball bearings must be mounted according to the instructions on the packaging labels. If there are no special customer requirements, our ball bearings are paired with a preload of 5N and a nominal contact angle of 15o. In principle this can, however, be altered to suit the operating conditions and requirements. The preload should not, however, be set higher than necessary as it will unnecessarily increase the torque. This has a direct influence on the life of the ball bearing.
The radial clearance should be set higher than usual for Duplex bearings so that the contact angle, the rigidity and the axial loading become greater.
In order to achieve optimum fits Duplex bearings are always calibrated into two groups on the bore and outside diameter and supplied packaged with the same code. They should also, if possible, be fitted with calibrated shafts and housings (see ‘Calibration of Bore and Outside Diameter’).
The ball bearing fits should therefore be selected carefully as an interference fit on the inner and outer ring would change the preload.
EXPLANATION OF BASIC TERMS
Closure
Protects the interior of the ball bearing against contamination and the components surrounding the ball bearing against escaping lubricant. The protection grade depends on the type of closure chosen and on the operating conditions. You will find more information on this in ‘Closures’.
Alignment
Mounting configuration where the axes of the two bearings are identical.
Retainer (Cage)
A ring with equally spaced ball pockets, which separates the balls from each other in the bearing raceway.
Combined Load
A force which is neither purely radial nor axial in nature, but simultaneously perpendicular and parallel to the axis.
Ball Pockets
The inner surfaces of a retainer which touch the ball surfaces.
Raceway Profile
The form of the raceway as seen in cross section.
Roundness
The roundness deviation is calculated by measuring the radius deviation using scanning equipment. You will find detailed information on this amongst other places in DIN ISO 4291 and DIN ISO 6318.
Curvature
The proportion of the radius of the raceway profile to the diameter of the ball.
Curvature [%] = 100 x radius of raceway profile
Ball diameter
Angular Contact Bearing, non-separable
(AC ball bearing) – Bearings with inner or outer ring lands relieved to facilitate snap-in assembly. This bearing, similar to a magneto bearing, can take axial loads in one direction only.
Angular Contact Bearing, separable
(L2T ball bearing) – Bearings with inner ring land relieved to facilitate removal of inner ring. The ball set is held in the outer ring by a special retainer. This bearing, similar to a magneto bearing, can take axial loads in one direction only.
Quality Grade
Term for the tolerances of a ball bearing. The individual tolerance values are defined in various standards such as DIN 620 T1, ISO 492, ISO 1224, AFBMA Std. 12 and 20. The definitions of the terms are defined among other places in DIN ISO 1132 and the measuring method in DIN 620 T1 and ISO TR 9274.
Full Complement Bearing
A bearing with a maximum number of balls. These bearings have no retainer. See ‘Retainer Types’ about the different types.
CLOSURES
Ball bearing closures fulfil two tasks at the same time: firstly they prevent contamination and secondly then contain lubricants.
Non-contact closures
Because of the proximity with the inner ring land the ball bearing closure forms an effective gap seal. It neither increases the torque nor influences the maximum speed compared with open ball bearings as the shields do not touch the inner ring. This is sufficient for most applications.
Metal shields
The shields are stamped from stainless steel on the majority of ball bearings. They are fastened to the outer ring with a circlip and can thus be removed. Ball bearings can also be fitted with pressed-in shields made from deep drawing steel sheet.
Rubber closures
The RZ closure is made of molded tuber with metal stiffener and can be used at temperatures from -30oC to 120oC. This closure is fastened in the outer ring by the rubber border.
Seal with inner ring contact
This ball bearing seal touches the inner ring land. This causes an increase in torque.
Teflon seal
The TS seal is made from glass-fibre reinforced Teflon which is fastened in the outer ring by a circlip.
Teflon seals can be used at working temperatures of -240oC to 300oC. They prevent contamination. However an hermetic sealing cannot be achieved. The torque is lower than for rubber seals due to the favourable low friction combination (PTFE/Steel) and the low contact force of the sealing lip.
TS seals are universally resistant to chemicals. The ball bearings are normally made from stainless steel, chrome steel can also be provided in appropriately large quantities.
Rubber seal
The RS seal is made of molded rubber with metal stiffener and can be used at temperatures of -30oC to 120oC.
The VS seal is made of molded Viton with metal stiffener and is suitable for temperatures of -20oC to 230oC.
Both seals are fastened in the outer ring by the rubber border.
We would like to remind you that certain lubricants cannot be used with rubber. Please contact us about difficult operating conditions.
Special closures
In addition to the standard closures GRW also manufacture special closures and combinations of different closers. Please contact us for further information.
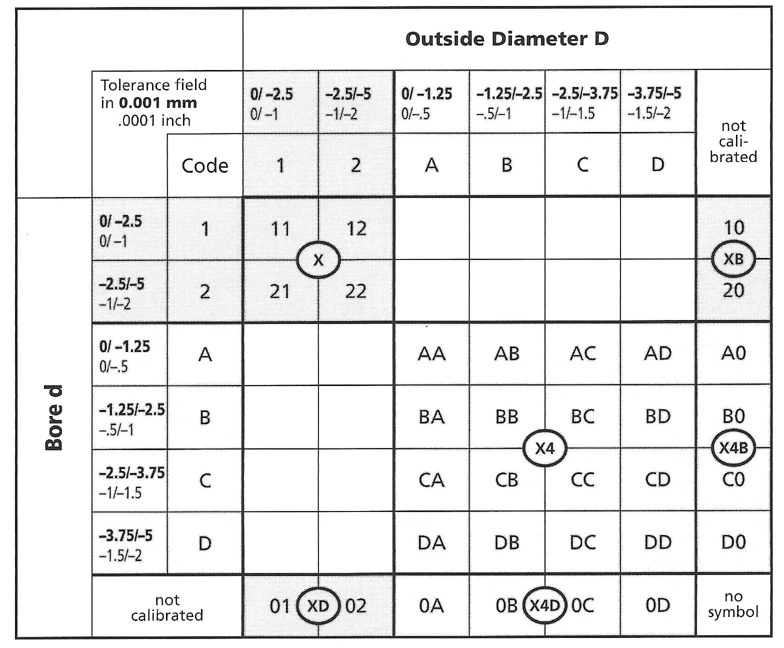
CALIBRATION OF BORE & OUTSIDE DIAMETER
| Calibration | In groups of 2.5mm or .0001 inch | In groups of 1.25mm or .00005 inch |
| Bore d and outside diameter D | X | X4 |
| Bore d only | XB | X4B |
| Outside diameter D only | XD | X4D |
Examples:
Code 21:
Bore -2.5/-5µm
O.D. 0/02.5µm
Code BC:
Bore -1.25/-2.5µm
O.D. -2.5/-3.75µm
Code A0:
Bore 0/-1.25µm
O.D. Not calibrated
Code 02:
Bore Not calibrated
O.D. -2.5/-5µm
Method of group classification:
Bore diameter: the smallest measured diameter determines the class
Outside diameter: the largest measured diameter determines the class
GRW Bearings LUBRICANTS
Lubricating oils
Lubricating oil is mainly used where minimum torque is required. GRW ball bearings, either open or with one closure, are preserved with oil ex works if no special lubrication is specified.Lubricating greases
GRW ball bearings with closures on both sides and also our ball bearings with one closure together with a snap retainer are greased ex works if no special lubrication is specified. Regarding this we would mention that lubricating greases with EP additives are not suitable for low-noise ball bearings. The ball bearings can be lubricated with oils and greases other than those listed in the tables upon request and in quantities agreed upon. There are around 250 lubricants to choose from. Please contact us for specific details.Special treatment
Special operating conditions go beyond the limits of application even for the special lubricants which are used. In such cases it is possible to specify suitable ball bearings by using different coatings. Galvanically applied precious metal layers, graphite, MoS2 etc. are used here. This treatment is used for ball bearings to work in vacuum systems up to ultra-high vacuums (UHV), in aviation and aerospace technology and at extreme temperatures. Hard coatings, for example, TiC, TiN or highest grade chromium are also applied for special applications. Please contact us for further information.Table 3: Lubricating Oils
| Code | Brand Name | Manu-facturer | Basic Oil | Operating Temperature Range | Viscosity at 40oC/100oC [mm2/s] | Specification |
| L001 | Aero Shell Fluid 12 | Shell | Ester | -40 to 100oC | 15/3.7 | MIL-L-6085 C |
| L010 | Isoflex PDP 38 | Klüber | Ester | -65 to 100oC | 12/3.2 | Following MIL-L-6085 |
| L014 | Krytox 143 AC | Du Pont | PFPE | -34 to 288oC | 200/30 | – |
| L020 | Shell Ensis L | Shell | Mineral | -10 to 100oC | 32/5.5 | – |
| L085 | Nyosil M 25 | Nye | Chlorphenyl-silikon | -70 to 200oC | 56/20 | – |
| L027 | Synthetic Oil 200 A (Winsor Lube L 245 X) | Nye | Ester | -54 to 200oC | 13/3.4 | MIL-L-6085 C |
| L065 | Gargoyle Arctic SHC 224 | Mobil Oil | Polyalphao-lefin | -45 to 140oC | 29/5.6 | USDA-H1 |
Table 3: Lubricating Process
| Code | Brand Name | Manu-facturer | Composition | Operating Temperature Range | Viscosity at 40oC/ 100oC [mm2/s] | Speed Factor | Specifi-cation |
| G305 | ASG 7 | Shell | Diester/ microgel | -73 to 149oC | 15/3.1 | Not known | MIL-G-23827 B |
| G310 | Asonic GLY 32 | Klüber | Ester + polyalpha-olefin/ lithium | -50 to 140oC | 25/5 | 1.000.000 | – |
| G315 | Barrierta L 55/2 | Klüber | PFPE/PTFE | -40 to 260oC | 400/38 | 300.000 | – |
| G316 | Nye Instrument Grease 704 B | Nye | Diester/ lithium | -65 to 150oC | 11.8/3.25 | 300.000 | – |
| G331 | Isoflex Super LDS 18 | Klüber | Mineral oil + ester / lithium | -50 to 120oC | 15/3.7 | 1.000.000 | – |
| G332 | Isoflex Topas NB 52 | Klüber | Polyalphao-lefin/barium complex | -50 to 150oC | 30/5.5 | 1.000.000 | Following MIL-G-81322 |
| G338 | Krytox 240 AC | Du Pont | PFPE/PTFE | -34 to 288oC | 200/30 | 400.000 | MIL-G-27617 Type III MIL-G-27616 |
| G340 | Longtime PD2 | Optimol | Mineral oil/lithium | -35 to 140oC | 95/9.0 | 1.000.000 | – |
| G366 | Nyogel 781 D (versilube G300) | Nye | Ghlorophe-nylsilicon/ lithium | -70 to 200oC | 53/18.9 | 200.000 | – |
| G462 | Unisilkon L50/2 | Klüber | Silicon/PTPE | -50 to 200oC | 112/27 | 200.000 | – |
| G463 | Mobilgrease FM 102 | Mobil Oil | White oil/ aluminium complex | -20 to 120oC | 108/10.5 | 400.000 | FDA 178.3570 USDA-H1 |
MATERIALS FOR RINGS & BALLS
| Prefix | – | SS |
| DIN DIN SAE AFNOR | 1O0Cr6 1.3505 52100 100Cr6 | X65Cr13 1.4037 |
| C % Si % Mn % P % S % Cr % Mo % | 0.95 – 1.19 0.15 – 0.35 0.25 – 0.45 0.03 max. 0.025 max. 1.35 – 1.65 – | 0.60 – 0.75 1 max. 1 max. 0.04 max. 0.03 max. 12 – 14 0.75 max. |
RETAINERS/CAGE TYPES FOR MINIATURE BALL BEARINGS
| GRW Retainer /Cage Code | Picture | Description/Material | Application Range/Purpose |
| E J Y |  | Two-piece ribbon retainer made of: – steel sheet (E) – stainless steel sheet (J) – brass sheet (Y) | For deep groove ball bearings. For stainless steel ball bearings; retainer from stainless steel sheet. This retainer can also be clinched loosely to reduce torque. |
| JH |  | One-piece stainless steel snap type retainer. | For deep groove ball bearings. Mainly used for small ball bearings at low and medium speeds. |
| TNH |  | One-piece moulded synthetic snap type retainer. | For deep groove ball bearings. Good running and torque characteristics for medium speed range. Working temperature -30oC to 80oC (short term 100oC). |
| TN9H | One-piece glass-fibre reinforced moulded synthetic snap type retainer. | For deep groove ball bearings. Speed range high than TNH retainer. Working temperature -30oC to 120oC (short term 180oC). | |
| THA THB |  | Machined one-piece snap type retainer made from reinforced phenolic resin. A = outer ring guided B = inner ring guided | For high speed deep groove ball bearings. High rigidity and emergency running characteristics. Working temperature -50oC to 140oC. Can be vacuum impregnated with oil. |
| TXHA TXHB | Machined one-piece snap type retainer made from special materials. X stands for a number indicating the material. A = outer ring guided B = inner ring guided | For high speed deep groove ball bearings. High rigidity and emergency running characteristics. Working temperature -50oC to 260oC depending on material. | |
| TA TB |  | Machined one-piece, solid retainer made from fabric reinforced phenolic resin. A = outer ring guided B = inner ring guided Only for AC types | For high speed angular contact/spindle ball bearings. High rigidity and emergency running characteristics. Working temperature -50oC to 140oC. Can be vacuum impregnated. |
| TXA TXB | Machined one-piece, solid retainer made from special material. X stands for a number indicating the material. A = outer ring guided B = inner ring guided Only for AC types | For high speed angular contact/spindle ball bearings. High rigidity and emergency running characteristics. Working temperature -50oC to 260oC. Can be vacuum impregnated. | |
| VAC1 VAC2 | Full complement ball bearing, without retainer, cannot be disassembled. VAC1 = one shoulder relieved on outer ring. VAC2 = one shoulder relieved on inner ring. | Used for medium speeds and high axial loads in one direction only. |
THREE TYPES OF DUPLEX ASSEMBLY FOR RADIAL BALL BEARINGS
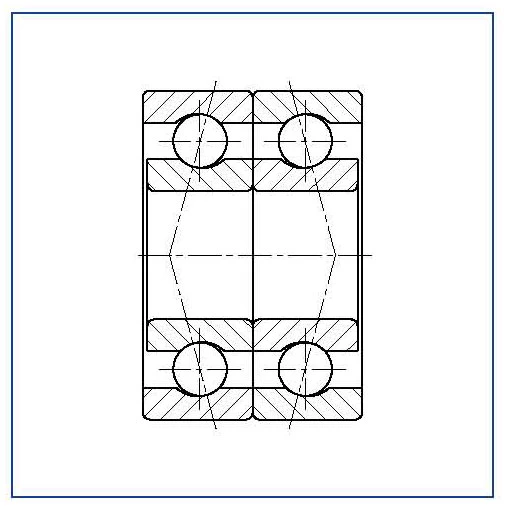
Back to Back
O arrangement (DB)
(reference 1)
With the ‘back to back’ bearing pair the inner rings are claimed together. The contact angle lines between the outer ring raceway, ball and inner raceway diverge. This results in a maximum spread giving high rigidity. This is the reason why this type of duplex bearing is most commonly used.
Figure 21 – back to back
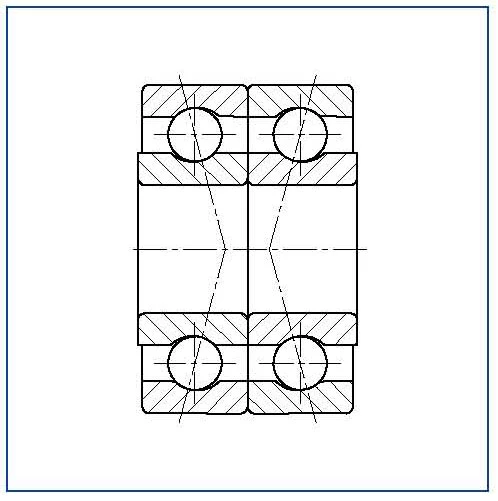
Face to Face
X arrangement (DF)
(reference 2)
With the ‘face to face’ bearing pair the outer rings are claimed together. The contact lines converge resulting in a smaller spread and more elastically.
Figure 22 – face to face
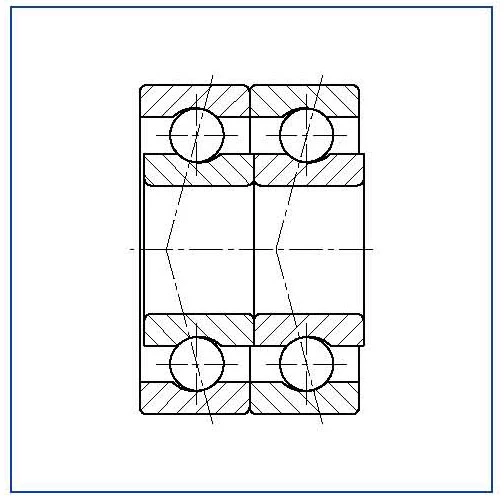
Tandem (DT)
(reference 3)
While duplex bearings mounted ‘back to back’ or ‘face to face’ are suitable to accommodate axial loading in both directions, a tandem mounted bearing pair is capable of accepting a very high axial load in one direction only. With this type of bearing pair, preloading and reduction of play can only be achieved, by preloading against another bearing or bearing pair.
Figure 23- tandem
FITTING
The fits of the ball bearing on the shaft and in the housing essentially determine the operational behaviour of miniature ball bearings. When selecting fitting tolerances, the following criteria should therefore be considered.
Rotation conditions
Rings with circumferential loading should have a tighter fit than rings with point loading.
Circumferential loading occurs in the case of rotating ring and stationery load or stationery ring and rotating load. Point loading occurs in the case of a stationery ring and stationery load or rating ring and rotating load.
Running accuracy
The same high standard of accuracy and surface quality expected of the bearing must be applied to shaft and housing.
Loading
High loads demand tighter fits.
Temperature
There may be temperature differences between the ball bearing and mating components while the ball bearing is in operation. The dimensional changes caused by differential expansion should be taken into consideration.
In the case of miniature bearings great important is placed on simple mounting and high running accuracy, hence only a close sliding or transition fit is usually possible. Furthermore it must be remembered that irregularities on the shaft or in the housing bore are transferred to the relatively thin-walled bearing rings. In order to improve the fit, it is possible to calibrate the bore and outside diameter into groups (see Calibration of bore & outside diameter section).
The values shown in tables 12 and 13 are only valid for materials with similar thermal expansion coefficients (11 . 10-6 . K-1).
If the expansion coefficient varies or if there are temperature variations between the outer ring and housing or between the outer ring and housing or between the inner ring and shaft, tolerances which ensure the appropriate fit at operating temperatures should be selected.
Shaft tolerances in µm
.0001”
Ball bearing bore Grade ® Tolerance in mm Tolerance in .0001 inch ® Operating Conditions | P0 0/-8 0/-3 | P5 0/-5 0/-2 | Calibration | Type of Fit | |
0/-2.5 0/-1 | -2.5/-5 -1/-2 | ||||
Low loading Medium speed No vibration | -5/-13 -2/-5 | -5/-11 -2/-4 | -5/-8 -2/-3 | -8/-11 -3/-4 | Sliding fit |
Low to medium loading Medium speed Low vibration | 0/-8 0/-3 | 0/-6 0/-2.5 | 0/-3 0/-1.2 | -3/-6 -1.2/-2.5 | Transition fit |
Heavy loading High speed High frequency vibrations | +4/-4 +1.6/-1.6 | +4/-2 +1.6/-1 | +4/+1 +1.6/+0.4 | +1/-2 +0.4/-1 | Press fit |
Table 12: Shaft tolerances
Housing tolerances in µm
.0001”
Ball bearing bore Grade ® Tolerance in mm Tolerance in .0001 inch ® Operating Conditions | P0 0/-8 0/-3 | P5 0/-5 0/-2 | Calibration | Type of Fit | |
0/-2.5 0/-1 | -2.5/-5 -1/-2 | ||||
Low loading Medium speed No vibration | +5/-3 +2/-1.2 | +5/-1 +2/-0.4 | +5/+2 +2/-1 | +2/-1 +1/-0.4 | Sliding fit |
Low to medium loading Medium speed Low vibration | 0/-8 0/-3 | 0/-6 0/-2.5 | 0/-3 0/-1.2 | -3/-6 -1.2/-2.5 | Transition fit |
Heavy loading High speed High frequency vibrations | -4/-12 -1.6/-5 | -3/-9 +1.2/-3.5 | -3/-6 +1.2/-2.5 | -6/-9 -2.5/-3.5 | Press fit |
Table 13: Housing tolerances
The information on this page applies to steel shafts and housings. The linear thermal expansion coefficient of other materials (e.g. aluminium housing) must be taken into consideration at operating temperatures other than ambient (20oC).
HIGH PRECISION BALL BEARING HANDLING & FAILURE ANALYSIS
High-precision ball bearing handling
GRW ball bearings are manufactured with extreme care and then packaged in order to avoid contamination and corrosion. During mounting of the bearings, the following advice should be heeded:
- Bearings should be stored in their original package in clean, dry rooms, under constant temperature conditions
- Bearings should only be removed from their original packaging shortly after installation if possible using tweezers or finger stalls
- Care should be taken that the place of assembly is clean and well lit and that all other parts are equally clean
- The bearings should not be subjected to shock and assembly force should only be applied to the ring being fitted, never transferred through the balls
- If glued connections are used care should be taken to ensure that excess glue does not enter the bearing
- Re-lubrication should only be carried out with the identical lubricant with identical purity. We recommend having the bearings lubricated by the manufacturer.
Failure analysis
Special examinations are essential in order to establish the cause of failure or to estimate the life expectancy of ball bearings. We will be pleased to assist you in this matter.
Valuable information is obtained if bearings are disassembled and examined after a certain time of operation and not only after failure.
If you dismount bearings, mark the bearing rings so you can reproduce the original position.
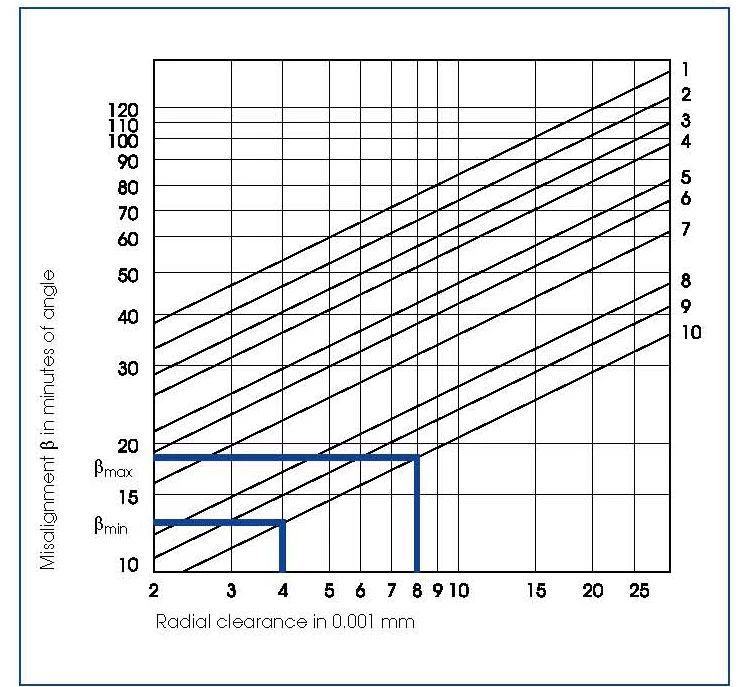
Bearing MISALIGNMENT
The misalignment of a bearing is the degree to which both rings can be titled relatively to each other. The misalignment angle depends on the radial clearance and the internal geometry of the bearing.
Too much misalignment of the rings should always be avoided, as even a small angle of 2’ to 3’ increases the noise level noticeably. Attention must be paid to accurate alignment when designing bearing seats and adjacent surfaces.
Figure 25 shows the free misalignment (without load) depending on radial clearance, for the complete bearing range.
| Basic Type | Graph | Basic Type | Graph | Basic Type | Graph |
| 681 | 1 | 695 | 8 | 1016 | 1 |
| 691 | 2 | 605 | 5 | 1191 | 1 |
| 68/1.5 | 1 | 625 | 9 | 1397 | 1 |
| 69/1.5 | 3 | 635 | 10 | 5/64 | 3 |
| 682 | 3 | 686 | 5 | 2380 | 3 |
| 692 | 3 | 696 | 6 | 3/32 | 4 |
| 67/2.35 | 3 | 626 | 10 | 3175 | 4 |
| 68/2.35 | 3 | 687 | 6 | 1/8A | 4 |
| 68/2.5 | 3 | 697 | 8 | 1/8B | 6 |
| 69/2.5 | 4 | 607 | 10 | 3967 | 6 |
| 60/2.5 | 4 | 627 | 10 | 4763A | 6 |
| 673 | 4 | 688A | 8 | 4763B | 5 |
| 683 | 4 | 688 | 8 | 3/16 | 5 |
| 693 | 4 | 698 | 8 | 6350A | 7 |
| 623 | 6 | 608 | 10 | 6350B | 5 |
| 674 | 5 | 689 | 8 | 1/4A | 7 |
| 684 | 6 | 699 | 9 | 1/4 | 10 |
| 694 | 7 | 609 | 10 | 7938 | 8 |
| 604 | 7 | 629 | 10 | 3/8 | 9 |
| 624 | 6 | 6800 | 9 | ||
| 634 | 9 | 6900 | 9 | ||
| 675 | 6 | 6000 | 10 | ||
| 685 | 7 |
MOUNTING OF BEARINGS
Flanged ball bearings
There are many advantages in using miniature and instrument ball bearings which have a flange on the outer ring. Steeped housing bores, which make it impossible or very difficult to maintain accurate alignment of both bearing fits, are not necessary. There is also no need for the use of circlips, which create difficulties in small housing bores or thinned walled housings (see Figure 7).
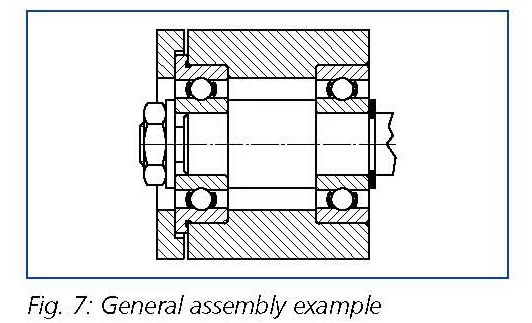
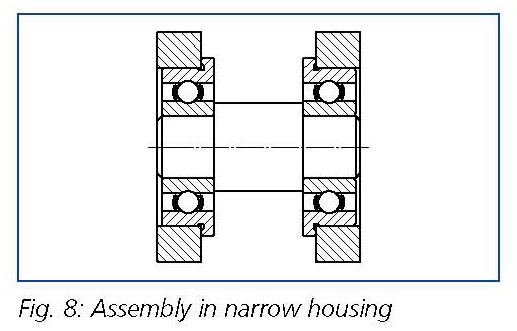
Furthermore the assembly of flanged bearings is relatively narrow housings (i.e. gearboxes) has proved effective (see Figure 8).
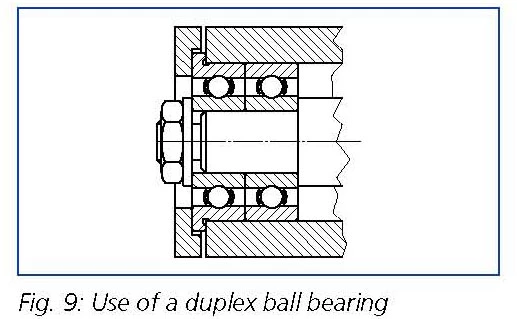
If duplex bearings are used, the use of a flange bearing simplifies the design of the locating bearing. The axial position of the Duplex bearing pair can be determined precisely for this arrangement (see Figure 9).
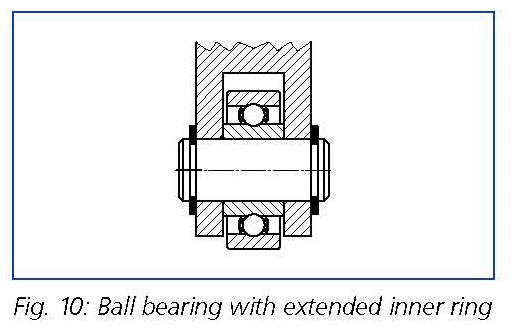
Ball bearings with extended inner rings
Ball bearings with an extended inner can simplify the design of various assemblies. Shims, washers and other spacers are unnecessary. Stepped shafts are also redundant (see Figure 10).
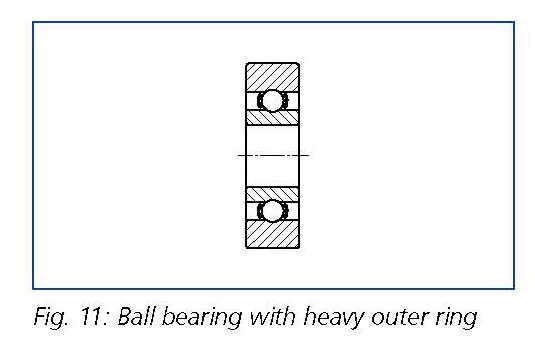
Ball bearings with heavy outer rings
Ball bearings with their outer rings supported by fitting in a housing can take highest loads. To increase the load capacity of ball bearings which are not built into housing different types such as ‘special ball bearings with heavy outer rings’ were developed and are used as so-called rollers (see Figure 11).
SHAFT & HOUSING SHOULDERS
The assembly conditions are very important for ball bearings to function correctly. The shoulders for the inner and outer ring should allow the axial load to be transferred safely without allowing the rings to tilt against each other.
These examples apply analogously to the ball bearing housing
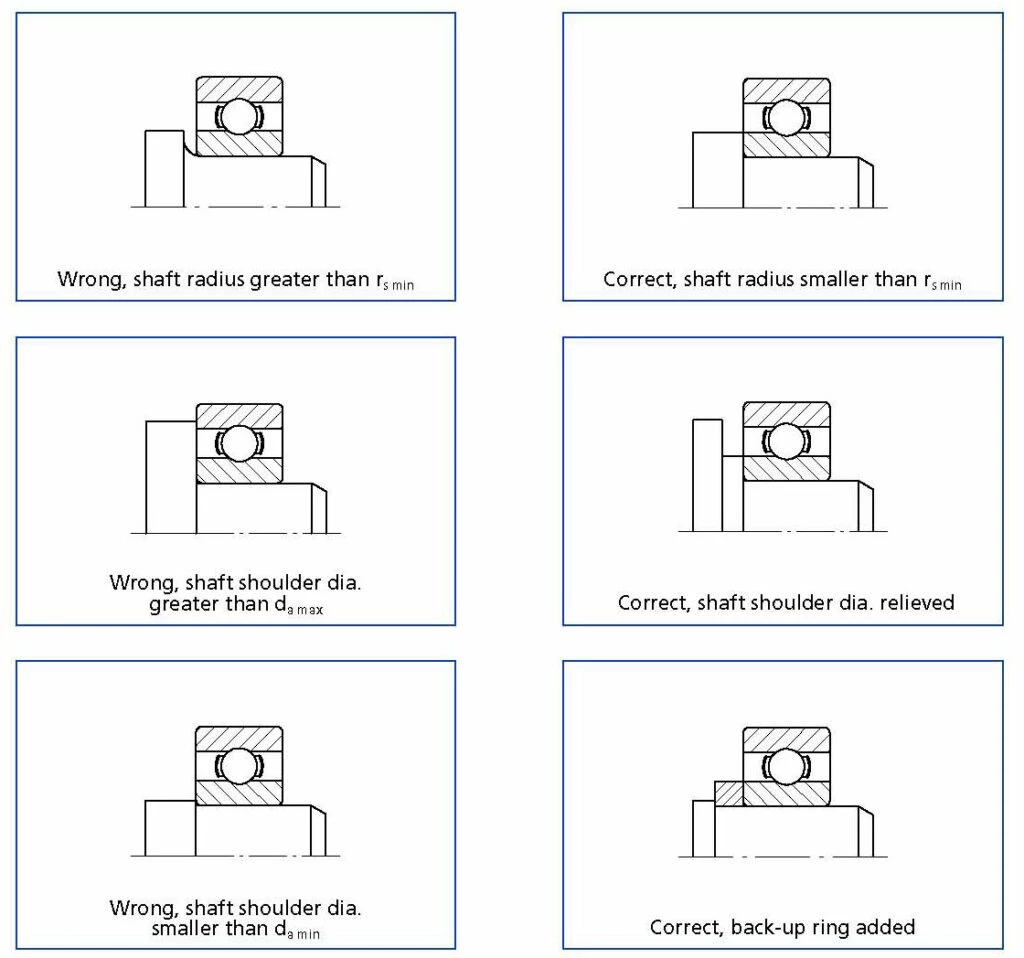
The values for the largest (da max) and for the smallest (da min) permissible shoulder diameter for the shaft and the values for the largest permissible shoulder diameter for the housing (Da max) are given in the dimension tables.
The following specifications should be taken into consideration:
- The shoulder diameter of the housing must in any case be smaller than Da max, the shoulder diameter of the shaft much not be smaller than da min.
- The radius on the shaft and housing must not be larger than the corner radius rs min of the ball bearing. An undercut if preferable here. The edge radii of the ball bearings are not suitable for locating the ball bearing in any way.
- The axial runout of the mating surfaces should not be greater than the maximum axial runout of the ball bearing used. The performance of the ball bearing could otherwise be influenced.
GRW Bearing TOLERANCES
Precision ball bearings are manufactured to standards established by the Annular Bearing Engineers Committee (ABEC) of the American Bearing Manufacturers Association (ABMA). These standards have been accepted by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and conform essentially to the standards set by the International Standards Organization (ISO).
The ABEC and ISO bearing standards are primarily concerned with bearing tolerances. While tolerance is an important factor in the performance of a bearing, there are many other factors that also affect the suitability of a bearing to its application.
ABEC and ISO standards do not cover: radial play, raceway curvature, surface finish, material, ball complement, number, size or precision level, retainer type, lubrication, torque, cleanliness at assembly, packaging and other factors that may be essential to the desired bearing performance.
GRW BEARINGs CAPACITIES
Static bearing capacity
In rolling bearing technology, we talk about the static bearing capacity when the ball bearing is loaded while stationery or during slow swinging movements. The calculations are made according to DIN ISO 76.
Basic static radial load rating Cor
The basic static radial load rating is the static radial load which corresponds to a calculated contact stress of 4200 MPa at the centre of the most heavily loaded rolling element/raceway contact.
Static equivalent radial load Por
The static equivalent radial load is the static radial load which would cause the same contact stress at the centre of the most heavily loaded rolling element/raceway contact that occurs under the actual load conditions.
Calculating the static equivalent radial load:
Por = Xo . Fr + Yo . Fa
Xo = 0.6
Yo = 0.5
Fr = greatest radial load occurring (N)
Fa = greatest axial load occurring (N)
If the calculation gives a value, Por < Fr, Por = Fr should be set.
Permanent deformation
Permanent deformation on raceways and rolling elements even occurs when a stationery ball bearing is only loaded moderately.
Experience shows that a deformation of 0.0001 x rolling element diameter on the most highly loaded point of contact between raceway and rolling elements will not noticeably effect the function of the ball bearing.
Even greater deformation is justifiable if the ball bearing is running at low speed and the requirements for noise are not high. On the other hand only slight permanent deformation is allowed if the noise and friction requirements are particularly stringent.
Dynamic bearing capacity
The dynamic bearing capacity is the stress on a rotating ball bearing. The additional term ‘dymanic’ indicates the operating condition of the bearing not the effect of the load. The calculations are made according to DIN ISO 281.
Basic dynamic radial loading Cr
The basic dynamic radial load rating for radial ball bearings is that constant radial load which a sufficiently large number of apparently identical ball bearings could theoretically endure for a basic rating life of one million revolutions.
Dynamic equivalent radial load Pr
The dynamic equivalent radial load for radial ball bearings is that constant radial load under the influence of which a rolling bearing would have the same life as it will attain under the actual load conditions.
The DIN load ratings are given in the ball bearing tables. The actual load ratings can deviate depending on the ball bearing type. The load ratings are approximately 30% lower for hybrid ball bearings than for comparable steel ball bearings.
Please contact us for the exact load ratings.
ELASTIC BEHAVIOUR OF DEEP GROVE BALL BEARING
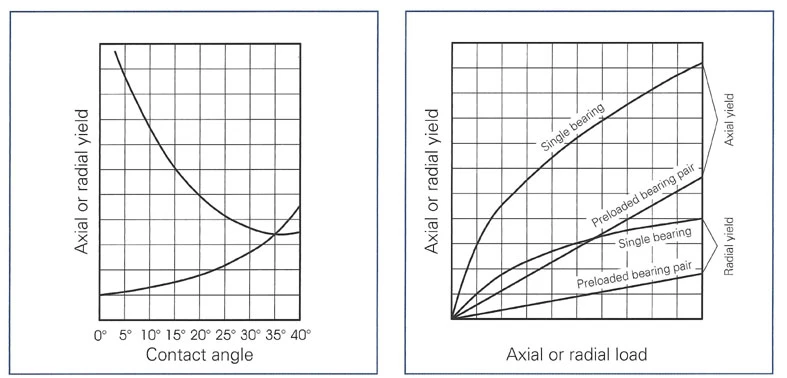
Two types of elastic yield should be distinguished with ball bearings: axial and radial yield.
Axial elastic yield
The axial elastic yield of a ball bearing is the distance which the inner ring moves axially compared with the outer ring when the axial clearance of the bearing has been removed, and the bearing is axially loaded. It does not increase linearly with the applied load as the contact areas between balls and raceways become larger with increasing load.
Radial elastic yield
The radial elastic yield is caused by a radial force component after radial play has been removed. Given similar conditions, with small contact angles the radial yield is considerably less than the axial yield. With increasing contact angle, the radial yield increases while the axial yield decreases, up to a contact angle of approx.. 35o, when values become practically the same.
Both types of yield depend on the internal construction of the bearing, the radial clearance and applied load.
The relatively large amount of yield can be reduced by using preloaded bearing pairs (see ‘Duplex Bearings’). Preloading will result not only in a reduction of the elastic yield, resulting in increased rigidity, but also in a near to linear relationship between loading and yield for a considerably wide range of applied load. For instance, a ball bearing pair with 10N preload will maintain linearity up to approx. 30N external axial load.
To estimate this, the following formula can be used:
Fv = Fa / 3
Fv = axial preload [N]
Fa = axial bearing loading [N]
Please contact us for further information.
GRW Bearings FUNCTIONAL TESTS
Noise test
The abbreviation GPR given in our numbering system stands for 100% noise tested ball bearings. We test the amplitude of the vibrations generated by the ball bearings at set speeds and frequencies.Torque test
Torque tested ball bearings are tested and packaged in rooms with a controlled atmosphere in laminar cabinets. We recommend instrument oils with a viscosity of <14 mm2/s at 40oC for low torque bearings. The starting torque is the torque required to start the rotation of one ring, with the other stationery. The torque is tested on a vertical shaft with axial loading. The measurements made with the tester according to MIL-STD-206A provide very exact and reliable values. During the test the outer ring is driven and the inner ring loaded with the standard load according to the bearing size. Due to the lack of a generally accepted standard torque comparisons of bearings of the same type can only be made in identical measuring conditions on the same measuring equipment. Table 4 gives reference values for the maximum starting torque of µNm. These values apply for instrument ball bearings without seals P5 or ABEC5 and better, which are lubricated with instrument oil with viscosity <14 mm2/s at 40oC. The value can be 10 to 40 times greater for ball bearings with grease lubrication. In this test the axial loading of the inner ring is 75g for ball bearings with an outside diameter up to 10mm. Ball bearings with a greater outside diameter are loaded with 400g. The running torque is the torque which is required to keep a ball bearing in rotation. In this case together with the user we agree upon a suitable measuring method for the test. Table 4: Maximum starting torque in µNm| Basic Type | Torque mNm | Load g | Basic Type | Torque mNm | Load g | Basic Type | Torque mNm | Load g |
| 681 | 15 | 75 | 695 | 69 | 400 | 1016 | 15 | 75 |
| 691 | 15 | 75 | 605 | 69 | 400 | 1191 | 15 | 75 |
| 68/1.5 | 15 | 75 | 625 | 69 | 400 | 1397 | 15 | 75 |
| 69/1.5 | 15 | 75 | 635 | 76 | 400 | 5/64 | 15 | 75 |
| 682 | 15 | 75 | 686 | 69 | 400 | 2380 | 15 | 75 |
| 692 | 15 | 75 | 696 | 69 | 400 | 3/32 | 15 | 75 |
| 67/2.35 | 15 | 75 | 626 | 76 | 400 | 3175 | 15 | 75 |
| 68/2.35 | 15 | 75 | 687 | 69 | 400 | 1/8A | 15 | 75 |
| 68/2.5 | 15 | 75 | 697 | 76 | 400 | 1/8B | 16 | 75 |
| 69/2.5 | 15 | 75 | 607 | 76 | 400 | 3967 | 15 | 75 |
| 60/2.5 | 16 | 75 | 627 | 80 | 400 | 4763A | 15 | 75 |
| 673 | 16 | 75 | 688A | 52 | 400 | 4763B | 16 | 75 |
| 683 | 16 | 75 | 688 | 76 | 400 | 3/16 | 52 | 400 |
| 693 | 16 | 75 | 698 | 76 | 400 | 6350A | 15 | 75 |
| 623 | 16 | 75 | 608 | 80 | 400 | 6350B | 52 | 400 |
| 674 | 16 | 75 | 689 | 76 | 400 | 1/4A | 60 | 400 |
| 684 | 16 | 75 | 699 | 80 | 400 | 1/4 | 70 | 400 |
| 694 | 65 | 400 | 609 | 80 | 400 | 7938 | 52 | 400 |
| 604 | 65 | 400 | 629 | 100 | 400 | 3/8 | 95 | 400 |
| 624 | 69 | 400 | 6800 | 80 | 400 | |||
| 634 | 69 | 400 | 6900 | 95 | 400 | |||
| 675 | 65 | 400 | 6000 | 100 | 400 | |||
| 685 | 65 | 400 |
Assembly of low torque bearings
For low torque bearings in particular, great care must be taken in the choice of fits and tolerances. Shaft and housing tolerances have to be selected so that a sliding fit results. Please refer to ‘Fitting’ and ‘Reduction of RadialClearance’ for information. Even small misalignment of the inner and outer ring can result in great torque of the bearing. Therefore particular attention must be paid to the alignment between shaft and housing bore, as well as, to the parallelism of the mating faces. Extreme cleanliness of the assembly area and parts is essential, in order to achieve a perfect low torque bearing. Even minute contamination causes torque peaks, which can be many times higher than the average torque level.| 1 mNm = | 1 cmp = | 1 oz.in. = | 1 cNcm = | |
| mNm | 1 | 100 | 7200 | 100 |
| cmp | 0.01 | 1 | 72 | 1 |
| oz.in. | 0.000139 | 0.0139 | 1 | 0.0139 |
| cNcm | 0.01 | 1 | 72 | 1 |
FATIGUE LIFE
The fatigue life (basic rating life) is the number of revolutions (or number of hours at constant speed) which 90% of a sufficiently large quantity of apparently identical ball bearings will complete or exceed before the first evidence of fatigue develops. The calculations are made according to DIN ISO 281.
Basic rating life in hours is calculated as follows:
Lh = | 106 . (Cr)3 |
| 60 . n (Pr) |
Ln = basic rating life [h]
n = speed of inner ring [rpm]
Cr = basic dynamic radial load [N]
Pr = dynamic equivalent radial load [N]
Calculation of the dynamic equivalent radial load Pr:
Pr = X . Fr + Y . Fa
Pr = dynamic equivalent radial load [N]
Fr = radial load of bearing [N]
Fa = axial load of bearing [N]
X = dynamic radial load factor
Y = dynamic axial load factor
The influence of load on the life is only to be taken into consideration in the above life equation. If the ball bearings listed are used for conventional bearing purposes, this life calculation will be sufficient.
As the life calculation only takes material fatigue as a cause of failure the calculated life will only correspond with the actual life of the ball bearing if the following requirements are fulfilled:
- Sufficient lubrication is guaranteed during the whole running time.
- The loads and speeds used in the calculation correspond with the actual operating conditions.
- Contamination of ball bearings and lubricant is avoided.
GRW Bearings LIMITING SPEEDS
The maximum speed for a ball bearing in operation is limited by various mechanical and kinematic criteria. Narrow tolerances of bearings and surrounding parts, special measures regarding lubrication and type of lubricant as well as special retainer materials and designs generally have a beneficial effect on the speed limit. The characteristical values for speed given in the tables only apply to specially set reference conditions. They therefore only give an indication of the relative speed suitability of the ball bearing. Please call us for more information if operating conditions are different.
The kinematically permissible speed nzul
The ‘kinematically permissible speed nzul’ applies to ball bearings with contact seals which do not have a thermal reference speed nur defined in the standard. It takes into consideration the special conditions resulting from the wiping contact between ball bearing inner ring and seals. In principle the same conditions as for the thermal reference speed nur otherwise apply.
The thermal reference speed nur
The reference conditions have been selected in DIN 732-1 so that the ‘thermal reference speed nur’ is identical for both types of lubrication: oil or grease. The essential operating conditions are:
- Reference temperature of the ball bearing on stationery outer ring 70oC
- Reference temperature of the ball bearing environment 20oC
- Reference loading P, of the ball bearing 5% of the static radial loading rating Cor
- Oil lubrication as oil bath lubrication with a conventional mineral oil without EP additives, with a kinematic viscosity of 12 mm2/s at 70oC
- Grease lubrication with a standard lithium soap grease with a mineral base oil without EP additives. The kinematic viscosity of the base oil is 22 mm2/s at 70oC. The grease quantity is approx. 30% of the free space in the ball bearing
- Ball bearings with standard designs, i.e. with standard accuracy, with standard radial play, with non-contact closures
- Ball bearing installed on a horizontal shaft with a stationery outer ring and installation dimensions and tolerances which do not reduce bearing radial clearance
The permissible thermal operating speed nu
The speed at which the average ball bearing temperature reaches the permissible value in real operating conditions is called the ‘permissible thermal operating speed nu’. It is calculated from the thermal reference speed by multiplying it with the factor ‘speed ration fn’ according to DIN 732-2: nu = fn . nur
Following the standard we use diagrams which make calculating this factor far easier. The different torque effects of oil and grease lubrication are taken into consideration.
Click on image to enlarge

Figure 6: Calculation of the permissible thermal operating speed nu
REDUCTION IN RADIAL CLEARANCE
Reduction in radial clearance due to heat
The ball bearing radial clearance relates to an ambient temperature of 20oC and excludes external loads with exception of the measuring load. Frictional heat to be dissipated or a temperature difference between rotor and stator have the effect of a temperature difference between the inner and outer ring. The differential expansion between inner ring and outer ring may lead to a reduction in radial clearance which should be taken into consideration in the set-up of the ball bearing: RV = Δda – Δdi| RV = | Radial clearance reduction (µm) | |
| Δda = | Diameter change on outer ring between the temperature t and the ambient temperature of 20oC (µm) | |
| Δdi = | Diameter change on inner ring between the temperature t and the ambient temperature of 20oC (µm) |
| d0a = | Raceway diameter on outer ring at 20oC (µm) | |
| d0i = | Raceway diameter on inner ring at 20oC (µm) | |
| α = | Length expansion coefficient [K-1], For 100Cr6 … 11.0 . 10-6 K-1 For X65Cr13 … 10.5 . 10-6 K-1 | |
| Δ = | Temperature difference between the temperature t and the ambient temperature 20oC (K) |
| d0a ≈ | (d+D)/2 + Dw ≈ (10+26)mm/2 + 4,763mm ≈ 22,763mm | |
| Δda = | d0a . α . Δt | |
| Δda = | (22,763 . 103) µm . 10.5 x 10-6 K-1 . 10 K = 2.4µm |
| d0i ≈ | (d+D)/2 + Dw ≈ (10+26)mm/2 + 4,763mm ≈ 13,237mm | |
| Δdi = | d0i . α . Δt | |
| Δdi = | (13,237 . 103) µm . 10.5 x 10-6 K-1 . 40 K = 5.6µm |
Reduction in radial clearance:
RV = Δda – Δdi RV = 2.4µm – 5.6µm = 3.2µm This gives a radial clearance reduction of 3.2µm. Our rough estimation does not take into consideration the influence of the balls which would only effect the result slightly. If the result is positive, an increase in radial clearance should be considered.Reduction in radial clearance due to irference fit
When selecting the fitting tolerances, you should note that an interference fit causes a reduction in radial clearance. This depends on the effective interference kit and also on the ring thickness ratio and may be calculated very simply. RV = k . Ü| RV= | Radial clearance reduction (µm) | |
| Ü= | Largest fitting sizes (µm) | |
| k= | Factor from table 14 whereby it is presumed that the inner ring is pressed onto a compete shaft or the outer ring is pressed into a stable, practically non-deformable housing |
| Bore | +0 / -5µm } = 9µm | |
| Shaft | +4 / -2µm } | |
| Outer diameter | +0 / -5µm } = 6µm | |
| Housing diameter | +0 / -2µm } |
Table 14: k-factor for inner ring (IR) and outer ring (OR)
| Basic Type | IR | OR | Basic Type | IR | OR | Basic Type | IR | OR |
| 681 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 695 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1016 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| 691 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 605 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1191 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| 68/1.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 625 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1397 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| 69/1.5 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 635 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 5/64 | 0.6 | 0.7 |
| 682 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 686 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 2380 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| 692 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 696 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 3/32 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| 67/2.35 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 626 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 3175 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| 68/2.35 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 687 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1/8A | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 68/2.5 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 697 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1/8B | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| 69/2.5 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 607 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 3967 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 60/2.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 627 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 4763A | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| 673 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 688A | 0.9 | 0.8 | 4763B | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| 683 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 688 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 3/16 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| 693 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 698 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 6350A | 0.9 | 0.9 |
| 623 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 608 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 6350B | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| 674 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 689 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1/4A | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| 684 | 0.8 | 0.8 | 699 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1/4 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| 694 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 609 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 7938 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| 604 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 629 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 3/8 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| 624 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 6800 | 0.8 | 0.9 | |||
| 634 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 6900 | 0.7 | 0.8 | |||
| 675 | 0.9 | 0.9 | 6000 | 0.7 | 0.8 | |||
| 685 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN RADIAL CLEARANCE, AXIAL CLEARANCE & CONTACT ANGLE
Radial Clearance
Radial clearance is a measured value of total movement of one ring relative to the other in a plane perpendicular to the bearing axis. Although radial clearance has no effect on the quality of the bearing, it has a significant effect on its performance.
Basically the selection of radial clearance depends on the fit of the bearing on the shaft and in the housing. Greater radial clearance than standard should be specified if the bearing is running under axial load conditions, operates at high speed, or when low torque is required.
Less than normal radial clearance should be specified if only radial load is applied or minimum noise is required. Small radial clearance is often recommended in order to reduce the axial clearance of an instrument. However, where low axial clearance is required, we advise to use matched bearings.
Axial Clearance
The axial clearance is the measured value in which one bearing ring can move axially in relation to the other. In bearings of the same type, axial clearance depends on the radial clearance.
Contact Angle
The contact angle is formed between the connecting line of the contact points ball/raceways and a plane perpendicular to the axis. It is formed when the axial clearance is removed by the opposite axial movement of the bearing rings. The contact angle is influenced by radial clearance, curvature and axial load of the bearing.
The average values for the axial clearance ad the contact angle in relation to the radial clearance and curvature of the ball bearing, can be taken from figure 20.
Table 19 lists the bearing basic types and graphs to be used.
Basic Type | Graph | Graph | Basic Type | Graph | Graph | Basic Type | Graph | Graph |
681 | 1 | A | 695 | 6 | B | 1016 | 2 | A |
691 | 3 | A | 605 | 7 | B | 1191 | 3 | A |
68/1.5 | 3 | A | 625 | 9 | C | 1397 | 4 | A |
69/1.5 | 3 | A | 635 | 10 | C | 5/64 | 4 | A |
682 | 3 | A | 686 | 7 | B | 2380 | 3 | A |
692 | 4 | A | 696 | 7 | B | 3/32 | 6 | A |
67/2.35 | 5 | B | 626 | 10 | C | 3175 | 4 | A |
68/2.35 | 4 | A | 687 | 7 | B | 1/8A | 6 | A |
68/2.5 | 4 | A | 697 | 9 | B | 1/8B | 6 | A |
69/2.5 | 5 | A | 607 | 10 | C | 3967 | 4 | A |
60/2.5 | 5 | A | 627 | 11 | C | 4763A | 4 | A |
673 | 10 | C | 688A | 5 | A | 4763B | 4 | A |
683 | 5 | A | 688 | 9 | B | 3/16 | 8 | A |
693 | 6 | B | 698 | 9 | B | 6350A | 4 | A |
623 | 6 | B | 608 | 11 | C | 6350B | 7 | A |
674 | 4 | A | 689 | 9 | B | 1/4A | 9 | A |
684 | 6 | B | 699 | 9 | B | 1/4 | 10 | B |
694 | 6 | B | 609 | 11 | C | 7938 | 5 | A |
604 | 6 | B | 629 | 12 | C | 3/8 | 10 | B |
624 | 8 | B | 6800 | 9 | B | |||
634 | 9 | C | 6900 | 10 | C | |||
675 | 4 | A | 6000 | 12 | C | |||
685 | 6 | B |
Table 19: Assignment of graphs for Figure 20
Example:
Ball bearing 623, radial clearance 0.015mm
From table 19: graph 6, graph B
From figure 20: contact angle 17o30’, axial clearance 0.097mm
DEEP GROOVE OPEN BALL BEARINGS

Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Open Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.05 | 681 | 82 | 22 | 140 | 7 | 0.5 | ||
| 1 | 4 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 691 | 160 | 43 | 126 | 6 | 0.794 | ||
| 1.5 | 4 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.05 | 68/1.5 | 2 | 163 | 44 | 113 | 6 | 0.794 |
| 1.5 | 5 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 69/1.5 | 192 | 59 | 93 | 7 | 0.794 | |
| 2 | 5 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.08 | 682 | 2.3 | 192 | 59 | 90 | 7 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 6 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 692 | 3.1 | 286 | 90 | 91 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.35 (7) | 5 | 1.5 | 0.08 | 67/2.35 | 192 | 59 | 93 | 7 | 0.794 | ||
| 2.35 (7) | 5.5 | 0.08 | 68/2.35 | 286 | 90 | 91 | 7 | 1 | |||
| 2.5 | 6 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 0.08 | 68/2.5 | 2.6 | 289 | 92 | 81 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 7 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 0.15 | 69/2.5 | 3.3 | 432 | 149 | 71 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 2.5 | 8 | 2.8 | 0.15 | 60/2.5 | 3.6 | 432 | 149 | 81 | 8 | 1.191 | |
| 3 | 6 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 673 | 195 | 60 | 81 | 8 | 1 | |
| 3 | 7 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 683 | 2.8 | 432 | 149 | 71 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 8 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.15 | 693 | 3.8 | 644 | 215 | 67 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 10 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | 623 | 4.8 | 725 | 265 | 62 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 7 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 674 | 345 | 130 | 63 | 9 | 1 | |
| 4 | 9 | 3.3 | 0.6 | 0.1 | 684 | 3.3 | 658 | 226 | 62 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 11 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | 694 | 4.8 | 730 | 271 | 66 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 12 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | 604 | 4.8 | 734 | 282 | 56 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 13 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 624 | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 52 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 4 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 634 | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 39 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 4 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 634D | 1.935 | 677 | 44 | 6 | 3.175 | |
| 5 | 8 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 675 | 390 | 160 | 52 | 11 | 1 | |
| 5 | 11 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 685 | 3.8 | 734 | 282 | 52 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 13 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 695 | 4.8 | 851 | 366 | 49 | 10 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 605 | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 50 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 5 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 625 | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 40 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 625D | 1.935 | 677 | 45 | 6 | 3.175 | |
| 5 | 19 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 635 | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 33 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 6 | 10 | 2.5 | 0.15 | 676 (8) | 503 | 215 | 46 | 10 | 1.191 | ||
| 6 | 13 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.15 | 686 | 4.3 | 1.096 | 437 | 44 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 15 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 696 | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 46 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 16 | 5 | 0.3 | 625/0002 | 1.646 | 663 | 41 | 8 | 2.5 | ||
| 6 | 19 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 626 | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 34 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 11 | 2.5 | 0.15 | 677 (8) | 462 | 199 | 40 | 9 | 1.191 | ||
| 7 | 14 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.15 | 687 | 4.3 | 1.186 | 505 | 41 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 7 | 17 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 697 | 5.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 39 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 7 | 19 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 607 | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 38 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 22 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 627 | 3.369 | 1.363 | 35 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 8 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.15 | 678 (8) | 551 | 270 | 35 | 12 | 1.191 | ||
| 8 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 688 | 4.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 38 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 19 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 698 | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 40 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 22 | 6 | 0.3 | 608/003 | 3.369 | 1.363 | 34 | 7 | 3.969 | ||
| 8 | 22 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 608 | 3.369 | 1.363 | 38 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 9 | 14 | 3 | 0.15 | 679 | 536 | 276 | 33 | 12 | 1.191 | ||
| 9 | 17 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 689 | 4.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 34 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 9 | 20 | 6 | 0.3 | 699 | 1.922 | 915 | 35 | 10 | 2.5 | ||
| 9 | 24 | 7 | 0.3 | 609 | 3.435 | 1.43 | 33 | 7 | 3.969 | ||
| 9 | 24 | 7 | 0.3 | 609D | 3.758 | 1.632 | 32 | 8 | 3.969 | ||
| 9 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 629 | 4.698 | 1.982 | 29 | 7 | 4.763 | ||
| 10 | 15 | 3 | 0.15 | 6700 (8) | 881 | 435 | 30 | 11 | 1.588 | ||
| 10 | 19 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 6800 | 5.8 | 1.922 | 915 | 34 | 10 | 2.5 |
| 10 | 22 | 6 | 0.3 | 6900 | 2.555 | 1.129 | 31 | 8 | 3.175 | ||
| 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 6000 | 4.698 | 1.982 | 32 | 7 | 4.763 | ||
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 6200 | 6.1 | 2.6 | 29 | 7 | 5.556 | ||
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 6200D | 5.236 | 2.374 | 27 | 8 | 4.763 | ||
| 12 | 21 | 5 | 0.3 | 6801 | 1.93 | 900 | 30 | 12 | 2.381 | ||
| 12 | 24 | 6 | 0.3 | 6901 | 2.971 | 1.452 | 34 | 10 | 3.175 | ||
| 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 6001 | 5.237 | 2.359 | 31 | 9 | 3.969 | ||
| 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6201 | 7.073 | 3.1 | 26 | 7 | 6 | ||
| 15 | 24 | 5 | 0.3 | 6802 | 2.08 | 1.1 | 24 | 14 | 2.381 | ||
| 15 | 28 | 7 | 0.3 | 6902 | 4.445 | 2.268 | 32 | 11 | 3.175 | ||
| 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 6002 | 5.676 | 2.819 | 26 | 9 | 4.763 | ||
| 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 6202 | 7.939 | 3.744 | 23 | 8 | 6 | ||
| 17 | 26 | 5 | 0.3 | 6803 | 2.24 | 1.27 | 22 | 16 | 2.381 | ||
| 17 | 30 | 7 | 0.3 | 6903 | 4.723 | 2.547 | 30 | 11 | 3.969 | ||
| 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6003 | 6.172 | 3.267 | 23 | 10 | 4.763 | ||
| 17 | 40 | 12 | 0.6 | 6203 | 9.811 | 4.734 | 20 | 8 | 6.747 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE OPEN BALL BEARINGS
Inch Series

Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Open Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0400 | 0.125 | 0.17098 | 0.0469 | 0.01299 | 0.003 | 1016 | 51 | 11 | 148 | 5 | 0.025 | |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0625 | 0.013 | 0.003 | 1191 | 0.0937 | 163 | 44 | 129 | 6 | 0.0313 |
| 0.0550 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0781 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 1397 | 0.1094 | 239 | 67 | 114 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 5/64 | 0.125 | 286 | 90 | 95 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0625 | 0.018 | 0.003 | 2380 | 0.0937 | 192 | 59 | 94 | 7 | 0.0313 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.005 | 3/32 | 0.1406 | 644 | 215 | 62 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 3175 | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1250 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 1/8A | 0.1406 | 644 | 215 | 65 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | 1/8B | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.5 | 0.1719 | 0.012 | 1/8B/083 | 720 | 260 | 74 | 8 | 0.0625 | |||
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 3967 | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1562 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | 3967/8 | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 69 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 4763A | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 4763B | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | 4763A/8 | 0.1406 | 391 | 162 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1562 | 0.012 | 3/16 | 1.339 | 488 | 50 | 7 | 0.0938 | |||
| 0.2500 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.003 | 6350A | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.2500 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.005 | 6350B | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 38 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.2500 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | 1/4A | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.2500 | 0.75 | 0.2188 | 0.016 | 1/4 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 35 | 8 | 0.125 | |||
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | 7938 | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
| 0.3750 | 0.875 | 0.2188 | 0.016 | 3/8 | 2.555 | 1.129 | 30 | 8 | 0.125 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE FLANGE EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Flange Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Complement Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Complement Size: Dw |
| 1.5 | 4 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.05 | F68/1.5 | 163 | 44 | 113 | 6 | 0.794 |
| 1.5 | 5 | 6.5 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.15 | F69/1.5 | 192 | 59 | 93 | 7 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 5 | 6.1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.08 | F682 | 192 | 59 | 90 | 7 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | F692 | 286 | 90 | 91 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 6 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 0.08 | F68/2.5 | 289 | 92 | 81 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 0.15 | F69/2.5 | 432 | 149 | 71 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 6 | 7.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | F673 | 195 | 60 | 81 | 8 | 1 |
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | F683 | 432 | 149 | 71 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.15 | F693 | 644 | 215 | 67 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | F623 | 725 | 265 | 62 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 7 | 8.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | F674 | 345 | 130 | 63 | 9 | 1 |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 3.3 | 0.6 | 0.1 | F684 | 658 | 226 | 62 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | F694 | 730 | 271 | 66 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | F604 | 734 | 282 | 56 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | F624 | 1.339 | 488 | 52 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F634 | 1.646 | 663 | 39 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 8 | 9.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | F675 | 390 | 160 | 52 | 11 | 1 |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | F685 | 734 | 282 | 52 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F695 | 851 | 366 | 49 | 10 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | F605 | 1.096 | 437 | 50 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F625 | 1.646 | 663 | 40 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F635 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 33 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.15 | F686 | 1.096 | 437 | 44 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | F696 | 1.186 | 505 | 46 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F626 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 34 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.15 | F687 | 1.186 | 505 | 41 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | F697 | 1.795 | 776 | 39 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F607 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 38 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F627 | 3.369 | 1.363 | 35 | 7 | 3.969 |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F688 | 1.795 | 776 | 38 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F698 | 1.798 | 797 | 40 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F608 | 3.369 | 1.363 | 38 | 7 | 3.969 |
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F689 | 1.798 | 797 | 34 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F6800 | 1.922 | 915 | 34 | 10 | 2.5 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE FLANGE EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS
Inch Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Flange Open Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0400 | 0.125 | 0.17098 | 0.0469 | 0.01299 | 0.003 | F1016 | 51 | 11 | 148 | 5 | 0.025 | |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0625 | 0.013 | 0.003 | F1191 | 0.0937 | 163 | 44 | 129 | 6 | 0.0313 |
| 0.0550 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0781 | 0.023 | 0.003 | F1397 | 0.1094 | 239 | 67 | 114 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.003 | F5/64 | 0.125 | 286 | 90 | 95 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0625 | 0.018 | 0.003 | F2380 | 0.0937 | 192 | 59 | 94 | 7 | 0.0313 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.005 | F3/32 | 0.1406 | 644 | 215 | 62 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.003 | F3175 | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1250 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | F1/8A | 0.1406 | 644 | 215 | 65 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | F1/8B | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | F3967 | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | F4763A | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.003 | F4763B | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.2500 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.003 | F6350A | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.2500 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.005 | F6350B | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 38 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.2500 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F7938 | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE OPEN EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Open Ext Inner Ring Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 1.5 | 4 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.05 | E68/1.5 | 2 | 163 | 44 | 113 | 6 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 5 | 6.1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.08 | E682 | 2.3 | 192 | 59 | 90 | 7 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | E692 | 3.1 | 286 | 90 | 91 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 6 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 0.08 | E68/2.5 | 2.6 | 289 | 92 | 81 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 0.15 | E69/2.5 | 3.3 | 432 | 149 | 71 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 2.5 | 8 | 2.8 | 0.15 | E60/2.5 | 3.6 | 432 | 149 | 81 | 8 | 1.191 | ||
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | E683 | 2.8 | 432 | 149 | 71 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.15 | E693 | 3.8 | 644 | 215 | 67 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | E623 | 4.8 | 725 | 265 | 62 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 3.3 | 0.6 | 0.1 | E684 | 3.3 | 658 | 226 | 62 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | E694 | 4.8 | 730 | 271 | 66 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | E604 | 4.8 | 734 | 282 | 56 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | E624 | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 52 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | E634 | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 39 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | E685 | 3.8 | 734 | 282 | 52 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | E695 | 4.8 | 851 | 366 | 49 | 10 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | E605 | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 50 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | E625 | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 40 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E635 | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 33 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.15 | E686 | 4.3 | 1.096 | 437 | 44 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | E696 | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 46 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E626 | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 34 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.15 | E687 | 4.3 | 1.186 | 505 | 41 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | E697 | 5.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 39 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E607 | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 38 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | E688 | 4.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 38 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E698 | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 40 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E608 | 3.369 | 1.363 | 38 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | E689 | 4.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 34 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | E6800 | 5.8 | 1.922 | 915 | 34 | 10 | 2.5 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE OPEN EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS
Inch Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring Open Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0625 | 0.013 | 0.003 | E1191 | 0.0937 | 163 | 44 | 129 | 6 | 0.0313 |
| 0.0550 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0781 | 0.023 | 0.003 | E1397 | 0.1094 | 239 | 67 | 114 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.003 | E5/64 | 0.125 | 286 | 90 | 95 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0625 | 0.018 | 0.003 | E2380 | 0.0937 | 192 | 59 | 94 | 7 | 0.0313 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.005 | E3/32 | 0.1406 | 644 | 215 | 62 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.003 | E3175 | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1250 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | E1/8A | 0.1406 | 644 | 215 | 65 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | E1/8B | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | E3967 | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1562 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/8 | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 69 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | E4763A | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.003 | E4763B | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/8 | 0.1406 | 391 | 162 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.2500 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.003 | E6350A | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.2500 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.005 | E6350B | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 38 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.2500 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E7938 | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE FLANGE EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS
Metric Series

- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE FLANGE EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS
Inch Series
| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Flange Ext Inner Ring Open Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0625 | 0.013 | 0.003 | FE1191 | 0.0937 | 163 | 44 | 129 | 6 | 0.0313 |
| 0.0550 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0781 | 0.023 | 0.003 | FE1397 | 0.1094 | 239 | 67 | 114 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.003 | FE5/64 | 0.125 | 286 | 90 | 95 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0625 | 0.018 | 0.003 | FE2380 | 0.0937 | 192 | 59 | 94 | 7 | 0.0313 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.005 | FE3/32 | 0.1406 | 644 | 215 | 62 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.003 | FE3175 | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1250 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | FE1/8A | 0.1406 | 644 | 215 | 65 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1250 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | FE1/8B | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | FE3967 | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.312 5 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.003 | FE4763A | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.003 | FE4763B | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.2500 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.003 | FE6350A | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.2500 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.005 | FE6350B | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 38 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.2500 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE1/4A | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | FE7938 | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z & 2RZ SHIELD BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2Z /2RZ Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 1.5 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.05 | 68/1.5-2Z | 163 | 44 | 153 | 6 | 0.794 | |
| 1.5 | 5 | 2 | 0.15 | 69/1.5/002-2Z | 192 | 59 | 93 | 7 | 0.794 | |||
| 1.5 | 5 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 69/1.5-2Z | 192 | 59 | 109 | 7 | 0.794 | |
| 2 | 5 | 6.1 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 682-2Z | 3.1 | 192 | 59 | 116 | 7 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | 692-2Z | 3.1 | 286 | 90 | 91 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.35 (7) | 5 | 2.3 | 0.08 | 67/2.35-2Z | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.794 | |||
| 2.5 | 6 | 7.1 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.08 | 68/2.5-2Z | 3.4 | 289 | 92 | 101 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.1 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 683/0001-2Z | 432 | 149 | 88 | 8 | 1.191 | |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 0.15 | 69/2.5-2Z | 4.3 | 432 | 149 | 87 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 2.5 | 8 | 2.8 | 0.15 | 60/2.5-2Z | 3.6 | 432 | 149 | 81 | 8 | 1.191 | ||
| 3 | 6 | 7.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 673-2Z | 195 | 60 | 81 | 8 | 1 | |
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 683-2Z | 3.8 | 432 | 149 | 90 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.15 | 693/002-2Z | 3.8 | 644 | 215 | 67 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 4 | 0.9 | 0.15 | 693-2Z | 4.8 | 644 | 215 | 80 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | 623-2Z | 4.8 | 725 | 265 | 65 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 7 | 8.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 674-2Z | 345 | 130 | 63 | 9 | 1 | |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 4 | 1 | 0.1 | 684-2Z | 4.8 | 658 | 226 | 82 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.1 | 684/10-2Z | 4.8 | 658 | 226 | 86 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | 694-2Z | 4.8 | 730 | 271 | 66 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | 604-2Z | 4.8 | 734 | 282 | 56 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 624-2Z | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 52 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 634-2Z | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 44 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 634D-2Z | 1.935 | 677 | 44 | 6 | 3.175 | |
| 5 | 8 | 9.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.08 | 675-2Z | 390 | 160 | 52 | 11 | 1 | |
| 5 | 10 | 4 | 0.08 | 694/1002-2Z | 730 | 271 | 66 | 8 | 1.588 | |||
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | 685/003-2Z | 734 | 282 | 62 | 8 | 1.588 | |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 5 | 1 | 0.15 | 685-2Z | 5.8 | 734 | 282 | 71 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 695-2Z | 4.8 | 851 | 366 | 49 | 10 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 13 | 5 | 0.2 | 624/0003-2Z | 1.339 | 488 | 53 | 7 | 2.381 | |||
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 605-2Z | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 50 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 625-2Z | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 42 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 625D-2Z | 1.935 | 677 | 45 | 6 | 3.175 | |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 635-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 35 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 6 | 12 | 4 | 0.15 | 695/1202-2Z | 851 | 366 | 49 | 10 | 1.588 | |||
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.15 | 686-2Z | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 55 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 696-2Z | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 46 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 16 | 5 | 0.3 | 625/0002-2Z | 1.646 | 663 | 41 | 8 | 2.5 | |||
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 626-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 34 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.15 | 687-2Z | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 50 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | 697-2Z | 5.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 39 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 607-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 38 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 627-2Z | 3.369 | 1.363 | 35 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 8 | 14 | 4 | 0.02 | 688A/142-2Z | 335 | 152 | 47 | 12 | 1.191 | |||
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 6 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 688-2Z | 6.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 48 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 688/003-2Z | 1.795 | 776 | 43 | 9 | 2.5 | |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 698-2Z | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 40 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 608-2Z | 3.369 | 1.363 | 38 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 6 | 1.3 | 0.2 | 689-2Z | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 44 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 9 | 20 | 6 | 0.3 | 699-2Z | 1.922 | 915 | 35 | 10 | 2.5 | |||
| 9 | 24 | 7 | 0.3 | 609-2Z | 3.435 | 1.43 | 33 | 7 | 3.969 | |||
| 9 | 24 | 7 | 0.3 | 609D-2Z | 3.758 | 1.632 | 32 | 8 | 3.969 | |||
| 9 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 629-2Z | 4.698 | 1.982 | 34 | 7 | 4.763 | |||
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 6800/002-2Z | 1.922 | 915 | 34 | 10 | 2.5 | |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6800-2Z | 7.8 | 1.922 | 915 | 42 | 10 | 2.5 |
| 10 | 22 | 6 | 0.3 | 6900-2Z | 2.555 | 1.129 | 31 | 8 | 3.175 | |||
| 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 6000-2Z | 4.698 | 1.982 | 32 | 7 | 4.763 | |||
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 6200-2Z | 6.1 | 2.6 | 29 | 7 | 5.556 | |||
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 6200D-2Z | 5.236 | 2.374 | 27 | 8 | 4.763 | |||
| 12 | 21 | 5 | 0.3 | 6801-2Z | 1.93 | 900 | 30 | 12 | 2.381 | |||
| 12 | 21 | 5 | 0.3 | 6801-2RZ | 1.93 | 900 | 30 | 12 | 2.381 | |||
| 12 | 24 | 6 | 0.3 | 6901-2Z | 2.971 | 1.452 | 27 | 10 | 3.175 | |||
| 12 | 24 | 6 | 0.3 | 6901-2RZ | 2.971 | 1.452 | 27 | 10 | 3.175 | |||
| 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 6001-2Z | 5.237 | 2.359 | 28 | 9 | 3.969 | |||
| 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6201-2Z | 7.073 | 3.1 | 26 | 7 | 6 | |||
| 15 | 24 | 5 | 0.3 | 6802-2Z | 2.08 | 1.1 | 25 | 14 | 2.381 | |||
| 15 | 24 | 5 | 0.3 | 6802-2RZ | 2.08 | 1.1 | 25 | 14 | 2.381 | |||
| 15 | 28 | 7 | 0.3 | 6902-2Z | 4.445 | 2.268 | 24 | 11 | 3.175 | |||
| 15 | 28 | 7 | 0.3 | 6902-2RZ | 4.445 | 2.268 | 24 | 11 | 3.175 | |||
| 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 6002-2Z | 5.676 | 2.819 | 26 | 9 | 4.763 | |||
| 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 6202-2Z | 7.939 | 3.744 | 23 | 8 | 6 | |||
| 17 | 26 | 5 | 0.3 | 6803-2Z | 2.24 | 1.27 | 22 | 16 | 2.381 | |||
| 17 | 26 | 5 | 0.3 | 6803-2RZ | 2.24 | 1.27 | 22 | 16 | 2.381 | |||
| 17 | 30 | 7 | 0.3 | 6903-2Z | 4.723 | 2.547 | 21 | 11 | 3.969 | |||
| 17 | 30 | 7 | 0.3 | 6903-2RZ | 4.723 | 2.547 | 21 | 11 | 3.969 | |||
| 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6003-2Z | 6.172 | 3.267 | 23 | 10 | 4.763 | |||
| 17 | 40 | 12 | 0.6 | 6203-2Z | 9.811 | 4.734 | 20 | 8 | 6.747 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z SHIELD FLANGE BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2Z Flange Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0937 | 0.013 | 0.003 | F1191-2Z | 0.125 | 163 | 44 | 164 | 6 | 0.03125 |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1397-2Z | 0.1406 | 239 | 67 | 140 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F5/64-2Z | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 117 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F2380-2Z | 0.125 | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.03125 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F3/32-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 72 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F3175-2Z | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 87 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1/8A-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 75 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1/8A/6-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 82 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | F1/8B-2Z | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F3967-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 68 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F4763A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F4763B-2Z | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F3/16-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 57 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A/0001-2Z | 1.651 | 670 | 41 | 8 | 0.0984 | ||
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F6350A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 0.005 | F6350B-2Z | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 49 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F7938-2Z | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.2182 | 0.062 | 0.016 | F3/8-2Z | 2.555 | 1.129 | 35 | 8 | 0.125 | |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.225 | 0.3125 | 0.062 | 0.016 | F1/2-2Z | 4.12 | 2.01 | 32 | 9 | 0.15625 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z & 2RZ FLANGE SHIELD BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2Z / 2RZ Flange Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 1.5 | 4 | 5 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.05 | F68/1.5 -2Z | 163 | 44 | 153 | 6 | 0.794 | |
| 1.5 | 5 | 6.5 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.15 | F69/1.5-2Z | 192 | 59 | 109 | 7 | 0.794 | |
| 2 | 5 | 6.1 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.08 | F682-2Z | 3.1 | 192 | 59 | 116 | 7 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | F692-2Z | 3.1 | 286 | 90 | 91 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 6 | 7.1 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.08 | F68/2.5-2Z | 3.4 | 289 | 92 | 101 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.1 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.1 | F683/0001-2Z | 432 | 149 | 88 | 8 | 1.191 | |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 0.15 | F69/2.5-2Z | 4.3 | 432 | 149 | 87 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.1 | F683-2Z | 3.8 | 432 | 149 | 90 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.15 | 693/002-2Z | 3.8 | 644 | 215 | 67 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 4 | 0.9 | 0.15 | F693-2Z | 4.8 | 644 | 215 | 80 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | F623-2Z | 4.8 | 725 | 265 | 65 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 4 | 1 | 0.1 | F684-2Z | 4.8 | 658 | 226 | 82 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.1 | F684/10-2Z | 4.8 | 658 | 226 | 86 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | 694-2Z | 4.8 | 730 | 271 | 66 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | F604-2Z | 4.8 | 734 | 282 | 56 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | F624-2Z | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 52 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F634-2Z | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 44 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | F685/003-2Z | 734 | 282 | 62 | 8 | 1.588 | |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 5 | 1 | 0.15 | F685-2Z | 5.8 | 734 | 282 | 71 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F695-2Z | 4.8 | 851 | 366 | 49 | 10 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | F605-2Z | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 50 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F625-2Z | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 42 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F635-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 35 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.15 | F686-2Z | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 55 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | F696-2Z | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 46 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F626-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 34 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.15 | F687-2Z | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 50 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | F697-2Z | 5.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 39 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F607-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 38 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F627-2Z | 3.369 | 1.363 | 35 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 6 | 1.3 | 0.2 | F688-2Z | 6.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 48 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.2 | F688/003-2Z | 1.795 | 776 | 43 | 9 | 2.5 | |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F698-2Z | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 40 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F608-2Z | 3.369 | 1.363 | 38 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 6 | 1.3 | 0.2 | F689-2Z | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 44 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F6800/002-2Z | 1.922 | 915 | 34 | 10 | 2.5 | |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6800-2Z | 7.8 | 1.922 | 915 | 42 | 10 | 2.5 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z SHIELD FLANGE EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Flanged Ext Inner Ring 2Z Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0937 | 0.013 | 0.003 | FE1191-2Z | 0.125 | 163 | 44 | 164 | 6 | 0.03125 |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE1397-2Z | 0.1406 | 239 | 67 | 140 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE5/64-2Z | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 117 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE2380-2Z | 0.125 | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.03125 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F3/32-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 72 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE3175-2Z | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 87 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE1/8A-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 75 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE1/8A/6-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 82 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | FE1/8B-2Z | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | FE3967-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 68 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | FE4763A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE4763B-2Z | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE3/16-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 57 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE1/4A/0001-2Z | 1.651 | 670 | 41 | 8 | 0.0984 | ||
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | FE6350A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 0.005 | FE6350B-2Z | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 49 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE1/4A-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | FE7938-2Z | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z & 2RZ FLANGE SHIELD EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Extended Inner Ring 2Z/2RZ Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 2 | 5 | 6.1 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.08 | E682-2Z | 3.1 | 192 | 59 | 116 | 7 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | E692-2Z | 3.1 | 286 | 90 | 91 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 6 | 7.1 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.08 | E68/2.5-2Z | 3.4 | 289 | 92 | 101 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 0.15 | E69/2.5-2Z | 4.3 | 432 | 149 | 87 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 2.5 | 8 | 2.8 | 0.15 | E60/2.5-2Z | 3.6 | 432 | 149 | 81 | 8 | 1.191 | ||
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.1 | E683-2Z | 3.8 | 432 | 149 | 90 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.15 | E693/002-2Z | 3.8 | 644 | 215 | 67 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 4 | 0.9 | 0.15 | E693-2Z | 4.8 | 644 | 215 | 80 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | E623-2Z | 4.8 | 725 | 265 | 65 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 4 | 1 | 0.1 | E684-2Z | 4.8 | 658 | 226 | 82 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.1 | E684/10-2Z | 4.8 | 658 | 226 | 86 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | E694-2Z | 4.8 | 730 | 271 | 66 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | E604-2Z | 4.8 | 734 | 282 | 56 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | E624-2Z | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 52 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | E634-2Z | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 44 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 5 | 1 | 0.15 | E685-2Z | 5.8 | 734 | 282 | 71 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | E695-2Z | 4.8 | 851 | 366 | 49 | 10 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | E605-2Z | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 50 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | E625-2Z | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 42 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E635-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 35 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.15 | E686-2Z | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 55 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | E696-2Z | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 46 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E626-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 34 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.15 | E687-2Z | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 50 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | E697-2Z | 5.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 39 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E607-2Z | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 38 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 6 | 1.3 | 0.2 | E688-2Z | 6.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 48 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E698-2Z | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 40 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E608-2Z | 3.369 | 1.363 | 38 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 6 | 1.3 | 0.2 | E689-2Z | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 44 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E6800-2Z | 7.8 | 1.922 | 915 | 42 | 10 | 2.5 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z SHIELD EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS
Inch Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2Z Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0937 | 0.013 | 0.003 | E1191-2Z | 0.125 | 163 | 44 | 164 | 6 | 0.03125 |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1397-2Z | 0.1406 | 239 | 67 | 140 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E5/64-2Z | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 117 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E2380-2Z | 0.125 | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.03125 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E3/32-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 72 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.003 | E3175/002-2Z | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E3175-2Z | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 87 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 75 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A/6-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 82 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | E1/8B-2Z | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/003-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E3967-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 68 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1562 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 69 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/002-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E4763A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E4763B-2Z | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 162 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E3/16-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 57 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A/0001-2Z | 1.651 | 670 | 41 | 8 | 0.0984 | ||
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E6350A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 0.005 | E6350B-2Z | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 49 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E7938-2Z | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z SHIELD EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2Z Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0937 | 0.013 | 0.003 | E1191-2Z | 0.125 | 163 | 44 | 164 | 6 | 0.03125 |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1397-2Z | 0.1406 | 239 | 67 | 140 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E5/64-2Z | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 117 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E2380-2Z | 0.125 | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.03125 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E3/32-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 72 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.003 | E3175/002-2Z | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E3175-2Z | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 87 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 75 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A/6-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 82 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | E1/8B-2Z | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/003-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E3967-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 68 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1562 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 69 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/002-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E4763A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E4763B-2Z | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 162 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E3/16-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 57 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A/0001-2Z | 1.651 | 670 | 41 | 8 | 0.0984 | ||
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E6350A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 0.005 | E6350B-2Z | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 49 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E7938-2Z | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z SHIELD EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2Z Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0937 | 0.013 | 0.003 | E1191-2Z | 0.125 | 163 | 44 | 164 | 6 | 0.03125 |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1397-2Z | 0.1406 | 239 | 67 | 140 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E5/64-2Z | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 117 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E2380-2Z | 0.125 | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.03125 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E3/32-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 72 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.003 | E3175/002-2Z | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E3175-2Z | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 87 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 75 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A/6-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 82 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | E1/8B-2Z | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/003-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E3967-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 68 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1562 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 69 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/002-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E4763A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E4763B-2Z | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 162 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E3/16-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 57 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A/0001-2Z | 1.651 | 670 | 41 | 8 | 0.0984 | ||
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E6350A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 0.005 | E6350B-2Z | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 49 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E7938-2Z | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z SHIELD EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2Z Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0937 | 0.013 | 0.003 | E1191-2Z | 0.125 | 163 | 44 | 164 | 6 | 0.03125 |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1397-2Z | 0.1406 | 239 | 67 | 140 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E5/64-2Z | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 117 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E2380-2Z | 0.125 | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.03125 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E3/32-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 72 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.003 | E3175/002-2Z | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E3175-2Z | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 87 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 75 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A/6-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 82 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | E1/8B-2Z | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/003-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E3967-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 68 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1562 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 69 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/002-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E4763A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E4763B-2Z | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 162 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E3/16-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 57 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A/0001-2Z | 1.651 | 670 | 41 | 8 | 0.0984 | ||
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E6350A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 0.005 | E6350B-2Z | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 49 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E7938-2Z | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z SHIELD EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2Z Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0937 | 0.013 | 0.003 | E1191-2Z | 0.125 | 163 | 44 | 164 | 6 | 0.03125 |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1397-2Z | 0.1406 | 239 | 67 | 140 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E5/64-2Z | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 117 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E2380-2Z | 0.125 | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.03125 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E3/32-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 72 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.003 | E3175/002-2Z | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E3175-2Z | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 87 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 75 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A/6-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 82 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | E1/8B-2Z | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/003-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E3967-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 68 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1562 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 69 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/002-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E4763A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E4763B-2Z | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 162 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E3/16-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 57 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A/0001-2Z | 1.651 | 670 | 41 | 8 | 0.0984 | ||
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E6350A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 0.005 | E6350B-2Z | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 49 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E7938-2Z | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2Z SHIELD EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2Z Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0937 | 0.013 | 0.003 | E1191-2Z | 0.125 | 163 | 44 | 164 | 6 | 0.03125 |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1397-2Z | 0.1406 | 239 | 67 | 140 | 6 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E5/64-2Z | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 117 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E2380-2Z | 0.125 | 192 | 59 | 120 | 7 | 0.03125 |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E3/32-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 72 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.003 | E3175/002-2Z | 0.125 | 292 | 97 | 80 | 7 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E3175-2Z | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 87 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 75 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E1/8A/6-2Z | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 82 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.012 | E1/8B-2Z | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 61 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/003-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 62 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E3967-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 68 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1562 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E3967/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 69 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/002-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 165 | 65 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E4763A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | E4763B-2Z | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 56 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1094 | 0.003 | E4763A/082-2Z | 0.1406 | 391 | 162 | 70 | 11 | 0.0394 | ||
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E3/16-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 57 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A/0001-2Z | 1.651 | 670 | 41 | 8 | 0.0984 | ||
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | E6350A-2Z | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 54 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 0.005 | E6350B-2Z | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 49 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E1/4A-2Z | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 43 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.005 | E7938-2Z | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 45 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2TS SEAL EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2TS Flange Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.078 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F5/64-2TS | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 65 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.094 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F3/32-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.109 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F3175-2TS | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 53 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1/8A-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1/8A/6-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.156 | 0.03 | 0.012 | F1/8B-2TS | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 44 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.156 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F3967-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 42 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.188 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F4763A-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 42 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.188 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F4763B-2TS | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 41 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F3/16-2TS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 37 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.188 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A/0001-2TS | 1.651 | 670 | 31 | 8 | 0.0984 | |
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F6350A-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 35 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.188 | 0.045 | 0.005 | F6350B-2TS | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 33 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A-2TS | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 31 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.313 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.156 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F7938-2TS | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 30 | 12 | 0.0469 |
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.218 | 0.062 | 0.016 | F3/8-2TS | 2.555 | 1.129 | 24 | 8 | 0.125 | |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.225 | 0.313 | 0.062 | 0.016 | F1/2-2TS | 4.12 | 2.01 | 21 | 9 | 0.1563 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2TS SEAL EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2TS Flange Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.078 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F5/64-2TS | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 65 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.094 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F3/32-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.109 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F3175-2TS | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 53 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1/8A-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1/8A/6-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.156 | 0.03 | 0.012 | F1/8B-2TS | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 44 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.156 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F3967-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 42 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.188 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F4763A-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 42 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.188 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F4763B-2TS | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 41 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F3/16-2TS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 37 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.188 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A/0001-2TS | 1.651 | 670 | 31 | 8 | 0.0984 | |
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F6350A-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 35 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.188 | 0.045 | 0.005 | F6350B-2TS | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 33 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A-2TS | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 31 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.313 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.156 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F7938-2TS | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 30 | 12 | 0.0469 |
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.218 | 0.062 | 0.016 | F3/8-2TS | 2.555 | 1.129 | 24 | 8 | 0.125 | |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.225 | 0.313 | 0.062 | 0.016 | F1/2-2TS | 4.12 | 2.01 | 21 | 9 | 0.1563 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2TS SEAL EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2TS Flange Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.078 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F5/64-2TS | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 65 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.094 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F3/32-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.109 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F3175-2TS | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 53 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1/8A-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F1/8A/6-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.156 | 0.03 | 0.012 | F1/8B-2TS | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 44 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.156 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F3967-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 42 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.188 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F4763A-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 42 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.188 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | F4763B-2TS | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 41 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F3/16-2TS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 37 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.188 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A/0001-2TS | 1.651 | 670 | 31 | 8 | 0.0984 | |
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | F6350A-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 35 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.188 | 0.045 | 0.005 | F6350B-2TS | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 33 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F1/4A-2TS | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 31 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.313 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.156 | 0.031 | 0.005 | F7938-2TS | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 30 | 12 | 0.0469 |
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.218 | 0.062 | 0.016 | F3/8-2TS | 2.555 | 1.129 | 24 | 8 | 0.125 | |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.225 | 0.313 | 0.062 | 0.016 | F1/2-2TS | 4.12 | 2.01 | 21 | 9 | 0.1563 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2TS SEAL FLANGE EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Flange Ext Inner Ring 2TS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 2 | 5 | 6.1 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.08 | FE6822TS | 3.1 | 192 | 59 | 71 | 7 | 0.794 |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | FE6922TS | 3.1 | 286 | 90 | 65 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 6 | 7.1 | 2.6 | 0.8 | 0.08 | FE68/2.52TS | 3.4 | 289 | 92 | 61 | 7 | 1 |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 0.15 | FE69/2.52TS | 4.3 | 432 | 149 | 53 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.1 | FE6832TS | 3.8 | 432 | 149 | 53 | 8 | 1.191 |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 4 | 0.9 | 0.15 | FE6932TS | 4.8 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | FE56232TS | 4.8 | 725 | 265 | 44 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 4 | 1 | 0.1 | FE6842TS | 4.8 | 658 | 226 | 45 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.1 | FE684/102TS | 4.8 | 658 | 226 | 86 | 7 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | FE6942TS | 4.8 | 730 | 271 | 41 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | FE6042TS | 4.8 | 734 | 282 | 37 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | FE6242TS | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 37 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | FE6342TS | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 31 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 5 | 1 | 0.15 | FE6852TS | 5.8 | 734 | 282 | 37 | 8 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | FE6952TS | 4.8 | 851 | 366 | 34 | 10 | 1.588 |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | FE6052TS | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 33 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | FE6252TS | 5.8 | 1.646 | 663 | 31 | 8 | 2.5 |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | FE6352TS | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 28 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.15 | FE6862TS | 5.8 | 1.096 | 437 | 33 | 8 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | FE6962TS | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 31 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | FE6262TS | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 28 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.15 | FE6872TS | 5.8 | 1.186 | 505 | 31 | 9 | 1.984 |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | FE6972TS | 5.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 28 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | FE6072TS | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 28 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | FE6272TS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 27 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 6 | 1.3 | 0.2 | FE6882TS | 6.8 | 1.795 | 776 | 28 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | FE6982TS | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 27 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | FE6082TS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 27 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 6 | 1.3 | 0.2 | FE6892TS | 6.8 | 1.798 | 797 | 27 | 9 | 2.5 |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | FE68002TS | 7.8 | 1.922 | 915 | 25 | 10 | 2.5 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2TS SEAL EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Flanged Ext Inner Ring 2TS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.078 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE5/64-2TS | 0.1719 | 286 | 90 | 65 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.094 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.005 | FE3/32-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.109 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE3175-2TS | 0.1406 | 292 | 97 | 53 | 7 | 0.0394 |
| 0.125 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE1/8A-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.141 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE1/8A/6-2TS | 0.1719 | 644 | 215 | 51 | 7 | 0.0625 |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.156 | 0.03 | 0.012 | FE1/8B-2TS | 0.1875 | 720 | 260 | 44 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.156 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | FE3967-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 42 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.188 | 0.313 | 0.359 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | FE4763A-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 42 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.188 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.031 | 0.003 | FE4763B-2TS | 0.1562 | 730 | 271 | 41 | 8 | 0.0625 |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE3/16-2TS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 37 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.036 | 0.003 | FE6350A-2TS | 0.1562 | 391 | 165 | 35 | 11 | 0.0394 |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.188 | 0.045 | 0.005 | FE6350B-2TS | 0.2188 | 730 | 271 | 33 | 8 | 0.0781 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE1/4A-2TS | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 31 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.313 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.156 | 0.031 | 0.005 | FE7938-2TS | 0.1875 | 539 | 279 | 30 | 12 | 0.0469 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
GRW DEEP GROOVE 2RS SEAL BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2RS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | 6242RS | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 634D2RS | 1.935 | 677 | 26 | 6 | 3.175 | |
| 5 | 16 | 5 | 0.3 | 625D2RS | 1.935 | 677 | 26 | 6 | 3.175 | |||
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6352RS | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 22 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6262RS | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 22 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6072RS | 6.8 | 2.522 | 1.057 | 22 | 8 | 3.175 |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6272RS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 21 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6082RS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 21 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 9 | 24 | 7 | 0.3 | 6092RS | 3.435 | 1.43 | 20 | 7 | 3.969 | |||
| 9 | 24 | 7 | 0.3 | 609D2RS | 3.758 | 1.632 | 20 | 8 | 3.969 | |||
| 9 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 6292RS | 4.698 | 1.982 | 19 | 7 | 4.763 | |||
| 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 60002RS | 4.698 | 1.982 | 19 | 7 | 4.763 | |||
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 62002RS | 6.1 | 2.6 | 18 | 7 | 5.556 | |||
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 6200D2RS | 5.236 | 2.374 | 18 | 8 | 4.763 | |||
| 12 | 21 | 5 | 0.3 | 68012RS | 1.93 | 900 | 19 | 12 | 2.381 | |||
| 12 | 24 | 6 | 0.3 | 69012RS | 2.971 | 1.452 | 19 | 10 | 3.175 | |||
| 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 60012RS | 5.237 | 2.359 | 31 | 9 | 3.969 | |||
| 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 62012RS | 7.073 | 3.1 | 18 | 7 | 6 | |||
| 15 | 24 | 5 | 0.3 | 68022RS | 2.08 | 1.1 | 18 | 14 | 2.381 | |||
| 15 | 28 | 7 | 0.3 | 69022RS | 4.445 | 2.268 | 18 | 11 | 3.175 | |||
| 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 60022RS | 5.676 | 2.819 | 17 | 9 | 4.763 | |||
| 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 62022RS | 7.939 | 3.744 | 17 | 8 | 6 | |||
| 17 | 26 | 5 | 0.3 | 68032RS | 2.24 | 1.27 | 17 | 16 | 2.381 | |||
| 17 | 30 | 7 | 0.3 | 69032RS | 4.723 | 2.547 | 17 | 11 | 3.969 | |||
| 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 60032RS | 6.172 | 3.267 | 17 | 10 | 4.763 | |||
| 17 | 40 | 12 | 0.6 | 62032RS | 9.811 | 4.734 | 16 | 8 | 6.747 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2RS SEAL & FLANGE SEAL BALL BEARINGS
Inch Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2RS Seal & 2RS Flange Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | 3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | 1/4A-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 24 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.281 | 0.016 | 1/4-2RS | 2.522 | 1.057 | 22 | 8 | 0.125 | |||
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.218 | 0.062 | 0.016 | 3/8-2RS | 2.555 | 1.129 | 21 | 8 | 0.125 | |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2RS SEAL FLANGE BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2TS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | E6242RS | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E6272RS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 21 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E6082RS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 21 | 7 | 3.969 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2RS SEAL & FLANGE SEAL BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | 2RS Seal & 2RS Flange Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | 3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | 1/4A-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.651 | 670 | 24 | 8 | 0.0984 |
| 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.281 | 0.016 | 1/4-2RS | 2.522 | 1.057 | 22 | 8 | 0.125 | |||
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.218 | 0.062 | 0.016 | 3/8-2RS | 2.555 | 1.129 | 21 | 8 | 0.125 | |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | F3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2RS SEAL EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2TS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | E6242RS | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E6272RS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 21 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E6082RS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 21 | 7 | 3.969 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2RS SEAL & FLANGE SEAL BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Std & Flange Ext Inner Ring 2RS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2RS SEAL FLANGE EXTENDED INNER RING BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Ext Inner Ring 2TS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | E6242RS | 5.8 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 2.381 |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E6272RS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 21 | 7 | 3.969 | |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | E6082RS | 3.369 | 1.363 | 21 | 7 | 3.969 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.
DEEP GROOVE 2RS SEAL & FLANGE SEAL BALL BEARINGS

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (FD) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (FB) | Radius (rs – min) (2) | Std & Flange Ext Inner Ring 2RS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Load Rating Cr (N) | Load Rating Cor (N) | Limiting Speed (6) Nur (x 1000 rpm) | Ball Comple ment Qty.: Z (5) | Ball Comple ment Size: Dw |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | E3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
| 0.188 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.012 | FE3/16-2RS | 0.2272 | 1.339 | 488 | 28 | 7 | 0.0938 |
- Ball bearings without closure may be supplied with recesses. Please advise if you require bearings without recesses.
- rs min = minimum single bearing chamfer or maximum shaft or housing fillet radius.
- Not applicable to bearings with extended inner ring.
- Not applicable to flanged bearings.
- The number of balls may vary due to different types of retainer.
- See ‘Limiting Speeds’.
- Tolerance of bore +12µm to +3µm.
- Available in different width with closure.