ABIS: Precision Bearings by IEC
Our ABIS range covers miniature precision bearings manufactured with ABEC 1 to ABEC 5 tolerances, with bore dimensions ranging from 0.6mm to 90mm. These high-quality bearings are essential for applications requiring extreme accuracy and reliability.



ABIS Precision Bearings: Delivered with IEC Expertise
For more than 85 years, IEC has built a reputation as a trusted partner in sourcing and distributing high-quality components.
All ABIS miniature precision bearings are produced by well-established partners specialising in the manufacture of precision ball bearings and are approved to ISO 9001 standards. This ensures that each bearing meets stringent quality requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of high-precision applications. The ABIS range includes metric and imperial sizes, open, shielded, and sealed variants, as well as options with or without flanges.
With materials ranging from high carbon chrome to stainless steel, and configurations like full complement and ceramic ball options, ABIS bearings are built for versatility and durability across a variety of sectors. Every ABIS product reflects the company’s commitment to quality and performance, and IEC ensures these high standards are maintained for UK customers.
A Legacy of Excellence and Innovation
IEC has been supporting ball bearing applications in many different industries since 1938. Our extensive experience and expertise in the field enables us to provide solutions tailored to the specific needs of our customers. We maintain a large stock of ABIS miniature precision bearings and bearing accessories at our Poole premises, ensuring quick availability and prompt delivery.
Benefits of ABIS Precision Bearings
- High Precision: ABIS bearings are manufactured to tight tolerances, delivering outstanding accuracy, optimal performance, and reliability in even the most demanding environments.
- Versatility: With an extensive range of configurations, ABIS bearings are suited for applications across numerous industries, including medical and dental, robotics, and industrial machinery.
- Exceptional Durability: ABIS bearings are made from high quality materials and rigorously tested, ensuring long-lasting performance that reduces downtime and enhances productivity.

Your Trusted UK Source for ABIS Bearings
With our commitment to quality, customer satisfaction, and decades of expertise, we are well-positioned to provide you with the precision-engineered solutions your business needs.

Miniature precision bearings are available in a variety of configurations to meet diverse application needs, including:
- Metric and imperial sizes.
- Open, shielded, and sealed.
- With and without flange.
- High carbon chrome and stainless steel.
- Full complement: Bearings without a cage, providing maximum load capacity.
- Ceramic balls: Offering reduced weight, increased speed, and lower friction.
ABIS bearings are suited for applications across numerous industries including:
- medical and dental
- robotics
- industrial machinery
Rolling element bearings consist of ball, roller or needle elements located between two metal rings which are then free to rotate relative to each other. They offer advantages over plain bushes without the higher costs of more sophisticated fluid bearings.
Ball bearings benefit over plain bearings in terms of torque levels, rotational accuracy and speed capability. In their standard form they can support both radial and axial loads.
- High Precision: Manufactured to tight tolerances for optimal performance.
- Durability: Made from high-quality materials for long service life.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications, including medical and dental, robotics, aerospace components and more.
- Reliability: Consistent performance in demanding environments.
ABIS Catalogue
ABIS Miniature Precision Bearings
Our ABIS range covers miniature precision bearings manufactured to ABEC 1 to ABEC 5 tolerances, with bore dimensions ranging from 0.6mm to 90mm. These high-quality bearings are essential for applications requiring extreme accuracy and reliability.
Miniature precision bearings are available in a variety of configurations to meet diverse application needs, including:
- Metric and imperial sizes: Ensuring compatibility with different measurement standards.
- Open, shielded, and sealed: Providing options for different levels of protection and lubrication.
- With and without flange: Offering flexibility in mounting and stability.
- High carbon chrome and stainless steel: Materials chosen for durability and resistance to corrosion.
- Full complement: Bearings without a cage, providing maximum load capacity.
- Ceramic balls: Offering reduced weight, increased speed, and lower friction.
All ABIS miniature precision bearings are produced by well-established partners specialising in the manufacture of precision ball bearings and are approved to ISO 9001 standards. This ensures that each bearing meets stringent quality requirements, making them suitable for a wide range of high-precision applications.
IEC has been closely involved with ball bearing applications in many different industries since 1938. Our extensive experience and expertise in the field enable us to provide solutions tailored to the specific needs of our customers. We maintain a large stock of ABIS miniature precision bearings and bearing accessories at our Poole premises, ensuring quick availability and prompt delivery.
ABIS Miniature Precision Bearings
- High Precision: Manufactured to tight tolerances for optimal performance.
- Durability: Made from high-quality materials for long service life.
- Versatility: Suitable for various applications, including medical and dental, robotics, aerospace components and more.
- Reliability: Consistent performance in demanding environments.
For more information on our range of miniature precision bearings, or to discuss your specific requirements, please contact IEC. Our team of experts is ready to assist you in finding the perfect bearing solution for your application.
Available Ball Bearings
Open Ball Bearings | Shielded Ball Bearings | Sealed Ball Bearings |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
Available Ball Bearings
Open Ball Bearings | Shielded Ball Bearings | Sealed Ball Bearings |
|---|---|---|
 |  |  |
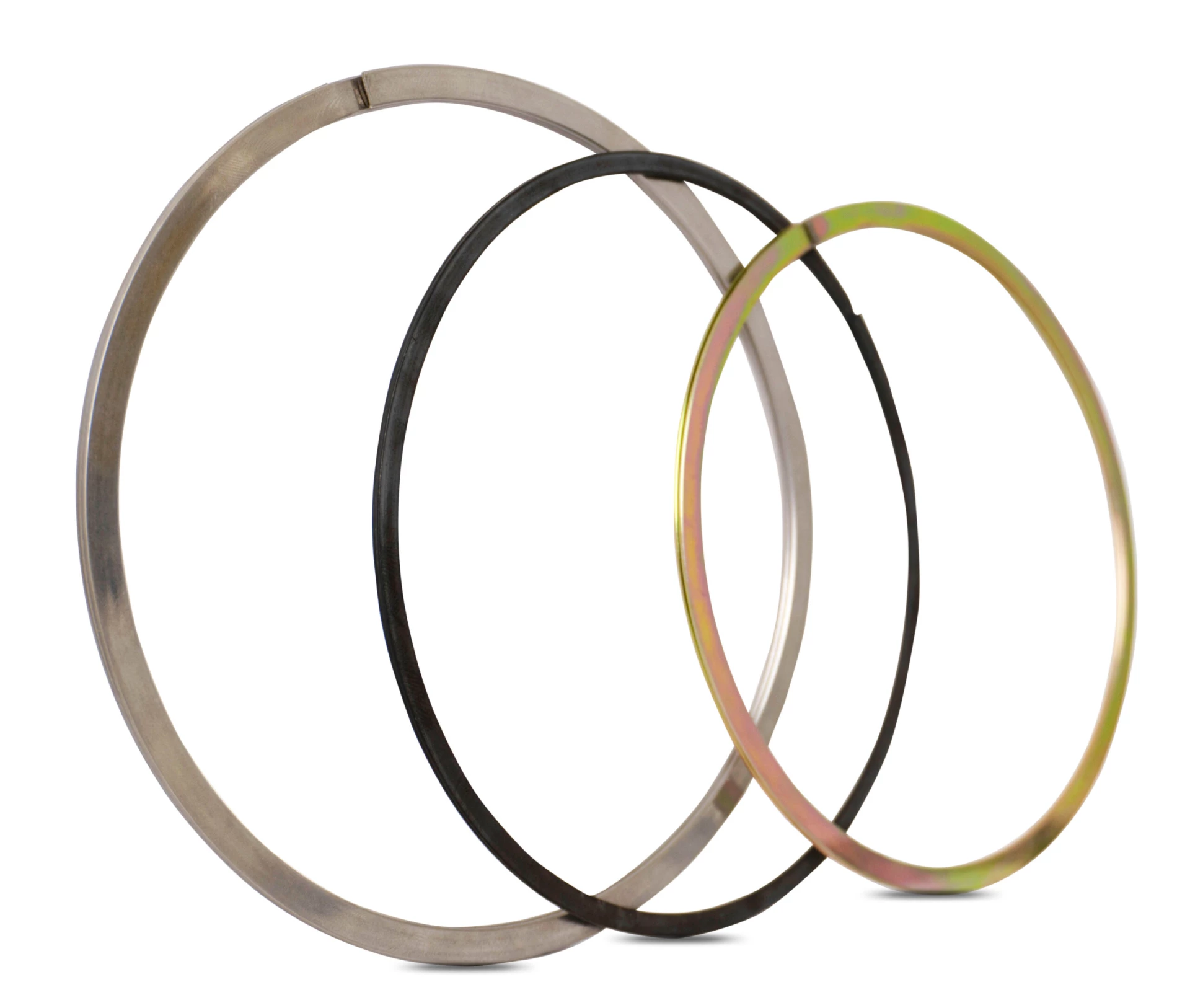
ACCESSORIES - Shaft Retaining Rings
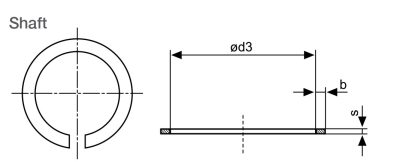
| Reference | Dimensions (mm) | |||||
| Shaft | Retaining Ring | Groove | ||||
| d1Ø | d3 max. | b+0.10 | s+0.02 | d2+0.05 | m+0.03 | |
| WSR3 | 3 | 2.60 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 2.70 | 0.33 |
| WSR4 | 4 | 3.60 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 3.70 | 0.33 |
| WSR5 | 5 | 4.50 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 4.60 | 0.44 |
| WSR6 | 6 | 5.45 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 5.60 | 0.44 |
| WSR7 | 7 | 6.45 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 6.60 | 0.44 |
| WSR8 | 8 | 7.35 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 7.50 | 0.55 |
| WSR9 | 9 | 8.30 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 8.50 | 0.55 |
| WSR10 | 10 | 9.25 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 9.50 | 0.55 |
Material: Spring Steel 1.4310/AISI 301
ACCESSORIES - shaft retaining rings
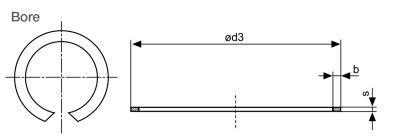
| Reference | Dimensions (mm) | |||||
| Bore | Retaining Ring | Groove | ||||
| d1Ø | d3 max. | b+0.10 | s+0.02 | d2+0.05 | m+0.03 | |
| BSR4 | 4 | 4.40 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 4.30 | 0.33 |
| BSR5 | 5 | 5.45 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 5.30 | 0.33 |
| BSR6 | 6 | 6.45 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 6.30 | 0.33 |
| BSR7 | 7 | 7.50 | 0.50 | 0.30 | 7.30 | 0.33 |
| BSR8 | 8 | 8.60 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 8.40 | 0.44 |
| BSR9 | 9 | 9.60 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 9.40 | 0.44 |
| BSR10 | 10 | 10.65 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 10.40 | 0.44 |
| BSR11 | 11 | 11.65 | 0.70 | 0.40 | 11.40 | 0.44 |
| BSR12 | 12 | 12.75 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 12.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR13 | 13 | 13.75 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 13.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR14 | 14 | 14.80 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 14.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR15 | 15 | 15.80 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 15.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR16 | 16 | 16.85 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 16.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR17 | 17 | 17.85 | 0.90 | 0.50 | 17.50 | 0.55 |
| BSR19 | 19 | 20.00 | 1.10 | 0.60 | 19.60 | 0.66 |
Material: Spring Steel 1.4310/AISI 301
ACCESSORIES - shims and spring washers
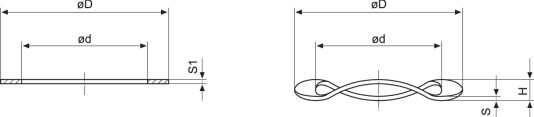
| Dimensions (mm) | Used for | |||||
| Shims | Spring Washers | |||||
| d x D Reference | S1 | d x D Reference | H | S | On Shaft | On Housing |
| AS1.55×2.50 | 0.15 – – | – WF1.60×2.90 WF1.90×2.80 | – 0.40 0.50 | – 0.06 0.08 | 68/1.5; 69/1.5 | – |
| AS2.00×4.30 | 0.10 0.16 0.20 | – | – | – | – | – |
| AS2.25×3.20 | 0.08 0.10 | WF2.15×3.10 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 682; 692; 5/64 | 1016 |
| AS2.80×3.90 | 0.08 0.10 | WF2.70×3.80 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 60/2.2; 68/2.5; 69/2.5; 3/32 | 68/1.5; 691; 1191 |
| AS3.05×4.50 | 0.10 0.16 0.20 | – | – | – | – | – |
| AS3.30×4.40 | 0.08 0.10 0.12 | WF3.20×4.30 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 623; 683; 693; 1/8A; 1/8B; 3175; 1/8A/6; 1/8B/083 | – |
| AS3.50×5.00 | 0.08 | – | – | – | – | – |
| AS3.80×4.90 | 0.08 0.10 0.12 | WF3.70×4.80 | 0.55 | 0.10 | – | 682; 69/1.5 |
| AS4.05×5.50 | 0.10 0.20 | – | – | – | – | – |
| AS4.30×5.85 | 0.10 0.12 0.15 | WF4.20×5.75 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 604; 624; 634; 684; 694; 3967 | 68/2.5; 692 |
| AS4.90×6.20 | 0.10 0.12 0.15 | WF4.80×6.10 | 0.60 | 0.12 | 3/16; 4763A; 4763B | 5/64; 3175 |
| AS5.20×6.75 | 0.15 | – | – | – | – | – |
| AS5.30×6.85 | 0.10 0.12 0.15 | WF5.20×6.75 | 0.65 | 0.12 | 625; 635; 685; 695 | 683; 69/2.5 |
| AS5.50×6.75 | 0.15 | – | – | – | – | – |
| AS6.30×7.85 | 0.12 0.15 0.18 | WF6.20×7.75 | 0.70 | 0.15 | 626; 686; 696 | 60/25; 693; 3/32; 1/BA; 3967; 4763A |
| AS6.70×9.40 | 0.10 | – | – | – | – | – |
| AS7.30×8.80 | 0.12 0.15 0.18 | WF7.20×8.70 | 0.90 | 0.15 | 607; 627; 687; 697 | 684 |
| WF7.20X12.00 | 1.55 | 0.13 | 607; 627 | 63508; 7938; 1/8B/083 | ||
| AS8.30×9.80 | 0.10 0.15 0.18 0.20 | WF8.20×9.70 | 0.85 | 0.18 | 608; 688; 698; 7938 | 623 |
| AS9.30×10.80 | 0.15 0.18 0.20 | WF9.20×10.70 | 1.15 | 0.18 | 609; 629; 689; 699 | 685; 694 |
| AS10.30×11.80 | 0.18 0.20 0.22 | WF10.20×11.70 | 1.05 | 0.20 | 6000; 6800; 6900; 3/8 | 604 |
| – | – | WF10.50×15.80* | 1.85 | 0.25 | 6000 | 625; 634 |
| AS11.30×12.80 | 0.18 0.20 0.22 | WF11.20×12.70 | 1.30 | 0.20 | – | 624; 686; 695 |
| AS12.30×13.80 | 0.20 0.22 0.25 | WF12.20×13.70 | 1.30 | 0.22 | – | 687 |
| AS13.30×14.80 | 0.20 0.22 0.25 | WF13.20×14.70 | 1.30 | 0.22 | – | 696 |
| AS14.35×15.80 | 0.22 0.25 0.30 | WF14.20×15.65 | 1.55 | 0.25 | – | 625; 634; 688; 1/4A |
| AS15.35×16.80 | 0.22 0.25 0.30 | WF15.20×16.65 | 1.55 | 0.25 | – | 689; 697 |
| AS16.00×22.00 | 0.10 | WF15.80×21.80 | 1.60 | 0.20 | – | 3/8 |
| AS16.40×18.80 | 0.25 0.30 0.35 | WF16.20×18.55 | 2.15 | 0.30 | 607; 626; 635; 6800; 698; ¼ | |
Material: Spring Steel 1.4310/AISI 301
ABIS Preload Springs For ball bearings
Preloading of bearings is a crucial process that involves applying an axial load to either the inner or outer ring of the bearing. This ensures that radial play is taken up, and running components are in consistent contact. Using a bearing preload spring is seen as a best practice as it significantly reduces noise and vibration, ultimately extending the life of the bearing.
There are essentially two methods to preload a bearing. Firstly, a solid preload, such as a threaded plug or circlip. Secondly, by a spring, specifically a disc spring. The disadvantage of a solid preload is that it cannot compensate for tolerance build-up or thermal expansion of the surrounding components, which may affect the running torque.
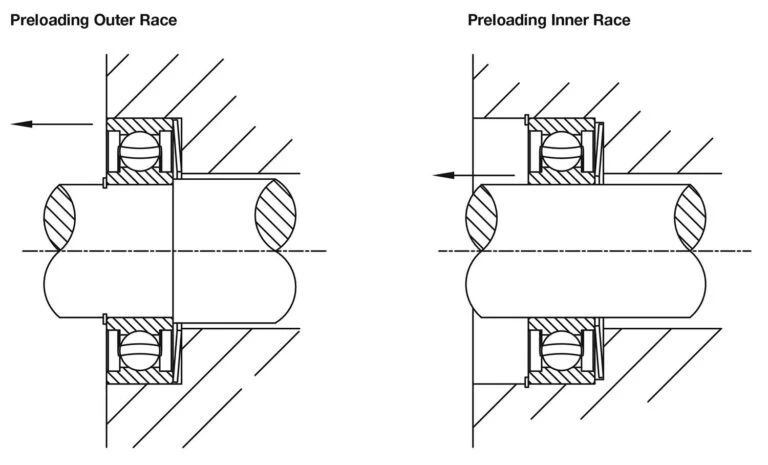
Bearing preload springs, particularly disc springs, offer a superior solution. The disc spring, by applying a constant load around the bearing ring, overcomes the limitations associated with solid preloads. In applications where a very light preload is required, the disc spring can be designed with radial slots to reduce the axial force applied.
IEC provides a comprehensive range of bearing preload springs from ABIS, designed to meet various application requirements. Our springs ensure consistent performance and reliability by maintaining optimal contact and load distribution in ball bearings.
Benefits of ABIS Bearing Preload Springs
- Noise Reduction: Preloading reduces operational noise, leading to quieter machinery.
- Vibration Control: Minimises vibration, improving overall equipment stability.
- Extended Bearing Life: Reduces wear and tear, extending the bearing’s lifespan.
- Thermal Compensation: Accommodates thermal expansion and tolerance variations, maintaining consistent performance.
For detailed size specifications, please refer to the links below. IEC is committed to providing high-quality bearing preload springs from ABIS to enhance your bearing applications’ performance and durability.
ABIS Bearing Lock Nuts Introduction
The bearing lock nut was developed to provide secure mounting and location of a bearing on a shaft. The manufacturer has more than 30 years experience in lock nut technology and their factory is TS 16949 approved.
Key Benefits
- Secure locking
- Available in Carbon and Stainless Steel
- Superior material for high integrity product
- Sizes from M10 to M100 available from stock
- Tab washers also available from stock
- Sockets/spanners available
- KM lock nuts to DIN 981:2009
Abis Size Range and Ordering Information (Unit: mm)
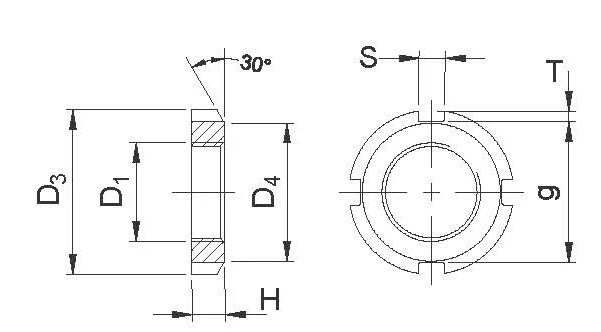
| Thread Size D1 | Carbon Steel | Stainless Steel | D3 | D4 | g | T | S | H | Tab Washer |
| M10 x0.75 | KM00 | KM00SS | 18 | 13.5 | 14 | 2 | 3 | 4 | MB0 |
| M12 x1.0 | KM01 | KM01SS | 22 | 17 | 18 | MB1 | |||
| M15 x1.0 | KM02 | KM01SS | 25 | 21 | 21 | 4 | 5 | MB2 | |
| M17 x1.0 | KM03 | KM03SS | 28 | 24 | 24 | MB3 | |||
| M20 x1.0 | KM04 | KM04SS | 32 | 26 | 28 | 6 | MB4 | ||
| M25 x1.5 | KM05 | KM05SS | 38 | 32 | 34 | 5 | 7 | MB5 | |
| M30 x1.5 | KM06 | KM06SS | 45 | 38 | 41 | MB6 | |||
| M35 x1.5 | KM07 | KM07SS | 52 | 44 | 48 | 8 | MB7 | ||
| M40 x1.5 | KM08 | KM08SS | 58 | 50 | 53 | 2.5 | 6 | 9 | MB8 |
| M45 x1.5 | KM09 | KM09SS | 65 | 56 | 60 | 10 | MB9 | ||
| M50 x1.5 | KM10 | KM10SS | 70 | 61 | 65 | 11 | MB10 | ||
| M55 x2.0 | KM11 | KM11SS | 75 | 67 | 69 | 3 | 7 | MB11 | |
| M60 x2.0 | KM12 | KM12SS | 80 | 73 | 74 | MB12 | |||
| M65 x2.0 | KM13 | KM13SS | 85 | 79 | 79 | 12 | MB13 | ||
| M70 x2.0 | KM14 | KM14SS | 92 | 85 | 85 | 3.5 | 8 | MB14 | |
| M75 x2.0 | KM15 | KM15SS | 98 | 90 | 91 | 13 | MB15 | ||
| M80 x2.0 | KM16 | KM16SS | 105 | 95 | 98 | 15 | MB16 | ||
| M85 x2.0 | KM17 | KM17SS | 110 | 102 | 103 | 16 | MB17 | ||
| M90 x2.0 | KM18 | KM18SS | 120 | 108 | 112 | 4 | 10 | MB18 | |
| M95 x2.0 | KM19 | KM19SS | 125 | 113 | 117 | 17 | MB19 | ||
| M100 x2.0 | KM20 | KM20SS | 130 | 120 | 122 | 18 | MB20 |
| Material | JIS | ISO | BS | |||
| Nut | Washer | Nut | Washer | Nut | Washer | |
| Carbon Steel | C45 | DC01 | 1.0503 | 1.0330 | 070M46 | CR4 |
| Stainless Steel | SUS304 | SUS304 | 1.4301 | 1.4301 | 304S31 | 304S31 |
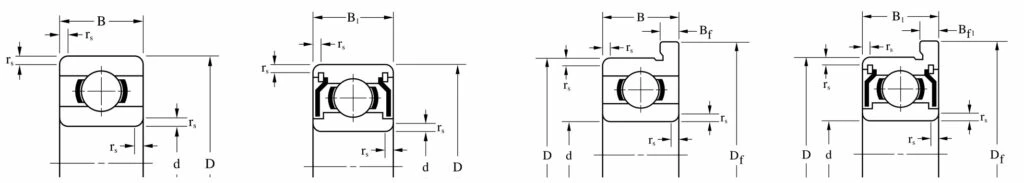
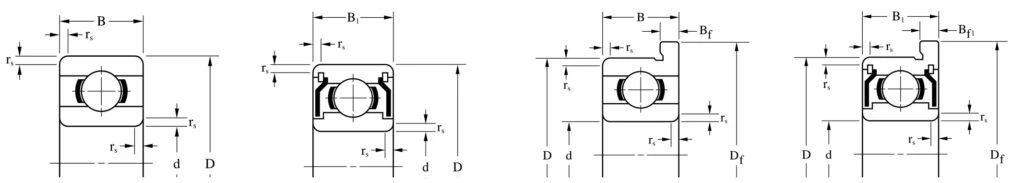
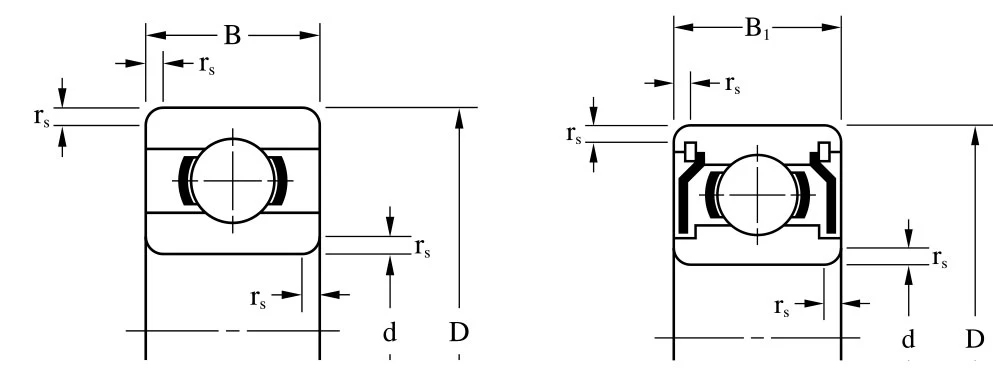
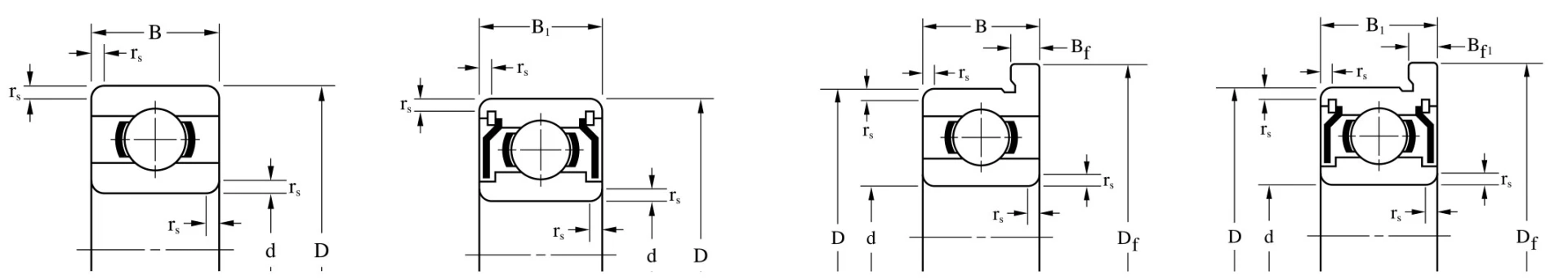
Abis Miniature Ball Bearings Structure
Rolling element bearings consist of ball, roller or needle elements located between two metal rings which are then free to rotate relative to each other. They offer advantages over plain bushes without the higher costs of more sophisticated fluid bearings.
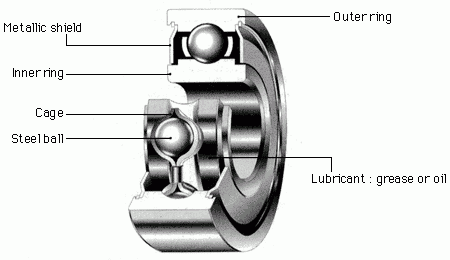
Ball bearings benefit over plain bearings in terms of torque levels, rotational accuracy and speed capability. In their standard form they can support both radial and axial loads.
Basic rules for selection & handling of bearings
Selection
- The efficiency of miniature or thin section bearings can be greatly affected by the precision of shaft and housing seats. The accuracy of the surrounding must be such that it will not adversely affect the operation of the bearing. If you have any questions, in particular regarding series 6700 and 6800, please contact us.
- In applications with steel crown type cages (W type), where high acceleration, heavy loads, shock loads or vertical shafts occur or where oil is the only lubricant available, please contact us.
- Selection of fitting clearance and grease type requires a careful consideration of rotating speed, load conditions and temperature in order to prevent premature bearing failure.
- Full complement ball bearings are suitable for low speed and heavy radial load conditions. There is a danger of ball being pushed out of the bearing through the filling slot, even under light axial load. For this reason, full complement ball bearings are not suitable for supporting axial loads.
Handling
- The actual assembly area should be kept free from dust as any contamination has a detrimental effect on the operation and life of rolling bearings. If there is any doubt concerning the cleanliness of a bearing, it can be washed with a suitable agent and then re-lubricated.
- When bearings are being fitted care should be taken to ensure that the ring concerned is presented squarely to the mating surface and that any fitting load required is applied via the ring being fitted – NOT UNDER ANY CIRUMSTANCES FROM ONE RING TO THE OTHER THROUGH THE BALLS. If it is necessary to heat the bearing to facilitate fitting, the temperature should not exceed +120oC.
- After assembly, the bearing should be rotated to check its correct operation. If the bearing does not appear to be functioning correctly, it should be re-examined to establish the cause of the malfunction.
- It is not advisable to mix oils and greases as this will affect the efficiency of the bearing.
- Bearings must be stored in a clean environment with stable temperature. They should be handled with care to avoid the possibility of corrosion and rusting.
- Lint-free cloth must be used to wipe shaft and housing seats to avoid the ingress of contaminants into the bearing.
Design & characteristics of radial ball bearings
In the majority of applications the size of the ball bearing is selected according to space considerations. Usually the load capacity which the selected bearing provides is more than adequate for the continuous loads to which it is subjected. In extreme cases, or which severe vibration or shock loading is known to occur, the load carrying capability should be checked.
The form which the bearing takes is entirely determined by the overall design philosophy.
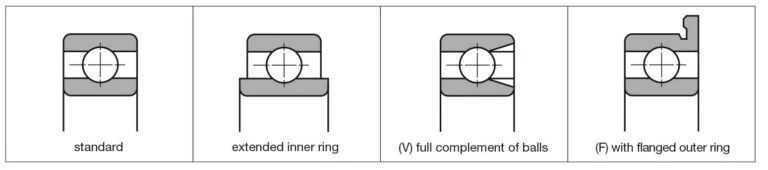
Open or closed – is the bearing likely to become contaminated? Is escape or outgassing of lubricant an issue?
Normal or extended inner – is there sufficient clearance axially between rotating and stationery components?
Load – single low radial ball bearings with balls separated by a cage can support radial loads, axial loads and tilting moments. A full complement V-type ball bearing can support only radial loads and some low axial loads.Generally a full complement bearing is used when a higher radial load is required than the standard bearing provides.
Speed – maximum permissible speeds for ball bearings are mainly related to the bearing design and size, cage type, bearing internal clearance, method and type of lubrication, manufacturing accuracy, sealing methods and loads.
Torque and noise level – single low radial ball bearings are precision components and have low torque and noise levels.
Inclination or inner/outer rings – shaft and housing seats with poor accuracy, fitting errors and shaft bending might cause inclination between the inner and outer rings although the internal clearance of the bearing will permit this to a certain extent. Generally, the maximum permissible inclination between the inner and outer rings is approximately 1 in 300.
Toughness – bearings under load deform elastically at the contact point between the rolling element and bearing ring. This is influenced by the bearing type, size, form and load.
Installation and removal – the single row radial ball bearing is a non-separable bearing. Therefore, shafts and housings should be so designed to enable bearing inspection and replacement when necessary.
Axial location – improved axial location is obtained with Thrust type bearings.
Two important internal parameters which must be considered and specified when a bearing is selected are:
Radial play & internal clearance – the total diametrical movement from contact at one side between rings and balls to similar contact at the other side. It is normally stated in increments of tenths of a thousandth of an inch or microns. This parameter effects the torque level, the axial movement, the load carrying capacity, especially in an axial direction and, according to installation, the noise level and smoothness of the bearing.
Lubrication – the choice of oil or grease and the particular type of each, has an influence on the bearing performance. Noise level, speed, environment temperature, load and life are some of the various factors which should be considered when selecting lubricant.
Installation
To obtain the best performance, certain basic rules should be observed in the installation.
Keep Parts Clean
The clearance involved between the balls and tracks is very small and so any dirt particles present in the area of the tracks cause rough, noisy rotation and perhaps even permanent damage.
Keep Components Round
The inner and outer rings are generally of fairly thin section and no mating parts must be of good roundness to prevent distortion of the rings with consequent inaccurate rotation and roughness.
Keep Assemblies Shockfree
Since radial loads are supported on several contact points, shock loading can result in permanent deformation of the tracks and balls. The resulting craters again give rough, noisy rotation.
ABIS Lubricants
Lubrication of a bearing serves to:
- Eliminate metal to metal contact
- Reduce friction
- Minimise temperature increase
- Improve low torque characteristics
- Reduce noise level
- Prevent corrosion
Two major forms of lubricant are available—oil and grease.
Oil
In general, oil is used as a lubricant where grease is unsuitable, for example, where low torque or high speed are considerations. Typical oils used are the same as those used as the base oils in greases. The operational life of oils is usually much less than that of equivalent greases due to evaporative losses. One exception is the perfluorinated hydrocarbon family of oils that have extremely low saturated vapor pressure (SVP), giving greatly extended life.
Grease
Grease lubricant is comprised of a base oil carried in a thickening agent, which delays migration and evaporation of the oil, lengthening its effective operational and shelf life. Additives may also be included in the basic grease formula to improve corrosion resistance, reduce oxidation, and otherwise improve the lubricant performance. Grease lubrication is recommended unless low torque or high speed is essential to the application.
Lubricating - oil & grease
| Lubricating Oil | Lubricating Grease | |
| Rotating speed | Low—Medium—High Speed | Low—Medium Speed |
| Lubricating efficiency | Excellent | Good |
| Cooling effect | Good | None |
| Torque | Comparatively low | Comparatively high |
| Lubricant life | Long | Comparatively short |
| Lubricant replacement | Easy | Difficult |
| Lubricant leakage | Should not be used where oil leakage is unacceptable | Little grease leakage |
| Impurities filtration | Easy | Difficult |
| Sealing equipment | Complex | Simple |
Grease filling VOLUME
| Symbol | Filing Volume (%) | Operating Conditions | |
| Speed | Load | ||
| M | 70 + 10 | Low | Heavy |
| S | 50 + 10 | Low | Medium |
| G | 40 + 10 | Medium | Medium |
| L Default Standard | 30 + 10 | Medium | Medium |
| Q | 25 + 5 | Medium | Medium |
| K | 20 + 5 | High | Light |
| X | 10 + 5 | High | Light |
Note: Light load (< 0.06Cr)
Standard load (< 0.12Cr)
ABIS Bearings Criteria for Lubricating Oil Selection
| Operating Temperature of Bearing (oC) | DN | ISO Viscosity Grade of Lubricating Oil (VG) | ||
| Medium Load | Heavy Load/Sock Load | |||
| -30~0 | Up to permissible rotating speed | 15/22/32 | 32/46 | |
| 0~+60 | Up to 15000 | 32/46/68 | 100 | |
| 15000~80000 | 32/46 | 68 | ||
| 80000~150000 | 22/32 | 32 | ||
| 150000~500000 | 10 | 22/32 | ||
| +60~100 | Up to 15000 | 150 | 220 | |
| 15000~800000 | 100 | 150 | ||
| 80000~150000 | 68 | 100/150 | ||
| 150000~500000 | 32 | 68 | ||
| +100~+150 | Up to permissible rotating speed | 320 | ||
Notes
1. If heavy loads occur at low speeds, a high viscosity lubricating oil should be used.
2. This table is for oil bath lubrication system and recirculating oil systems.
3. dn = bearing bore diameter d(mm) x rotating speed n (r.p.m)
Common oil brands
| Code | Brand | Lubricant Base | Viscosity (m2/s) | Operating Temperature (oC) | Approved Standard | Comments |
| AF2* | Aero Shell Fluid 12 | Diester | 8.9 (54.4oC) | -50~+205 | MIL-PRF-6085D | Low viscosity, wide temperature range and high operating temperature. Good general purpose oil for instrument/ aircraft applications. |
| AF3 | Aero Shell Fluid 3 | Mineral | 10.0 (38oC) | -47~+115 | MIL-PRF-7870C | Low viscosity, good general purpose oil for instrument/ aircraft applications. |
| KAZ | Krytox 143AZ | Fluorinated | 12.4 (40oC) | -54~+149 | – | Inert, high temperature capability suitable for low speed/load. Impervious plastics/ elastomers. |
| PD8 | Isoflex PDB38 | Diester | 12.0 (40oC) | -55~+100 | – | Low viscosity, good general purpose oil for instrument/ aircraft applications. |
* Default lubricant and will be supplied unless otherwise specified.
** If you have a specific requirement for another oil please contact us for advice.
Common Grease Brands
| Code | Brand | Thickening Agent | Lubricant Base | Operating Temperature (oC) | Approved Standard | Comments |
| SRL* | Multemp SRLa | Lithium | Diester, Mineral | -50 – +205 | – | Good temperature range, load capacity and water resistance. |
| AV2 | Alvania 2S | Lithium | Mineral | -25 – +120 | – | Good temperature range, load capacity and water resistance. |
| AG7 | Aero Shell No. 7 | Microgel | Diester | -73 – +149 | MIL-PRF-8328D | Good temperature range, load capacity and water resistance. |
| AG2 | Aero Shell No. 22 | Microgel | Synthetic Hydrocarbon | -65 – +204 | MIL-PRF-81322F | Good temperature range, high load/speed capacity and water resistance. |
| A3S | Aero Shell No. 33MS | Lithium | Synthetic Hydrocarbon Ester | -73 – +121 | MIL-G-21164D | Low temperature, high load capacity and water resistance. |
| PS2 | Multemp PS No. 2 | Lithium | Diester, Mineral | -55 – +130 | – | Good temperature range, load capacity and water resistance. |
| SL8 | Isoflex Super LDS18 | Lithium | Diester | -60 – +130 | MIL-G-7118-A | Good temperature range, load capacity and water resistance |
| K24 | Krytox 240AC | PFPE | Fluorinated | -35 – +238 | MIL-G-27617 | Suitable for high temperature applications. High viscosity at room temperature. |
| B32 | Beacon 325 | Lithium | Diester | -60 – +120 | – | Suitable for low torque/quiet running applications. |
* Default lubricant and will be supplied unless otherwise specified.
** If you have a specific requirement for another grease please contact us for advice.
BALL BEARING TECHNICAL DATA
- Materials
- Noise testing
- Cage/Retainer Types
- Closures
- Radial Play
- Internal Clearance
- Lubricants
- Importance of Correct Fitting of Bearings
- Faults, Causes and Remedies
- Tolerances
ABIS Miniature Ball Bearing Materials
| Material | Sizes | Designation | Symbol | Chemical Composition (Wt%) | ||||||
| C | Si | Mn | P | S | Cr | Mo | ||||
| Chromium Steel | All | SUJ2 SAE 52100 100Cr6 | – | 0.95-1.10 | 0.15-0.35 | <0.50 | <0.025 | <0.025 | 1.30-1.60 | <0.08 |
| Stainless Steel | d<25mm & D<52mm | KS440 (ACD34), X65Cr6 | S, H | 0.95-1.20 | <1.00 | <1.00 | <0.040 | <0.030 | 16.0-18.0 | <0.75 |
| d>25mm & D<52mm | SUS440C, AIS1440C, X102CrMo17 | S, H | 0.60-0.75 | <1.00 | <1.00 | <0.030 | <0.020 | 11.5-13.0 | <0.030 | |
ABIS Miniature Bearing Noise Testing
Bearing acoustical noise is a function of both the bearing itself and the way in which it is used. Bearings can be specified as 100% noise-tested during manufacture. Bearing noise is not generally influenced by ABEC precision, but rather by manufacturers’ internal quality standards, particularly raceway finish. There are no fixed reference standards among manufacturers for noise testing.
Noise Testing
The standard instrument used for bearing noise testing is the Anderon Meter (sometimes called Anderometer) made by Sugawara Laboratories. This measures noise with an accelerometer contacting the outer race of the bearing while the inner race is rotated at 1,800 RPM. Noise levels are separated into 3 bands, designated as follows:
High band 1,800 – 10,000 Hz
Medium band 300 – 1,800 Hz
Low band 50 – 300 Hz
According to the type of bearing (material and noise grade), a different attenuation is used for each band. Meters are calibrated in Anderons. Standard testing procedure requires that bearings are washed clean of any lubricant and 2 drops of fresh MIL-L-6085A oil lubricant added prior to testing.
Typical attenuation values for each band are given in the table below, according to bearing material and noise grade. A “pass” for any bearing grade is defined as < 40% of full scale on the Anderon meters for each band. In this case, this translates to pass levels of Low < 6.4, Med < 2.4, High < 3.2.
Anderon Meter Attenuation Settings | ||||
| Material | Noise Rating | Low Band | Mid Band | High Band |
| 5100 chrome steel | Standard | 16 | 6 | 8 |
| EMQ | 16 | 6 | 8 | |
| EMQ2 | 12 | 6 | 8 | |
| 440C/Martensitic stainless | Standard | 16 | 10 | 24 |
| EMQ | 16 | 10 | 24 | |
| EMQ2 | 16 | 8 | 10 | |
Anderon Meter <40% = good bearing | ||||
Abis Bearings RETAINER Cages
| W One-Piece Steel Crown Type | J Two-Piece Steel Ribbon Type | RJ Two-Piece Steel Rivet type | TW One-Piece Nylon Crown Type | V Full Complement of Balls |
| The stainless steel pressed cage is inner ring guided. It shows excellent performance in low torque, low speed applications. | Consists of two mating steel pressings, the cover side and the finger side. Usually guided by the rolling elements and designed to reduce frictional torque. | The RJ type case is suitable for larger bearings with a high load carrying capacity. The two pieces are riveted together and are strong enough to withstand higher levels of vibration and acceleration. The cage is guided by the balls and reduces frictional torque. | Moulded nylon cage. Reduces the fluctuation in running torque. Suitable for high speeds. Guided by the rolling elements. NYLON CAGE operating temperature range from -30 to +120oC. | This type of bearing has no cage but maximum possible number of balls. Due to the fact that the inner and outer ring have a filling slot, the axial load carrying capacity of this bearing type is low. This type of bearing is suitable for high radial load, low speed applications. |
| Material | JIS | ISO | BS | |||
| Nut | Washer | Nut | Washer | Nut | Washer | |
| Carbon Steel | C45 | DC01 | 1.0503 | 1.0330 | 070M46 | CR4 |
| Stainless Steel | SUS304 | SUS304 | 1.4301 | 1.4301 | 304S31 | 304S31 |
Closures
A shield (non-contact) or seal (contact) is often installed to retain lubricant and to prevent contamination from entering the bearing raceways. These are available in a variety of materials and configurations.
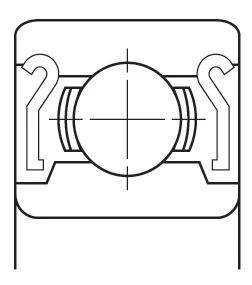
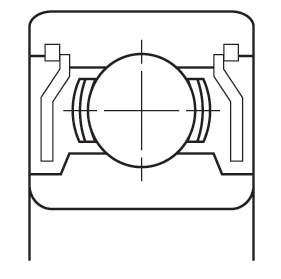
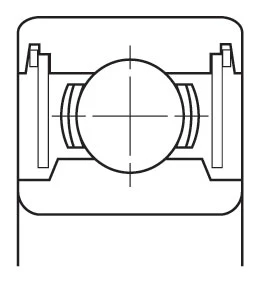
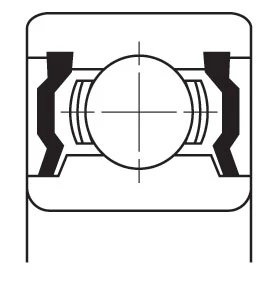
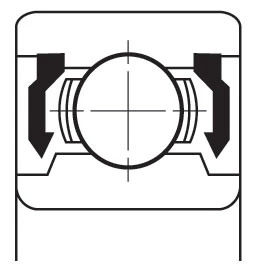
| ZZ Pressed Steel Shield | ZZS Steel Shield with Snap Ring | TTS Teflon Seal with Snap Ring | 2RS Contact Rubber Seal | 2RU Non-Contact Rubber Seal |
| Non-contact shield pressed into outer ring. Very little grease leakage and low ingress of contaminants. | Non-contact shield retained in outer ring. Low ingress of contaminants. Mainly used for smaller or narrower bearings. | Teflon seal reinforced with glass fibre is retained in outer ring by snap ring. Low ingress of contaminants. Mainly used for smaller or narrower bearings. Seal can flex to accommodate internal pressure changes. TEFLON SEAL operating temperature range from –100 to +260oC. | Rubber seal fitted into outer ring. Light contact with inner ring, retains grease and prevents ingress of external contaminants. NBR SEAL operating temperature range from –40 to +120oC. FKM (VITON) SEAL operating temperature range from –30 to +230oC. | Non-contact rubber seal fitted into outer ring, still provides effective sealing. NBR SEAL operating temperature range from –40 to +120oC. FKM (VITON) SEAL operating temperature range from –30 to +230oC. |
ABIS Bearings Radial Play
| Service requirements | RADIAL PLAY | Remarks | ||||||||||
| Miniature Bearings | Standard Metric Bearings | |||||||||||
| l/D | <10 | 10 only | 10+ -18 | 18+ -24 | 24+ -30 | 30+ -40 | 40+ -50 | |||||
| 0.001 mm | 0.001 inch | Ref | 0.001mm | Ref | ||||||||
| Small bearing clearance required axially without the use of preload shims or springs. Low torque not the prime requirement. High thrust loads will not occur. | TIGHT | 0-5 3-8 | 0-2 1-3 | MC1 MC2 | 0-7 | 0-9 | 0-10 | 1-11 | 1-11 | 1-11 | C2 | Interference fits must be avoided. Beware differential expansion. Careful attention should be paid to any excessive temperature rise in service. |
| Moderate torque acceptable. Moderate thrust loads may occur. | MEDIUM | 5-10 | 2-4 | MC3 (Std) | 2-13 | 3-18 | 5-20 | 5-20 | 6-20 | 6-23 | CN (CO) Std | Interference fits are not recommended. |
| 8-13 | 3-5 | MC4 | 8-23 | 11-25 | 13-28 | 13-28 | 15-33 | 18-36 | C3 | |||
| Minimal torque required. Or High thrust load capability. | LOOSE | 13-20 | 5-8 | MC5 | 14-29 | 18-33 | 20-36 | 23-41 | 28-46 | 30-51 | C4 | Moderate interference fits can be applied. Axial play may require to be controlled by shims or springs. |
| 20-28 | 8-11 | MC6 | 20-37 | 25-45 | 28-48 | 30-53 | 40-64 | 45-73 | C5 | |||
| Material | JIS | ISO | BS | |||
| Nut | Washer | Nut | Washer | Nut | Washer | |
| Carbon Steel | C45 | DC01 | 1.0503 | 1.0330 | 070M46 | CR4 |
| Stainless Steel | SUS304 | SUS304 | 1.4301 | 1.4301 | 304S31 | 304S31 |
ABIS Bearings Internal clearance
This is generally referred to as radial play although it also incorporates axial play as well because it is actually the amount of space between the rolling elements of the bearing, namely inner ring, outer ring and balls.
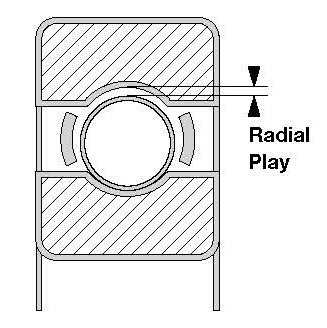
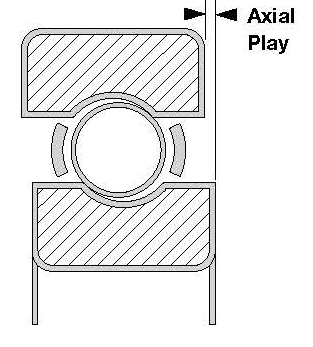
| Radial Play – is clearance perpendicular to the axis of the bearing and better described as the movement available to the outer ring when inner is fixed. This can be more accurately defined as follows: average diameter outer ring raceway minus average diameter of inner ring minus x2 ball diameter. | Axial Play – is the opposite of radial play as it is the movement of the rings relative to each other along the axis of the bearing. The amount of axial play is controlled by the bearing raceway curvature but as a general rule is around x10 the value of radial play. |
Importance of correct fitting of bearings
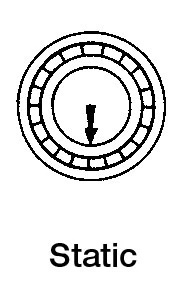
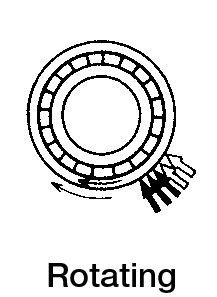
A bearing can only perform to its full capacity when it is correctly fitted on the shaft and in the housing. Insufficient interference on fitting surfaces could cause bearing rings to creep in a circumferential direction. Once this happens, considerable wear occurs on the fitting surface and both shaft and housing can be damaged. Furthermore, abrasive particles may enter the bearing causing vibration, excessive heat and damage to raceways. It is therefore necessary to provide bearing rings under rotating load with an adequate interference fit to prevent creep. When using thin-type bearings under low load, the bearings should be fastened by a nut. Statically loaded bearings generally do not need to be fitted with an interference fit. Only when subject to a high degree of vibration do both inner and outer rings require fitting with an interference fit.
| Fitting of Bearing and Shaft | ||||
| Condition (Steel Shaft) | Shaft Bore Diameter | Shaft Tolerance Class | ||
| Thin-Type | Others | |||
| Inner ring rotating load or indeterminate load direction | Light load ≤ 0.06C or fluctuating load | 10 ≤ d ≤ 18 18 ≤ d ≤ 30 30 ≤ d ≤ 50 | h5 h5 h5 | js5 js5 js5 |
| Standard load = 0.06 – 0.11C | 10 ≤ d ≤ 18 18 ≤ d ≤ 30 30 ≤ d ≤ 50 | js5 js5 js5 | j5 k5 k5 | |
| Outer ring rotating load | Necessary for inner ring turning easily around shaft | All bore diameters | g6 | g6 |
| Unnecessary for inner ring turning easily around shaft | All bore diameters | h6 | h6 | |
| Fitting of Bearing and Housing | ||||
| Condition (One-Piece Housing) | Axial Directional Movement of Outer Ring | Tolerance Class of Housing Seats | ||
| Thin-Type | Others | |||
| Inner ring rotating load | Varying loads | Easy to move | H7 | H7 |
| Light or standard loads | Easy to move | H8 | H8 | |
| High temperature of inner ring and shaft | Easy to move | G7 | G7 | |
| Light or standard load Precision rotation | As a rule, impossible to move | K6 | K6 | |
| Possible to move | JS6 | J6 | ||
| Quiet operations | Easy to move | H6 | H6 | |
| Indeterminate load direction | Light or standard load | In general, possible to move | JS7 | J7 |
| Standard or heavy load | As a rule, impossible to move | K7 | K7 | |
| Large shock load | Impossible to move | M7 | M7 | |
| Light or fluctuating load | Impossible to move | M7 | M7 | |
| Outer ring rotating load | Standard or heavy load | Impossible to move | N7 | N7 |
| Thin-type housing seats heavy or large shock load | Impossible to move | P7 | P7 | |
| Characteristics of Load and Fitting | |||
| Rotating Ring | Load | Load Condition | Fitting |
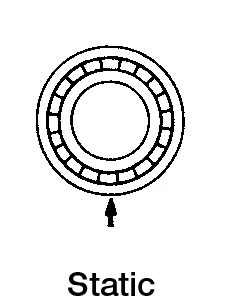
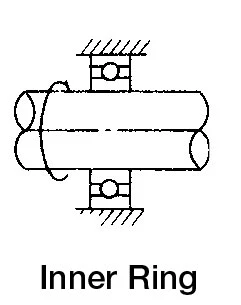 |  | Inner ring rotating loadOuter ring static load | Interference fit for inner ringClearance fit for outer ring |
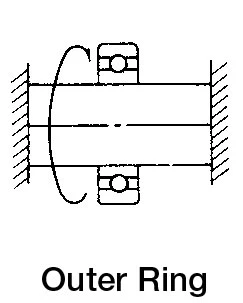 |  | ||
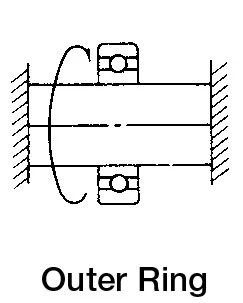 |  | Outer ring rotating loadInner ring static load | Clearance fit for inner ringInterference fit for outer ring |
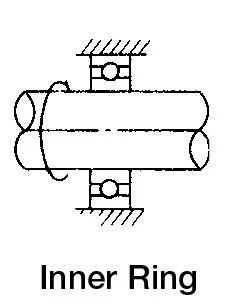 | 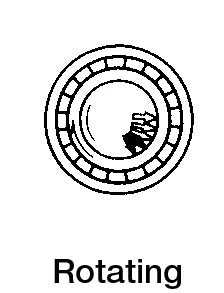 | ||
| In case of fluctuating load direction or unbalanced load | Rotating or static | Indeterminate load direction | Interference fit for inner and outer ring |
Faults, Causes & Remedies
| Problem | Causes | Remedy | |
| Noise | High pitched metallic noise | Poor lubrication Clearance to small Poor fitting Excessive load | Improve lubrication Correct clearance Investigate mounting method and seating Examine shaft and housing tolerances for closing effect |
| Low pitched metallic noise | Brinelled raceway surface | Avoid shock loads | |
| Regular noise | Rust and damage Flaking of raceway surface | Check and replace seals and re-lubricate Improve lubrication and check fitting, clearance and fixing method | |
| Irregular noise | Ingress of foreign matter Excessive clearance Damage and flaking of rolling element | Check and replace seals and re-lubricate Correct clearance Reduce loads and/or clearance | |
| Variable noise | Variable clearance due to temperature changes Damage to raceways | Check fits taking housing materials and temperature into clearance Improve lubrication and check fitting, clearance and fixing method | |
| Heavy vibration | Flaking of raceway and rolling element Ingress of foreign matter Excessive clearance Poor location | Improve lubrication and check fitting, clearance and fixing method Check and replace seals and re-lubricate Correct clearance Ensure abutment face and fitting diameter are perpendicular | |
| Excessive heat generation | Clearance too small Poor location Excessive load Poor lubrication Creep | Correct clearance Ensure abutment face and fitting diameter are perpendicular Examine shaft and housing tolerances for closing effect Improve lubrication Maintain recommended shaft and housing fits | |
| Lubrication failure | Too much grease Ingress of foreign matter | Use the correct lubricant quantity Check and replace seals and re-lubricate | |
ABIS BEaring Tolerances
For inch bearings tolerances are based on Section 3 of the AFBMA Standards for ABEC Class 1 and Section 12 for ABEC Class 3. Refer to Table 1.
For metric series bearings up to 9mm outer diameter tolerances are based on AFBMA Standards as above. For diameters over 9mm they are based on ISO R492-R1648 tolerances Class P0, P6 and P5. Refer to Tables 1 & 2.
N.B. Thin section bearings, Series E only, are available in tolerance Class P5.
Bearings with bore sizes 0-0.375 inches, 0-18mm. Outside diameters 0-30mm
| ABEC | Parameters | ISO | ||||||||||
| Unit 0.0001 Inch | Unit 0.001mm | |||||||||||
| Class 1 | Class 3 | Class 5 | Class 0 | Class 6 | Class 5 | |||||||
| High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | Inner Ring Diameter | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low |
| 0 | -3 | 0 | -3 | 0 | -2 | Mean value of bore dm | 0 | -8 | 0 | -7 | 0 | -5 |
| +1 | -4 | +1 | -3 | 0 | -2 | Absolute value of bore d | +2 | -10 | +1 | -8 | 0 | -5 |
| 3 | – | 2 | – | 1.5 | – | Radial run out (max.) | 10 | – | 6 | 5 | ||
| 0 | -50 | 0 | -50 | 0 | -10 | Width B | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -25 |
| – | – | – | – | – | 2 | Width variation (max.) | 12 | – | 15 | – | – | 5 |
| High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | Outer Ring Diameter | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low |
| 0 | -3 | 0 | -3 | – | -2 | Mean value of OD (open) Dm | 0 | -8 | 0 | -7 | 0 | -5 |
| +1 | -4 | +1 | -4 | – | -2 | Absolute value of OD (open) D | +2 | -10 | +1 | -8 | 0 | -5 |
| +2 | -5 | +2 | -5 | – | – | Absolute value of OD (closed) D | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| 6 | – | 4 | 2 | – | Radial run out (max.) | 15 | – | 8 | – | 5 | – | |
| 0 | -50 | 0 | -50 | 0 | -10 | Width B | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -25 |
| – | – | +50 | -10 | – | – | Flange diameter Df | +125 | -50(1) | +125 | -50(1) | – | – |
| – | – | 0 | -50 | – | – | Flange width Bf | 0 | -50(1) | 0 | -50(1) | – | – |
Table 2 Bearings with bore sizes 20-34mm. Outside diameter 31-80mm.
| Parameters | ISO | |||||||||||
| Unit 0.001mm | ||||||||||||
| Class 0 | Class 6 | Class 5 | ||||||||||
| Inner Ring Diameter | 20-30 | 35-45 | 20-30 | 35-45 | 20-30 | 35-45 | ||||||
| High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | |
| Mean value of bore dm | 0 | -10 | 0 | 12 | 0 | -8 | 0 | -10 | 0 | -6 | 0 | -8 |
| Absolute value of bore d | +3 | -13 | +3 | -15 | +1 | -9 | +1 | -11 | 0 | -6 | – | -8 |
| Radial run out (max.) | 13 | – | 15 | – | 8 | – | 10 | – | 4 | – | 5 | – |
| Width B | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 |
| Width variation (max.) | 20 | – | 20 | – | 20 | – | 20 | – | 5 | – | 5 | – |
| Outer Ring Diameter | 32-50 | 52-80 | 32-50 | 52-80 | 32-50 | 52-80 | ||||||
| High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High | Low | |
| Mean value of OD (open) Dm | 0 | -11 | 0 | -13 | 0 | -9 | 0 | -11 | 0 | -7 | 0 | -9 |
| Absolute value of OD (open) D | +3 | -14 | +4 | -17 | +2 | -11 | +2 | -13 | 0 | -7 | 0 | -9 |
| Absolute value of OD (closed) D | +7 | -18 | +10 | -23 | +6 | -15 | +7 | -18 | – | – | – | – |
| Radial run out (max.) | 20 | – | 25 | – | 10 | – | 13 | – | 7 | – | 8 | – |
| Width B | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 | 0 | -120 |
Open Ball Bearings
Metric Series
| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Radius (rs – min) | Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 0.6 | 2.5 | 1 | 0.05 | 68/0.6 | 68 | 16 | 142 | 160 | W |
| 1 | 3 | 1 | 0.05 | 681 | 96 | 26 | 130 | 150 | W |
| 1 | 3 | 1.5 | 0.05 | MR31 | 96 | 26 | 130 | 150 | W |
| 1 | 4 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 691 | 141 | 37 | 100 | 120 | W |
| 1.2 | 4 | 1.8 | 0.1 | MR41X | 112 | 33 | 110 | 130 | W |
| 1.5 | 4 | 1.2 | 0.05 | 681X | 112 | 33 | 100 | 120 | W |
| 1.5 | 5 | 2 | 0.15 | 691X | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 1.5 | 6 | 2.5 | 0.15 | 601X | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | W |
| 2 | 4 | 1.2 | 0.5 | 672 | 124 | 40 | 91 | 104 | W |
| 2 | 5 | 1.5 | 0.08 | 682 | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 2 | 5 | 2 | 0.1 | MR52 | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 2 | 6 | 2.3 | 0.15 | 692 | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | W/J/TW |
| 2 | 6 | 2.5 | 0.15 | MR62 | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | WJ |
| 2 | 7 | 2.5 | 0.15 | MR72 | 386 | 129 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 2 | 7 | 2.8 | 0.15 | 602 | 386 | 129 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 2.5 | 6 | 1.8 | 0.08 | 682X | 209 | 74 | 71 | 80 | W |
| 2.5 | 7 | 2.5 | 0.15 | 692X | 386 | 129 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 2.5 | 8 | 2.5 | 0.2 | MR82X | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W |
| 2.5 | 8 | 2.8 | 0.15 | 602X | 552 | 177 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 3 | 6 | 2 | 0.1 | MR63 | 209 | 74 | 71 | 80 | W |
| 3 | 7 | 2 | 0.1 | 683 | 311 | 112 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 3 | 8 | 2.5 | 0.15 | MR83 | 395 | 141 | 60 | 67 | J |
| 3 | 8 | 3 | 0.15 | 693 | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W/J/TW |
| 3 | 9 | 2.5 | 0.2 | MR93 | 571 | 189 | 56 | 67 | W |
| 3 | 9 | 3 | 0.15 | 603 | 571 | 189 | 56 | 67 | W |
| 3 | 10 | 4 | 0.15 | 623 | 631 | 219 | 50 | 60 | J/TW |
| 3 | 13 | 5 | 0.2 | 633 | 1301 | 488 | 40 | 48 | J |
| 4 | 7 | 2 | 0.1 | MR74 | 311 | 115 | 60 | 67 | W |
| 4 | 8 | 2 | 0.15 | MR84 | 395 | 141 | 56 | 67 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 9 | 2.5 | 0.1 | 684 | 641 | 227 | 53 | 63 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 10 | 3 | 0.2 | MR104 | 711 | 272 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 11 | 4 | 0.15 | 694 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 12 | 4 | 0.2 | 604 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 13 | 5 | 0.2 | 624 | 1301 | 488 | 40 | 48 | J |
| 4 | 16 | 5 | 0.3 | 634 | 1340 | 523 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 5 | 8 | 2 | 0.1 | MF85 | 308 | 120 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 5 | 9 | 2.5 | 0.15 | MR95 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 10 | 3 | 0.15 | MR105 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 11 | 0.15 | MR115 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J | |
| 5 | 11 | 3 | 0.15 | 685 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J/TW |
| 5 | 13 | 4 | 0.2 | 695 | 1077 | 432 | 43 | 50 | J |
| 5 | 14 | 5 | 0.2 | 605 | 1329 | 507 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 5 | 16 | 5 | 0.3 | 625 | 1729 | 675 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 5 | 19 | 6 | 0.3 | 635 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 6 | 10 | 2.5 | 0.15 | MR106 | 496 | 218 | 45 | 53 | W |
| 6 | 12 | 3 | 0.2 | MR126 | 716 | 295 | 43 | 50 | W/J/TW |
| 6 | 13 | 3.5 | 0.15 | 686 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 6 | 15 | 5 | 0.2 | 696 | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 16 | 5 | 0.2 | 696A | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 17 | 6 | 0.3 | 606 | 2263 | 846 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 19 | 6 | 0.3 | 626 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 6 | 22 | 7 | 0.3 | 636 | 3333 | 1423 | 30 | 36 | J/TW |
| 7 | 11 | 2.5 | 0.15 | MR117 | 455 | 202 | 43 | 50 | W |
| 7 | 13 | 3 | 0.2 | MR137 | 541 | 276 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 7 | 14 | 3.5 | 0.15 | 687 | 1173 | 513 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 7 | 17 | 5 | 0.3 | 697 | 1605 | 719 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 7 | 19 | 6 | 0.3 | 607 | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 7 | 22 | 7 | 0.3 | 627 | 3287 | 1379 | 30 | 36 | J/TW |
| 7 | 26 | 9 | 0.3 | 637 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J |
| 8 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.15 | MR128 | 543 | 274 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 8 | 14 | 3.5 | 0.2 | MR148 | 817 | 386 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 8 | 16 | 4 | 0.2 | 688 | 1252 | 592 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 8 | 19 | 6 | 0.3 | 698 | 2237 | 917 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 8 | 22 | 7 | 0.3 | 608 | 3293 | 1379 | 34 | 40 | J/TW |
| 8 | 24 | 8 | 0.3 | 628 | 3333 | 1423 | 28 | 34 | J |
| 8 | 28 | 9 | 0.3 | 638 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J |
| 9 | 14 | 3 | 0.1 | 679 | 919 | 468 | 36 | 42 | J |
| 9 | 17 | 4 | 0.2 | 689 | 1327 | 668 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 9 | 20 | 6 | 0.3 | 699 | 2467 | 1081 | 34 | 40 | J |
| 9 | 24 | 7 | 0.3 | 609 | 3356 | 1444 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 9 | 26 | 8 | 0.60(5) | 629 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J |
| 9 | 30 | 10 | 0.6 | 639 | 4659 | 2080 | 24 | 30 | J |
Open ball bearings
Inch series
| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 0.04 | 0.125 | 0.0469 | 0.013 | 0.0039 | R09 | 106 | 28 | 130 | 150 | W |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.0625 | 0.013 | 0.0039 | R0* | 112 | 33 | 110 | 130 | W |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.0781 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R1* | 232 | 67 | 90 | 110 | W |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R1-4* | 284 | 96 | 67 | 80 | W |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.0625 | 0.018 | 0.0039 | R133 | 189 | 60 | 80 | 95 | W |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0059 | R1-5* | 552 | 176 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R144J* | 311 | 110 | 67 | 80 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R144* | 284 | 96 | 67 | 80 | W |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R2-5* | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W/J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0059 | R2-6* | 640 | 227 | 53 | 63 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.0118 | R2* | 631 | 219 | 56 | 67 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.5 | 0.1719 | 0.0118 | R2A | 640 | 227 | 53 | 63 | J | |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R155* | 359 | 150 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R156* | 359 | 150 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R166* | 709 | 272 | 50 | 60 | J |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.1562 | 0.0118 | R3* | 1301 | 488 | 43 | 53 | J | |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.196 | 0.0118 | R3A | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J | |
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | R168* | 373 | 172 | 48 | 56 | W |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.0059 | R188* | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.0118 | R4* | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.2188 | 0.0157 | R4A | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J | |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.0059 | R1810* | 542 | 276 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.2188 | 0.062 | 0.0157 | R6 | 3332 | 1411 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 0.25 | 0.062 | 0.0157 | R8 | 5108 | 2413 | 27 | 32 | J |
| 0.625 | 1.375 | 0.2812 | 0.0315 | R10 | 5999 | 3265 | 21 | 25 | RJ | |
| 0.75 | 1.625 | 0.3125 | 0.0315 | R12 | 9384 | 5057 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
Notes
*Available with inner ring width extended by 0.0156″ (0.3962mm) each side
Bearings also available with stainless materials: prefix S
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Extra thin open ball bearings - 6700 6800 6900
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 10 | 15 | 16.5 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 6700 | 855 | 435 | 15 | 17 | W |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 6800 | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 | J/TW |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 63800 | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 | J/TW |
| 10 | 22 | 25 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6900 | 2695 | 1273 | 34 | 41 | J |
| 12 | 18 | 19.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6701 | 926 | 530 | 13 | 15 | W |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 6801 | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 | J/TW |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 63801 | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 | J/W |
| 12 | 24 | 26.5 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6901 | 2886 | 1446 | 31 | 36 | J |
| 15 | 21 | 22.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6702 | 937 | 582 | 11 | 13 | W |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 6802 | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 | J/TW |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 63802 | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 | J/TW |
| 15 | 28 | 30.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6902 | 4321 | 2259 | 26 | 30 | J |
| 17 | 23 | 24.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6703 | 1000 | 658 | 9.5 | 11 | W |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 6803 | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 | J/TW |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 63803 | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 | J/TW |
| 17 | 30 | 32.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6903 | 4588 | 2565 | 23 | 38 | J |
| 20 | 27 | 28.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6704 | 1402 | 729 | 8.5 | 10 | W |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6804 | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 | J/RJ |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 63804 | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 | J/RJ |
| 20 | 37 | 40 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 6904 | 6381 | 3682 | 19 | 23 | RJ |
| 25 | 32 | 34 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 6705 | 1091 | 838 | 7 | 8 | W |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6805 | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 | J/RJ |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 63805 | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 | J/RJ |
| 25 | 42 | 45 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 6905 | 7001 | 4540 | 16 | 19 | RJ |
| 30 | 37 | 39 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 6706 | 1143 | 947 | 5.5 | 7 | W |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6806 | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 | J/RJ |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 63806 | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 | J/RJ |
| 30 | 47 | 50 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 6906 | 7242 | 5003 | 14 | 17 | RJ |
| 35 | 44 | 5 | 0.3 | 6707 | 1866 | 1635 | 4.9 | 6 | W | ||
| 35 | 47 | 50 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6807 | 4729 | 3821 | 13 | 16 | J/RJ |
| 35 | 55 | 58 | 10 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 6907 | 10900 | 7818 | 12 | 14 | RJ |
| 40 | 50 | 6 | 0.3 | 6708 | 2516 | 2233 | 4.3 | 5 | W | ||
| 40 | 52 | 55 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6808 | 4923 | 4178 | 12 | 14 | J |
| 40 | 62 | 65 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 6908 | 13678 | 9968 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 45 | 55 | 6 | 0.3 | 6709 | 2580 | 2397 | 3.9 | 4.6 | W | ||
| 45 | 58 | 61 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6809 | 6187 | 5381 | 11 | 13 | J |
| 45 | 68 | 71 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 6909 | 14100 | 10830 | 9.7 | 11 | RJ |
| 50 | 62 | 6 | 0.3 | 6710 | 2670 | 2640 | 3.5 | 4.1 | W | ||
| 50 | 65 | 68 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6810 | 6610 | 6090 | 9.6 | 11 | J/RJ |
| 50 | 72 | 75 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 6910 | 14540 | 11710 | 9 | 11 | RJ |
| 55 | 72 | 9 | 0.3 | 6811 | 8800 | 8100 | 8.7 | 10 | RJ | ||
| 55 | 80 | 13 | 1 | 6911 | 16600 | 14100 | 8.1 | 9.6 | RJ | ||
| 60 | 78 | 10 | 0.3 | 6812 | 11500 | 10600 | 8 | 9.4 | RJ | ||
| 60 | 85 | 13 | 1 | 6912 | 20200 | 17300 | 7.5 | 8.9 | RJ | ||
| 65 | 85 | 10 | 0.6 | 6813 | 11900 | 11500 | 7.3 | 8.6 | RJ | ||
| 65 | 90 | 13 | 1 | 6913 | 17400 | 16100 | 7.1 | 8.4 | RJ | ||
| 70 | 90 | 10 | 0.6 | 6814 | 12100 | 11900 | 6.8 | 8.1 | RJ | ||
| 70 | 100 | 16 | 1 | 6914 | 23700 | 21200 | 6.4 | 7.6 | RJ | ||
| 75 | 95 | 10 | 0.6 | 6815 | 12500 | 12900 | 12.5 | 12.9 | RJ | ||
| 75 | 105 | 16 | 1 | 6915 | 24400 | 22600 | 6.1 | 7.2 | RJ | ||
| 80 | 100 | 10 | 0.6 | 6816 | 12700 | 13300 | 12.7 | 13.3 | RJ | ||
| 80 | 110 | 16 | 1 | 6916 | 25000 | 24000 | 5.7 | 6.8 | RJ | ||
| 85 | 110 | 13 | 1 | 6817 | 18700 | 19000 | 5.6 | 6.6 | RJ | ||
| 85 | 120 | 18 | 1.1 | 6917 | 31900 | 29600 | 5.3 | 6.3 | RJ | ||
| 90 | 115 | 13 | 1 | 6818 | 19000 | 19700 | 5.3 | 6.3 | RJ | ||
| 90 | 125 | 18 | 1.1 | 6918 | 32800 | 31600 | 5.1 | 6 | RJ |
Notes
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
LARGE SIZE STAINLESS STEEL OPEN BALL BEARINGS 6000H 6200H 6300H
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Radius (rs – min) | Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 6000H* | 3860 | 1570 | 31 | 36 | J |
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 6200H* | 4340 | 1920 | 24 | 29 | RJ/TW |
| 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 6300H | 6870 | 2750 | 22 | 27 | RJ |
| 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 6001H* | 4340 | 1910 | 27 | 32 | J/TW |
| 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6201H | 5770 | 2450 | 22 | 27 | RJ/TW |
| 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 6301H | 8240 | 3360 | 20 | 25 | RJ |
| 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 6002H* | 4750 | 2270 | 23 | 27 | RJ/TW |
| 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 6202H | 6490 | 3000 | 20 | 24 | RJ/TW |
| 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 6302H | 9710 | 4370 | 17 | 20 | RJ |
| 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6003H | 5090 | 2630 | 21 | 25 | RJ/TW |
| 17 | 40 | 12 | 0.6 | 6203H | 8130 | 3850 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
| 17 | 47 | 14 | 1 | 6303H | 11550 | 5330 | 15 | 18 | RJ |
| 20 | 42 | 12 | 0.6 | 6004H | 7960 | 4050 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
| 20 | 47 | 14 | 1 | 6204H | 10910 | 5360 | 15 | 17 | RJ/TW |
| 20 | 52 | 15 | 1.1 | 6304H | 13490 | 6310 | 14 | 17 | RJ |
| 25 | 47 | 12 | 0.6 | 6005H | 8550 | 4690 | 15 | 18 | RJ/TW |
| 25 | 52 | 15 | 1 | 6205H | 11900 | 7390 | 13 | 15 | RJ/TW |
| 25 | 62 | 17 | 1.1 | 6305H | 17490 | 9060 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 30 | 55 | 13 | 1 | 6006H | 11240 | 6610 | 13 | 15 | RJ/TW |
| 30 | 62 | 16 | 1 | 6206H | 16530 | 9080 | 11 | 13 | RJ/TW |
| 30 | 72 | 19 | 1.1 | 6306H | 22630 | 12080 | 9.6 | 12 | RJ |
| 35 | 62 | 14 | 1 | 6007H | 13560 | 8250 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 35 | 72 | 17 | 1.1 | 6207H | 21810 | 12360 | 9.2 | 11 | RJ |
| 35 | 80 | 21 | 1.5 | 6307H | 28290 | 15270 | 8.5 | 10 | RJ |
| 40 | 68 | 15 | 1 | 6008H | 14250 | 9220 | 10 | 12 | RJ |
| 40 | 80 | 18 | 1.1 | 6208H | 24730 | 14330 | 8.3 | 10 | RJ |
| 45 | 75 | 16 | 1 | 6009H | 15150 | 9660 | 9.2 | 11 | RJ |
| 45 | 85 | 19 | 1.1 | 6209H | 27790 | 16300 | 7.7 | 9.2 | RJ |
| 50 | 80 | 16 | 1 | 6010H | 18510 | 13260 | 8.4 | 9.9 | RJ |
| 50 | 90 | 20 | 1.1 | 6210H | 29800 | 18610 | 7.1 | 8.5 | RJ |
EXTRA THIN OPEN BALL BEARINGS - ET, ER
Metric series
| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Shield/ Seal Width (B1) | Radius (rs – min) | Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 15 | 20 | 3.5 | 0.15 | ET2015 | 942 | 582 | 22 | 26 | W | |
| 15 | 21 | 3.5 | 0.15 | ET2115 | 939 | 581 | 22 | 26 | W | |
| 16 | 22 | 4 | 0.15 | ET2216 | 968 | 619 | 20 | 24 | W | |
| 16 | 23 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 0.15 | ET2316 | 968 | 619 | 20 | 24 | W |
| 18 | 24 | 4 | 0.15 | ET2418 | 988 | 654 | 18 | 21 | W | |
| 20 | 25 | 4 | 4 | 0.15 | ET2520 | 1011 | 691 | 17 | 20 | W |
Abis Flange Open Ball Bearings
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | Flange Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 1 | 3 | 3.8 | 1 | 0.3 | 0.05 | F681 | 96 | 26 | 130 | 150 | W |
| 1 | 4 | 5 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 0.1 | F691 | 141 | 37 | 100 | 120 | W |
| 1.2 | 4 | 4.8 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 0.1 | MF41X | 112 | 33 | 110 | 130 | W |
| 1.5 | 4 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0.05 | F681X | 112 | 33 | 100 | 120 | W |
| 1.5 | 5 | 6.5 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.15 | F691X | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 1.5 | 6 | 7.5 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.15 | F601X | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | W |
| 2 | 5 | 6.1 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.08 | F682 | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 2 | 5 | 6.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | MF52 | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 2.3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | F692 | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | W/J/TW |
| 2 | 6 | 7.2 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF62 | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | WJ |
| 2 | 7 | 8.2 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF72 | 386 | 129 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 2 | 7 | 8.5 | 2.8 | 0.7 | 0.15 | F602 | 386 | 129 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 2.5 | 6 | 7.1 | 1.8 | 0.5 | 0.08 | F682X | 209 | 74 | 71 | 80 | W |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 2.5 | 0.7 | 0.15 | F692Z | 386 | 129 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 2.5 | 8 | 9.2 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | MF82X | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W |
| 2.5 | 8 | 9.5 | 2.8 | 0.7 | 0.15 | F602X | 552 | 177 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 3 | 6 | 7.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | MF63 | 209 | 74 | 71 | 80 | W |
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 2 | 0.5 | 0.1 | F683 | 311 | 112 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 3 | 8 | 9.2 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF83 | 395 | 141 | 60 | 67 | J |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.15 | F693 | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W/J/TW |
| 3 | 9 | 10.2* | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | MF93 | 571 | 189 | 56 | 67 | W |
| 3 | 9 | 10.5 | 3 | 0.7 | 0.15 | F603 | 571 | 189 | 56 | 67 | W |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | F623 | 631 | 219 | 50 | 60 | J/TW |
| 4 | 7 | 8.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | MF74 | 311 | 115 | 60 | 67 | W |
| 4 | 8 | 9.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF84 | 395 | 141 | 56 | 67 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.1 | F684 | 641 | 227 | 53 | 63 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 10 | 11.2* | 3 | 0.6 | 0.2 | MF104 | 711 | 272 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.15 | F694 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F604 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | F624 | 1301 | 488 | 40 | 48 | J |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F634 | 1340 | 523 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 5 | 8 | 9.2 | 2 | 0.6 | 0.1 | MF85 | 308 | 120 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 5 | 9 | 10.2 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF95 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 10 | 11.2* | 3 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF105 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 11 | 12.6 | 0.15 | MF115 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J | ||
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | F685 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J/TW |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F695 | 1077 | 432 | 43 | 50 | J |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 5 | 1 | 0.2 | F605 | 1329 | 507 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F625 | 1729 | 675 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F635 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 6 | 10 | 11.2 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF106 | 496 | 218 | 45 | 53 | W |
| 6 | 12 | 13.2* | 3 | 0.6 | 0.2 | MF126 | 716 | 295 | 43 | 50 | W/J/TW |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.15 | F686 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.2 | F696 | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 17 | 19 | 6 | 1.2 | 0.3 | F606 | 2263 | 846 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F626 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J,TW |
| 7 | 11 | 12.2 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF117 | 455 | 202 | 43 | 50 | W |
| 7 | 13 | 14.2* | 3 | 0.6 | 0.2 | MF137 | 541 | 276 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 3.5 | 1 | 0.15 | F687 | 1173 | 513 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 5 | 1.2 | 0.3 | F697 | 1605 | 719 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F607 | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F627 | 3287 | 1379 | 30 | 36 | J/TW |
| 8 | 12 | 13.2* | 2.5 | 0.6 | 0.15 | MF128 | 543 | 274 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 8 | 14 | 15.6 | 3.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 | MF148 | 817 | 386 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F688 | 1252 | 592 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F698 | 2237 | 917 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F608 | 3293 | 1379 | 34 | 40 | J/TW |
| 9 | 14 | 15.5 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.1 | F679 | 919 | 468 | 36 | 42 | J |
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F689 | 1327 | 668 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 9 | 20 | 23 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F699 | 2467 | 1081 | 34 | 40 | J |
| 9 | 24 | 27 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F609 | 3356 | 1444 | 32 | 38 | J |
Notes for all bearing lists
* This dimension is increased by 0.4mm for shielded or seal version
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix S or H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
TTS(4) uses smaller ball, load rating is lower than standard
Value (5) is not based up upon JIS B 1521
Flange open ball bearings
Inch series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | Flange Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 0.04 | 0.125 | 0.171 | 0.0469 | 0.013 | 0.0039 | FR09 | 106 | 28 | 130 | 150 | W |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0625 | 0.013 | 0.0039 | FR0** | 112 | 33 | 110 | 130 | W |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0781 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR1** | 232 | 67 | 90 | 110 | W |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR1-4** | 284 | 96 | 67 | 80 | W |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0625 | 0.018 | 0.0039 | FR133 | 189 | 60 | 80 | 95 | W |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0059 | FR1-5** | 552 | 176 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR144J** | 311 | 110 | 67 | 80 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0937 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR144** | 284 | 96 | 67 | 80 | W |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR2-5** | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W/J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0059 | FR2-6** | 640 | 227 | 53 | 63 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 0.0118 | FR2** | 631 | 219 | 56 | 67 | J |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR155** | 359 | 150 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.1094 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR156** | 359 | 150 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR166** | 709 | 272 | 50 | 60 | J |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.0118 | FR3** | 1301 | 488 | 43 | 53 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.0039 | FR168** | 373 | 172 | 48 | 56 | W |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.125 | 0.023 | 0.0059 | FR188** | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.196 | 0.042 | 0.0118 | FR4** | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 0.0059 | FR1810 | 542 | 276 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.2188 | 0.062 | 0.0157 | FR6** | 3332 | 1411 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.2252 | 0.25 | 0.062 | 0.0157 | FR8** | 5108 | 2413 | 27 | 32 | J |
Notes
** Available with inner ring width extended by 0.0156″ (0.3962mm) each side
Bearings also available with stainless materials: prefix S
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Extra thin flange open ball bearings - 6700 6800 6900
Metric Series
| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | Flange Open Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 10 | 15 | 16.5 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | F6700 | 855 | 435 | 15 | 17 | W |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F6800 | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 | J/TW |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F63800 | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 | J/TW |
| 10 | 22 | 25 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6900 | 2695 | 1273 | 34 | 41 | J |
| 12 | 18 | 19.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | F6701 | 926 | 530 | 13 | 15 | W |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | F6801 | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 | J/TW |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F63801 | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 | J/TW |
| 12 | 24 | 26.5 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6901 | 2886 | 1446 | 31 | 36 | J |
| 15 | 21 | 22.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | F6702 | 937 | 582 | 11 | 13 | W |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | F6802 | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 | J/TW |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F63802 | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 | J/TW |
| 15 | 28 | 30.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6902 | 4321 | 2259 | 26 | 30 | J |
| 17 | 23 | 24.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | F6703 | 1000 | 658 | 9.5 | 11 | W |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | F6803 | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 | J/TW |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F63803 | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 | J/TW |
| 17 | 30 | 32.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6903 | 4588 | 2565 | 23 | 38 | J |
| 20 | 27 | 28.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | F6704 | 1402 | 729 | 8.5 | 10 | W |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6804 | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 | J/RJ |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | F63804 | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 | J/RJ |
| 20 | 37 | 40 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | F6904 | 6381 | 3682 | 19 | 23 | RJ |
| 25 | 32 | 34 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F6705 | 1091 | 838 | 7 | 8 | W |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6805 | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 | J/RJ |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | F63805 | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 | J/RJ |
| 25 | 42 | 45 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | F6905 | 7001 | 4540 | 16 | 19 | RJ |
| 30 | 37 | 39 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | F6706 | 1143 | 947 | 5.5 | 7 | W |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6806 | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 | J/RJ |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | F63806 | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 | J/RJ |
| 30 | 47 | 50 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | F6906 | 7242 | 5003 | 14 | 17 | RJ |
| 35 | 47 | 50 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6807 | 4729 | 3821 | 13 | 16 | J/RJ |
| 35 | 55 | 58 | 10 | 2.5 | 0.6 | F6907 | 10900 | 7818 | 12 | 14 | RJ |
| 40 | 52 | 55 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6808 | 4923 | 4178 | 12 | 14 | J |
| 40 | 62 | 65 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | F6908 | 13678 | 9968 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 45 | 58 | 61 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6809 | 6187 | 5381 | 11 | 13 | J |
| 45 | 68 | 71 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | F6909 | 14100 | 10830 | 9.7 | 11 | RJ |
| 50 | 65 | 68 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6810 | 6610 | 6090 | 9.6 | 11 | J/RJ |
| 50 | 72 | 75 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | F6910 | 14540 | 11710 | 9 | 11 | RJ |
Notes
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Shield ball bearings inch
Extra thin shield ball bearings - 6700 6800 6900
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | Shield Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 10 | 15 | 16.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 6700ZZS | 855 | 435 | 15 | 17 | W |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 6800ZZ | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 | J/TW |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 63800ZZ | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 | J/TW |
| 10 | 22 | 25 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6900ZZ | 2695 | 1273 | 34 | 41 | J |
| 12 | 18 | 19.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6701ZZS | 926 | 530 | 13 | 15 | W |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 6801ZZ | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 | J/TW |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 63801ZZ | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 | J/TW |
| 12 | 24 | 26.5 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6901ZZ | 2886 | 1446 | 31 | 36 | J |
| 15 | 21 | 22.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6702ZZS | 937 | 582 | 11 | 13 | W |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 6802ZZ | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 | J/TW |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 63802ZZ | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 | J/TW |
| 15 | 28 | 30.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6902ZZ | 4321 | 2259 | 26 | 30 | J |
| 17 | 23 | 24.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6703ZZS | 1000 | 658 | 9.5 | 11 | W |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 6803ZZ | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 | J/TW |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 63803ZZ | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 | J/TW |
| 17 | 30 | 32.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6903ZZ | 4588 | 2565 | 23 | 38 | J |
| 20 | 27 | 28.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6704ZZS | 1402 | 729 | 8.5 | 10 | W |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6804ZZ | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 | J/RJ |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 63804ZZ | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 | J/RJ |
| 20 | 37 | 40 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 6904ZZ | 6381 | 3682 | 19 | 23 | RJ |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6805ZZ | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 | J/RJ |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 63805ZZ | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 | J/RJ |
| 25 | 42 | 45 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 6905ZZ | 7001 | 4540 | 16 | 19 | RJ |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6806ZZ | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 | J/RJ |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 63806ZZ | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 | J/RJ |
| 30 | 47 | 50 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 6906ZZ | 7242 | 5003 | 14 | 17 | RJ |
| 35 | 47 | 50 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6807ZZ | 4729 | 3821 | 13 | 16 | J/RJ |
| 35 | 55 | 58 | 10 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 6907ZZ | 10900 | 7818 | 12 | 14 | RJ |
| 40 | 52 | 55 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6808ZZ | 4923 | 4178 | 12 | 14 | J |
| 40 | 62 | 65 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 6908ZZ | 13678 | 9968 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 45 | 58 | 61 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6809ZZ | 6187 | 5381 | 11 | 13 | J |
| 45 | 68 | 71 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 6909ZZ | 14100 | 10830 | 9.7 | 11 | RJ |
| 50 | 65 | 68 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 6810ZZ | 6610 | 6090 | 9.6 | 11 | J/RJ |
| 50 | 72 | 75 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 6910ZZ | 14540 | 11710 | 9 | 11 | RJ |
| 55 | 72 | 9 | 0.3 | 6811ZZ | 8800 | 8100 | 8.7 | 10 | RJ | ||
| 55 | 80 | 13 | 1 | 6911ZZ | 16600 | 14100 | 8.1 | 9.6 | RJ | ||
| 60 | 78 | 10 | 0.3 | 6812ZZ | 11500 | 10600 | 8 | 9.4 | RJ | ||
| 60 | 85 | 13 | 1 | 6912ZZ | 20200 | 17300 | 7.5 | 8.9 | RJ | ||
| 65 | 85 | 10 | 0.6 | 6813ZZ | 11900 | 11500 | 7.3 | 8.6 | RJ | ||
| 65 | 90 | 13 | 1 | 6913ZZ | 17400 | 16100 | 7.1 | 8.4 | RJ | ||
| 70 | 90 | 10 | 0.6 | 6814ZZ | 12100 | 11900 | 6.8 | 8.1 | RJ | ||
| 70 | 100 | 16 | 1 | 6914ZZ | 23700 | 21200 | 6.4 | 7.6 | RJ | ||
| 75 | 95 | 10 | 0.6 | 6815ZZ | 12500 | 12900 | 12.5 | 12.9 | RJ | ||
| 75 | 105 | 16 | 1 | 6915ZZ | 24400 | 22600 | 6.1 | 7.2 | RJ | ||
| 80 | 100 | 10 | 0.6 | 6816ZZ | 12700 | 13300 | 12.7 | 13.3 | RJ | ||
| 80 | 110 | 16 | 1 | 6916ZZ | 25000 | 24000 | 5.7 | 6.8 | RJ | ||
| 85 | 110 | 13 | 1 | 6817ZZ | 18700 | 19000 | 5.6 | 6.6 | RJ | ||
| 85 | 120 | 18 | 1.1 | 6917ZZ | 31900 | 29600 | 5.3 | 6.3 | RJ | ||
| 90 | 115 | 13 | 1 | 6818ZZ | 19000 | 19700 | 5.3 | 6.3 | RJ | ||
| 90 | 125 | 18 | 1.1 | 6918ZZ | 32800 | 31600 | 5.1 | 6 | RJ |
Notes
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Carbon Chrome bearings use RJ type retainer, stainless steel bearings use J type retainer
Thrust Series FM With Raceway Ball Bearings
Metric series

| Bearing Ref | Inner Ring Bore Ø | Outer Ring Bore Ø | Inner Ring Bore Ø | Inner Ring Bore Ø | Radius | Height | Load Rating | Max Speed (x1000rpm) | Cage Type | ||
| d | D | d1 | D1 | rs (min) | H | ||||||
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ca(N) | Coa(N) | Grease | Oil | ||
| F3-8M | 3 | 8 | 3.2 | 7.8 | 0.15 | 3.5 | 993 | 590 | 19 | 28 | TP |
| F4-9M | 4 | 9 | 4.2 | 8.8 | 0.15 | 4.0 | 944 | 640 | 17 | 25 | TP |
| F4-10M | 4 | 10 | 4.2 | 9.8 | 0.15 | 4.0 | 925 | 661 | 16 | 24 | TP |
| F5-12M | 5 | 12 | 5.2 | 11.8 | 0.20 | 4.0 | 1056 | 942 | 14 | 22 | TP |
| F6-12M | 6 | 12 | 6.2 | 11.8 | 0.20 | 4.5 | 1819 | 1588 | 14 | 20 | TP |
| F6-14M | 6 | 14 | 6.25 | 13.8 | 0.20 | 5.0 | 2155 | 1701 | 12 | 18 | TP |
| F7-13M | 7 | 13 | 7.2 | 16.8 | 0.20 | 4.5 | 1767 | 1645 | 13 | 20 | TP |
| F7-17M | 7 | 17 | 7.2 | 16.8 | 0.30 | 6.0 | 3086 | 2675 | 10 | 15 | TP |
| F8-16M | 8 | 16 | 8.2 | 15.8 | 0.30 | 5.0 | 3917 | 3394 | 11 | 17 | TP |
| F8-19M | 8 | 19 | 8.2 | 18.8 | 0.30 | 7.0 | 3939 | 3476 | 9 | 13 | TP |
| F9-20M | 9 | 20 | 9.2 | 19.8 | 0.30 | 7.0 | 3855 | 3571 | 8 | 13 | TP |
| F10-18M | 10 | 18 | 10.2 | 17.8 | 0.30 | 5.5 | 2470 | 2721 | 10 | 15 | TP |
ABIS flange shield ball bearings
Metric Series

| Bore Øs (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Radius (rs – min) | Flange Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Shield Flange Width (Bf1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 1.2 | 4 | 4.8 | 0.1 | MF41XZZ | 2.5 | 112 | 33 | 110 | 130 | W | |
| 1.5 | 4 | 5 | 0.05 | F681XZZ | 2 | 0.6 | 112 | 33 | 100 | 120 | W |
| 1.5 | 5 | 6.5 | 0.15 | F691XZZ | 2.6 | 0.8 | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 1.5 | 6 | 7.5 | 0.15 | F601XZZ | 3 | 0.8 | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | W |
| 2 | 5 | 6.1 | 0.08 | F682ZZ | 2.3 | 0.6 | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 2 | 5 | 6.2 | 0.1 | MF52ZZ | 2.5 | 0.6 | 169 | 50 | 85 | 100 | W |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 0.15 | F692ZZ | 3 | 0.8 | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | W/J/TW |
| 2 | 6 | 7.2 | 0.15 | MF62ZZ | 2.5 | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | WJ | |
| 2 | 7 | 8.2 | 0.15 | MF72ZZS | 3 | 0.6 | 386 | 129 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 2 | 7 | 8.5 | 0.15 | F602ZZS | 3.5 | 0.9 | 386 | 129 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 2.5 | 6 | 7.1 | 0.08 | F682XZZ | 2.6 | 0.8 | 209 | 74 | 71 | 80 | W |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 0.15 | F692XZZS | 3.5 | 0.9 | 386 | 129 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 2.5 | 8 | 9.5 | 0.15 | F602XZZ | 4 | 0.9 | 552 | 177 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 3 | 6 | 7.2 | 0.1 | MF63ZZ | 2.5 | 0.6 | 209 | 74 | 71 | 80 | W |
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 0.1 | F683ZZ | 3 | 0.8 | 311 | 112 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 3 | 8 | 9.2 | 0.15 | MF83ZZ | 3 | 395 | 141 | 60 | 67 | J | |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 0.15 | F693ZZ | 4 | 0.9 | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W/J/TW |
| 3 | 9 | 10.2* | 0.2 | MF93ZZ | 4 | 0.8 | 571 | 189 | 56 | 67 | W |
| 3 | 9 | 10.5 | 0.15 | F603ZZ | 5 | 1 | 571 | 189 | 56 | 67 | W |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 0.15 | F623ZZ | 4 | 1 | 631 | 219 | 50 | 60 | J/TW |
| 4 | 7 | 8.2 | 0.1 | MF74ZZ | 2.5 | 0.6 | 255 | 108 | 60 | 67 | W |
| 4 | 8 | 9.2 | 0.1 | MF84ZZ | 3 | 0.6 | 395 | 141 | 56 | 67 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 0.1 | F684ZZ | 4 | 1 | 641 | 227 | 53 | 63 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 10 | 11.2* | 0.15 | MF104ZZ | 4 | 0.8 | 711 | 272 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 0.15 | F694ZZ | 4 | 1 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 0.2 | F604ZZ | 4 | 1 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 0.2 | F624ZZ | 5 | 1 | 1301 | 488 | 40 | 48 | J |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 0.3 | F634ZZ | 5 | 1 | 1340 | 523 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 5 | 8 | 9.2 | 0.1 | MR85ZZ | 2.5 | 0.6 | 218 | 90 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 5 | 9 | 10.2 | 0.15 | MF95ZZ | 3 | 0.6 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 10 | 11.2* | 0.15 | MF105ZZ | 4 | 0.8 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 11 | 12.6 | 0.15 | MF115ZZ | 4 | 0.8 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 0.15 | F685ZZ | 5 | 1 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J/TW |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 0.2 | F695ZZ | 4 | 1 | 1077 | 432 | 43 | 50 | J |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 0.2 | F605ZZ | 5 | 1 | 1329 | 507 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 0.3 | F625ZZ | 5 | 1 | 1729 | 675 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | F635ZZ | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 6 | 10 | 11.2 | 0.1 | MF106ZZ | 3 | 0.6 | 496 | 218 | 45 | 53 | W |
| 6 | 12 | 13.2* | 0.15 | MF126ZZ | 4 | 0.8 | 716 | 295 | 43 | 50 | W/J/TW |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 0.15 | F686ZZ | 5 | 1.1 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 0.2 | F696ZZ | 5 | 1.2 | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 17 | 19 | 0.3 | F606ZZ | 6 | 1.2 | 2263 | 846 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | F626ZZ | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 7 | 11 | 12.2 | 0.1 | MF117ZZS | 3 | 0.6 | 455 | 202 | 43 | 50 | W |
| 7 | 13 | 14.2* | 0.15 | MF137ZZ | 4 | 0.8 | 541 | 276 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 0.15 | F687ZZ | 5 | 1.1 | 1173 | 513 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 0.3 | F697ZZ | 5 | 1.2 | 1605 | 719 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | F607ZZ | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 0.3 | F627ZZ | 7 | 1.5 | 3287 | 1379 | 30 | 36 | J/TW |
| 8 | 12 | 13.2* | 0.1 | MF128ZZ | 3.5 | 0.8 | 543 | 274 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 8 | 14 | 15.6 | 0.15 | MF148ZZ | 4 | 0.8 | 817 | 386 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 0.2 | F688ZZ | 5 | 1.1 | 1252 | 592 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | F698ZZ | 6 | 1.5 | 2237 | 917 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 0.3 | F608ZZ | 7 | 1.5 | 3293 | 1379 | 34 | 40 | J,TW |
| 9 | 14 | 15.5 | 0.1 | F679ZZS | 4.5 | 0.8 | 919 | 468 | 36 | 42 | J |
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 0.2 | F689ZZ | 5 | 1.1 | 1327 | 668 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 9 | 20 | 23 | 0.3 | F699ZZ | 6 | 1.5 | 2467 | 1081 | 34 | 40 | J |
| 9 | 24 | 27 | 0.3 | F609ZZ | 7 | 1.5 | 3356 | 1444 | 32 | 38 | J |
Notes
* This dimension is increased by 0.4mm for shielded or seal version
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix S or H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
TTS(4) uses smaller ball, load rating is lower than standard
Value (5) is not based up upon JIS B 1521
Flange shield ball bearings
Inch series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Radius (rs – min) | Flange Shield Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Shield Flange Width (Bf1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 0.0469 | 0.1562 | 0.203 | 0.0039 | FR0ZZ** | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 112 | 33 | 110 | 130 | W |
| 0.055 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0039 | FR1ZZ** | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 232 | 67 | 90 | 110 | W |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0039 | FR1-4ZZ** | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 284 | 96 | 67 | 80 | W |
| 0.0937 | 0.1875 | 0.234 | 0.0039 | FR133ZZS** | 0.0937 | 0.031 | 144 | 53 | 80 | 95 | W |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.0059 | FR1-5ZZS** | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 552 | 176 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0039 | FR144JZZ** | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 311 | 110 | 67 | 80 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0039 | FR144ZZ** | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 284 | 96 | 67 | 80 | W |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.0039 | FR2-5ZZ** | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W/J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.0059 | FR2-6ZZ** | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 640 | 227 | 53 | 63 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.0118 | FR2ZZ** | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 631 | 219 | 56 | 67 | J |
| 0.1562 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.0039 | FR155ZZS** | 0.125 | 0.036 | 359 | 150 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.0039 | FR156ZZS** | 0.125 | 0.036 | 359 | 150 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.0039 | FR166ZZ* | 0.125 | 0.031 | 709 | 272 | 50 | 60 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.0039 | FR168ZZS** | 0.125 | 0.036 | 373 | 172 | 48 | 56 | W |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.0059 | FR188ZZ** | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.0118 | FR4ZZ** | 0.196 | 0.0633 | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.0059 | FR1810ZZS | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 542 | 276 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.0157 | FR6ZZ** | 0.2812 | 0.062 | 3332 | 1411 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.2252 | 0.0157 | FR8ZZ** | 0.3125 | 0.062 | 5108 | 2413 | 27 | 32 | J |
| 0.625 | 1.375 | 1.49 | 0.0315 | FR10ZZ | 0.3438 | 0.0687 | 5999 | 3265 | 21 | 25 | RJ |
Notes
** Available with inner ring width extended by 0.0156″ (0.3962mm) each side
Bearings also available with stainless materials: prefix S
Ball bearings also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Extra thin flange open ball bearings - 6700 6800 6900
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | Flange Shield Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 10 | 15 | 16.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.15 | F6700ZZS | 855 | 435 | 15 | 17 | W |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | F6800ZZ | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 | J/TW |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F63800ZZ | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 | J/TW |
| 10 | 22 | 25 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6900ZZ | 2695 | 1273 | 34 | 41 | J |
| 12 | 18 | 19.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | F6701ZZS | 926 | 530 | 13 | 15 | W |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | F6801ZZ | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 | J/TW |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F63801ZZ | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 | J/TW |
| 12 | 24 | 26.5 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6901ZZ | 2886 | 1446 | 31 | 36 | J |
| 15 | 21 | 22.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | F6702ZZS | 937 | 582 | 11 | 13 | W |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | F6802ZZ | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 | J/TW |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F63802ZZ | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 | J/TW |
| 15 | 28 | 30.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6902ZZ | 4321 | 2259 | 26 | 30 | J |
| 17 | 23 | 24.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | F6703ZZS | 1000 | 658 | 9.5 | 11 | W |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | F6803ZZ | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 | J/TW |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F63803ZZ | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 | J/TW |
| 17 | 30 | 32.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6903ZZ | 4588 | 2565 | 23 | 38 | J |
| 20 | 27 | 28.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | F6704ZZS | 1402 | 729 | 8.5 | 10 | W |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6804ZZ | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 | J/RJ |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | F63804ZZ | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 | J/RJ |
| 20 | 37 | 40 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | F6904ZZ | 6381 | 3682 | 19 | 23 | RJ |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6805ZZ | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 | J/RJ |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | F63805ZZ | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 | J/RJ |
| 25 | 42 | 45 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | F6905ZZ | 7001 | 4540 | 16 | 19 | RJ |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6806ZZ | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 | J/RJ |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | F63806ZZ | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 | J/RJ |
| 30 | 47 | 50 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | F6906ZZ | 7242 | 5003 | 14 | 17 | RJ |
| 35 | 47 | 50 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6807ZZ | 4729 | 3821 | 13 | 16 | J/RJ |
| 35 | 55 | 58 | 10 | 2.5 | 0.6 | F6907ZZ | 10900 | 7818 | 12 | 14 | RJ |
| 40 | 52 | 55 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6808ZZ | 4923 | 4178 | 12 | 14 | J |
| 40 | 62 | 65 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | F6908ZZ | 13678 | 9968 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 45 | 58 | 61 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6809ZZ | 6187 | 5381 | 11 | 13 | J |
| 45 | 68 | 71 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | F6909ZZ | 14100 | 10830 | 9.7 | 11 | RJ |
| 50 | 65 | 68 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | F6810ZZ | 6610 | 6090 | 9.6 | 11 | J/RJ |
| 50 | 72 | 75 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | F6910ZZ | 14540 | 11710 | 9 | 11 | RJ |
Notes
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Carbon Chrome bearings use RJ type retainer, stainless steel bearings use J type retainer
ABIS 2RS Seal Ball Bearings
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Radius (rs – min) | 2RS Seal Part No | Flange 2RS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Shield Flange Width (Bf1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 3 | 8 | 9.5 | 0.15 | 6932RS | F6932RS | 4 | 0.9 | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W/J/TW |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 0.15 | 6232RS | F6232RS | 4 | 1 | 631 | 219 | 50 | 60 | J/TW |
| 3 | 13 | 0.2 | 6332RS | 5 | 1301 | 488 | 40 | 48 | J | |||
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 0.1 | 6842RS | F6842RS | 4 | 1 | 641 | 227 | 53 | 63 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 10 | 11.2* | 0.2 | MR1042RS | MF1042RS | 4 | 0.8 | 711 | 272 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 0.15 | 6942RS | F6942RS | 4 | 1 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 0.2 | 6042RS | F6042RS | 4 | 1 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 0.2 | 6242RS | F6242RS | 5 | 1 | 1301 | 488 | 40 | 48 | J |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 0.3 | 6342RS | F6342RS | 5 | 1 | 1340 | 523 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 5 | 10 | 11.2* | 0.15 | MR1052RS | MF1052RS | 4 | 0.8 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 11 | 12.6 | 0.15 | MR1152RS | MF1152RS | 4 | 0.8 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 0.15 | 6852RS | F6852RS | 5 | 1 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J/TW |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 0.2 | 6952RS | F6952RS | 4 | 1 | 1077 | 432 | 43 | 50 | J |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 0.2 | 6052RS | F6052RS | 5 | 1 | 1329 | 507 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 0.3 | 6252RS | F6252RS | 5 | 1 | 1729 | 675 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 6352RS | F6352RS | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 6 | 12 | 13.2* | 0.15 | MR1262RS | MF1262RS | 4 | 0.8 | 716 | 295 | 43 | 50 | W/J/TW |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 0.15 | 6862RS | F6862RS | 5 | 1.1 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J,TW |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 0.2 | 6962RS | F6962RS | 5 | 1.2 | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 16 | 0.2 | 696A2RS | 5 | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J | |||
| 6 | 17 | 19 | 0.3 | 6062RS | F6062RS | 6 | 1.2 | 2263 | 846 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 6262RS | F6262RS | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 6 | 22 | 0.3 | 6362RS | 7 | 3333 | 1423 | 30 | 36 | J/TW | |||
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 0.15 | 6872RS | F6872RS | 5 | 1.1 | 1173 | 513 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 0.3 | 6972RS | F6972RS | 5 | 1.2 | 1605 | 719 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 6072RS | F6072RS | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 0.3 | 6272RS | F6272RS | 7 | 1.5 | 3287 | 1379 | 30 | 36 | J/TW |
| 7 | 26 | 0.3 | 6372RS | 9 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 8 | 14 | 15.6 | 0.2 | MR1482RS | MF1482RS | 4 | 0.8 | 817 | 386 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 0.2 | 6882RS | F6882RS | 5 | 1.1 | 1252 | 592 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 6982RS | F6982RS | 6 | 1.5 | 2237 | 917 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 0.3 | 6082RS | F6082RS | 7 | 1.5 | 3293 | 1379 | 34 | 40 | J/TW |
| 8 | 24 | 0.3 | 6282RS | 8 | 3333 | 1423 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 8 | 28 | 0.3 | 6382RS | 9 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 0.2 | 6892RS | 6892RS | 5 | 1.1 | 1327 | 668 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 9 | 20 | 23 | 0.3 | 6992RS | 6992RS | 6 | 1.5 | 2467 | 1081 | 34 | 40 | J |
| 9 | 24 | 27 | 0.3 | 6092RS | F6092RS | 7 | 1.5 | 3356 | 1444 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 9 | 26 | 0.60(5) | 6292RS | 8 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 9 | 30 | 0.6 | 6392RS | 10 | 4659 | 2080 | 24 | 30 | J |
Notes
*This dimension is increased by 0.4mm for shielded or sealed version
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix S or H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
TTS(4) uses smaller ball, load rating is lower than standard
Value (5) is not based up upon JIS B 1521
IEC are one of the biggest bearing distributors in the UK.
ABIS 2RS Seal Ball Bearings
Inch series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Radius (rs – min) | 2RS Seal Part No | Flange 2RS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Shield Flange Width (Bf1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.0059 | R262RS** | FR262RS** | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 640 | 227 | 53 | 63 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.0118 | R22RS** | FR22RS** | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 631 | 219 | 56 | 67 | J |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.0118 | R22RS** | 0.196 | 0.042 | 1301 | 488 | 43 | 53 | J | |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.0118 | R3A2RS | 0.196 | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J | |||
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.0059 | R1882RS** | FR1882RS** | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.0118 | R42RS** | FR42RS** | 0.196 | 0.0633 | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.0157 | R4A2RS | 0.2812 | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J | |||
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.0157 | R62RS | FR62RS** | 0.2812 | 0.062 | 3332 | 1411 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.2252 | 0.0157 | R82RS | FR82RS** | 0.3125 | 0.062 | 5108 | 2413 | 27 | 32 | J |
| 0.625 | 1.375 | 1.49 | 0.0315 | R102RS | FR102RS | 0.3438 | 0.0687 | 5999 | 3265 | 21 | 25 | RJ |
| 0.75 | 1.625 | 0.0315 | R122RS | 0.4375 | 9384 | 5057 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
Notes
** Available with inner ring width extended by 0.0156″ (0.3962mm) each side
Bearings also available with stainless materials: prefix S
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Extra Thin 2RS Seal Ball Bearings - 6700 6800 6900
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | 2RS Seal Part No | Flange 2RS Seal Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) |
| 10 | 15 | 16.5 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 67002RS | 855 | 435 | 15 | 17 | |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 68002RS | F68002RS | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 638002RS | F638002RS | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 |
| 10 | 22 | 25 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 69002RS | F69002RS | 2695 | 1273 | 34 | 41 |
| 12 | 18 | 19.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 67012RS | F67012RS | 926 | 530 | 13 | 15 |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 68012RS | F68012RS | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 638012RS | F638012RS | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 |
| 12 | 24 | 26.5 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 69012RS | F69012RS | 2886 | 1446 | 31 | 36 |
| 15 | 21 | 22.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 67022RS | F67022RS | 937 | 582 | 11 | 13 |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 68022RS | F68022RS | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 638022RS | F638022RS | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 |
| 15 | 28 | 30.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 69022RS | F69022RS | 4321 | 2259 | 26 | 30 |
| 17 | 23 | 24.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 67032RS | F67032RS | 1000 | 658 | 9.5 | 11 |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 68032RS | F68032RS | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 638032RS | F638032RS | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 |
| 17 | 30 | 32.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 69032RS | F69032RS | 4588 | 2565 | 23 | 38 |
| 20 | 27 | 28.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 67042RS | F67042RS | 1402 | 729 | 8.5 | 10 |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68042RS | F68042RS | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 638042RS | F638042RS | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 |
| 20 | 37 | 40 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 69042RS | F69042RS | 6381 | 3682 | 19 | 23 |
| 25 | 32 | 34 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 67052RS | F67052RS | 1091 | 838 | 7 | 8 |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68052RS | F68052RS | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 638052RS | F638052RS | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 |
| 25 | 42 | 45 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 69052RS | F69052RS | 7001 | 4540 | 16 | 19 |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68062RS | F68062RS | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 638062RS | F638062RS | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 |
| 30 | 47 | 50 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 69062RS | F69062RS | 7242 | 5003 | 14 | 17 |
| 35 | 44 | 5 | 0.3 | 67072RS | 1866 | 1635 | 4.9 | 6 | |||
| 35 | 47 | 50 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68072RS | F68072RS | 4729 | 3821 | 13 | 16 |
| 35 | 55 | 58 | 10 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 69072RS | F69072RS | 10900 | 7818 | 12 | 14 |
| 40 | 50 | 6 | 0.3 | 67082RS | 2516 | 2233 | 4.3 | 5 | |||
| 40 | 52 | 55 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68082RS | F68082RS | 4923 | 4178 | 12 | 14 |
| 40 | 62 | 65 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 69082RS | F69082RS | 13678 | 9968 | 11 | 13 |
| 45 | 55 | 6 | 0.3 | 67902RS | 2580 | 2397 | 3.9 | 4.6 | |||
| 45 | 58 | 61 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68092RS | F68092RS | 6187 | 5381 | 11 | 13 |
| 45 | 68 | 71 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 69092RS | F69092RS | 14100 | 10830 | 9.7 | 11 |
| 50 | 62 | 6 | 0.3 | 67102RS | 2670 | 2640 | 3.5 | 4.1 | |||
| 50 | 65 | 68 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68102RS | F68102RS | 6610 | 6090 | 9.6 | 11 |
| 50 | 72 | 75 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 69102RS | F69102RS | 14540 | 11710 | 9 | 11 |
| 55 | 72 | 9 | 0.3 | 68112RS | 8800 | 8100 | 8.7 | 10 | |||
| 55 | 80 | 13 | 1 | 69112RS | 16600 | 14100 | 8.1 | 9.6 | |||
| 60 | 78 | 10 | 0.3 | 68122RS | 11500 | 10600 | 8 | 9.4 | |||
| 60 | 85 | 13 | 1 | 69122RS | 20200 | 17300 | 7.5 | 8.9 | |||
| 65 | 85 | 10 | 0.6 | 68132RS | 11900 | 11500 | 7.3 | 8.6 | |||
| 65 | 90 | 13 | 1 | 69132RS | 17400 | 16100 | 7.1 | 8.4 | |||
| 70 | 90 | 10 | 0.6 | 68142RS | 12100 | 11900 | 6.8 | 8.1 | |||
| 70 | 100 | 16 | 1 | 68142RS | 23700 | 21200 | 6.4 | 7.6 | |||
| 75 | 95 | 10 | 0.6 | 68152RS | 12500 | 12900 | 12.5 | 12.9 | |||
| 75 | 105 | 16 | 1 | 69152RS | 24400 | 22600 | 6.1 | 7.2 | |||
| 80 | 100 | 10 | 0.6 | 68162RS | 12700 | 13300 | 12.7 | 13.3 | |||
| 80 | 110 | 16 | 1 | 69162RS | 25000 | 24000 | 5.7 | 6.8 | |||
| 85 | 110 | 13 | 1 | 68172RS | 18700 | 19000 | 5.6 | 6.6 | |||
| 85 | 120 | 18 | 1.1 | 69172RS | 31900 | 29600 | 5.3 | 6.3 | |||
| 90 | 115 | 13 | 1 | 68182RS | 19000 | 19700 | 5.3 | 6.3 | |||
| 90 | 125 | 18 | 1.1 | 69182RS | 32800 | 31600 | 5.1 | 6 |
Notes
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Carbon Chrome bearings use RJ type retainer, stainless steel ball bearings use J type retainer
Large Size Stainless Steel 2RS Seal Ball Bearings 6000H 6200H 6300H
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Radius (rs – min) | 2RS Seal Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 6000H2RS* | 3860 | 1570 | 31 | 36 | J |
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 6200H2RS* | 4340 | 1920 | 24 | 29 | RJ/TW |
| 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 6300H2RS | 6870 | 2750 | 22 | 27 | RJ |
| 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 6001H2RS* | 4340 | 1910 | 27 | 32 | J/TW |
| 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6201H2RS | 5770 | 2450 | 22 | 27 | RJ/TW |
| 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 6301H2RS | 8240 | 3360 | 20 | 25 | RJ |
| 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 6002H2RS* | 4750 | 2270 | 23 | 27 | RJ/TW |
| 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 6202H2RS | 6490 | 3000 | 20 | 24 | RJ/TW |
| 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 6302H2RS | 9710 | 4370 | 17 | 20 | RJ |
| 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6003H2RS | 5090 | 2630 | 21 | 25 | RJ/TW |
| 17 | 40 | 12 | 0.6 | 6203H2RS | 8130 | 3850 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
| 17 | 47 | 14 | 1 | 6303H2RS | 11550 | 5330 | 15 | 18 | RJ |
| 20 | 42 | 12 | 0.6 | 6004H2RS | 7960 | 4050 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
| 20 | 47 | 14 | 1 | 6204H2RS | 10910 | 5360 | 15 | 17 | RJ,/W |
| 20 | 52 | 15 | 1.1 | 6304H2RS | 13490 | 6310 | 14 | 17 | RJ |
| 25 | 47 | 12 | 0.6 | 6005H2RS | 8550 | 4690 | 15 | 18 | RJ/TW |
| 25 | 52 | 15 | 1 | 6205H2RS | 11900 | 7390 | 13 | 15 | RJ/TW |
| 25 | 62 | 17 | 1.1 | 6305H2RS | 17490 | 9060 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 30 | 55 | 13 | 1 | 6006H2RS | 11240 | 6610 | 13 | 15 | RJ/TW |
| 30 | 62 | 16 | 1 | 6206H2RS | 16530 | 9080 | 11 | 13 | RJ/TW |
| 30 | 72 | 19 | 1.1 | 6306H2RS | 22630 | 12080 | 9.6 | 12 | RJ |
| 35 | 62 | 14 | 1 | 6007H2RS | 13560 | 8250 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 35 | 72 | 17 | 1.1 | 6207H2RS | 21810 | 12360 | 9.2 | 11 | RJ |
| 35 | 80 | 21 | 1.5 | 6307H2RS | 28290 | 15270 | 8.5 | 10 | RJ |
| 40 | 68 | 15 | 1 | 6008H2RS | 14250 | 9220 | 10 | 12 | RJ |
| 40 | 80 | 18 | 1.1 | 6208H2RS | 24730 | 14330 | 8.3 | 10 | RJ |
| 45 | 75 | 16 | 1 | 6009H2RS | 15150 | 9660 | 9.2 | 11 | RJ |
| 45 | 85 | 19 | 1.1 | 6209H2RS | 27790 | 16300 | 7.7 | 9.2 | RJ |
| 50 | 80 | 16 | 1 | 6010H2RS | 18510 | 13260 | 8.4 | 9.9 | RJ |
| 50 | 90 | 20 | 1.1 | 6210H2RS | 29800 | 18610 | 7.1 | 8.5 | RJ |
ABIS Miniature And Precision 2RU Seal Ball Bearings
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Radius (rs – min) | 2RU Seal Part No | Flange 2RU Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Shield Flange Width (Bf1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 3 | 10 | 11.5 | 0.15 | 6232RU | F6232RU | 4 | 1 | 631 | 219 | 50 | 60 | J/TW |
| 3 | 13 | 0.2 | 6332RU | 5 | 1301 | 488 | 40 | 48 | J | |||
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 0.1 | 6842RU | F6842RU | 4 | 1 | 641 | 227 | 53 | 63 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 10 | 11.2* | 0.2 | MR1042RU | MF1042RU | 4 | 0.8 | 711 | 272 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 11 | 12.5 | 0.15 | 6942RU | F6942RU | 4 | 1 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 12 | 13.5 | 0.2 | 6042RU | F6042RU | 4 | 1 | 957 | 350 | 48 | 56 | J |
| 4 | 13 | 15 | 0.2 | 6242RU | F6242RU | 5 | 1 | 1301 | 488 | 40 | 48 | J |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 0.3 | 6342RU | F6342RU | 5 | 1 | 1340 | 523 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 5 | 10 | 11.2* | 0.15 | MR1052RU | MF1052RU | 4 | 0.8 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 11 | 12.6 | 0.15 | MR1152RU | MF1152RU | 4 | 0.8 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J |
| 5 | 11 | 12.5 | 0.15 | 6852RU | F6852RU | 5 | 1 | 716 | 282 | 45 | 53 | J/TW |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 0.2 | 6952RU | F6952RU | 4 | 1 | 1077 | 432 | 43 | 50 | J |
| 5 | 14 | 16 | 0.2 | 6052RU | F6052RU | 5 | 1 | 1329 | 507 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 0.3 | 6252RU | F6252RU | 5 | 1 | 1729 | 675 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 5 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 635-2RU | F6352RU | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 6 | 12 | 13.2* | 0.15 | MR1262RU | MF1262RU | 4 | 0.8 | 716 | 295 | 43 | 50 | W/J/TW |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 0.15 | 6862RU | F6862RU | 5 | 1.1 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J/W |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 0.2 | 6962RU | F6962RU | 5 | 1.2 | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 16 | 0.2 | 696A2RU | 5 | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J | |||
| 6 | 17 | 19 | 0.3 | 6062RU | F6062RU | 6 | 1.2 | 2263 | 846 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 6262RU | F6262RU | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 6 | 22 | 0.3 | 6362RU | 7 | 3333 | 1423 | 30 | 36 | J/TW | |||
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 0.15 | 6872RU | F6872RU | 5 | 1.1 | 1173 | 513 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 7 | 17 | 19 | 0.3 | 6972RU | F6972RU | 5 | 1.2 | 1605 | 719 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 6072RU | F6072RU | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 0.3 | 6272RU | F6272RU | 7 | 1.5 | 3287 | 1379 | 30 | 36 | J/TW |
| 7 | 26 | 0.3 | 6372RU | 9 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 8 | 14 | 15.6 | 0.2 | MR1482RU | MF1482RU | 4 | 0.8 | 817 | 386 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 0.2 | 6882RU | F6882RU | 5 | 1.1 | 1252 | 592 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 8 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 6982RU | F6982RU | 6 | 1.5 | 2237 | 917 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 0.3 | 6082RU | F6082RU | 7 | 1.5 | 3293 | 1379 | 34 | 40 | J/TW |
| 8 | 24 | 0.3 | 6282RU | 8 | 3333 | 1423 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 8 | 28 | 0.3 | 6382RU | 9 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 9 | 17 | 19 | 0.2 | 6892RU | F6892RU | 5 | 1.1 | 1327 | 668 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 9 | 20 | 23 | 0.3 | 6992RU | F6992RU | 6 | 1.5 | 2467 | 1081 | 34 | 40 | J |
| 9 | 24 | 27 | 0.3 | 6092RU | F6092RU | 7 | 1.5 | 3356 | 1444 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 9 | 26 | 0.60(5) | 6292RU | 8 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 9 | 30 | 0.6 | 6392RU | 10 | 4659 | 2080 | 24 | 30 | J |
Notes
* This dimension is increased by 0.4mm for shielded or seal version
Ball bearing assemblies also available with stainless materials: suffix S or H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
TTS(4) uses smaller ball, load rating is lower than standard
Value (5) is not based up upon JIS B 1521
2RU Seal Ball Bearings
Inch series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Radius (rs – min) | 2RU Seal Part No | Flange 2RU Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Shield Flange Width (Bf1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.0059 | R262RU* | FR262RU* | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 640 | 227 | 53 | 63 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.44 | 0.0118 | R22RS* | FR22RU* | 0.1562 | 0.03 | 631 | 219 | 56 | 67 | J |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.0118 | R22RU* | 0.196 | 0.042 | 1301 | 488 | 43 | 53 | J | |
| 0.1875 | 0.625 | 0.0118 | R3A2RU | 0.196 | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J | |||
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.0059 | R1882RU* | FR1882RU* | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.0118 | R42RU* | FR42RU* | 0.196 | 0.0633 | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.75 | 0.0157 | R4A2RU | 0.2812 | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J | |||
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.0157 | R62RU | R62RU* | 0.2812 | 0.062 | 3332 | 1411 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.2252 | 0.0157 | R82RU | FR82RU* | 0.3125 | 0.062 | 5108 | 2413 | 27 | 32 | J |
| 0.625 | 1.375 | 1.49 | 0.0315 | R102RU | FR102RU | 0.3438 | 0.0687 | 5999 | 3265 | 21 | 25 | RJ |
| 0.75 | 1.625 | 0.0315 | R122RU | 0.4375 | 9384 | 5057 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
Notes
*Available with inner ring width extended by 0.0156″ (0.3962mm) each side
Bearings also available with stainless materials: prefix S
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
2RU Extra thin flange open ball bearings - 6700 6800 6900
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | 2RU Seal Part No | Flange 2RU Seal Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x 1000 rpm) |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 5 | 1 | 0.3 | 68002RU | F68002RU | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 |
| 10 | 19 | 21 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 638002RU | F638002RU | 1716 | 840 | 37 | 43 |
| 10 | 22 | 25 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 69002RU | F69002RU | 2695 | 1273 | 34 | 41 |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 68012RU | F68012RU | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 |
| 12 | 21 | 23 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 638012RU | F638012RU | 1915 | 1041 | 33 | 39 |
| 12 | 24 | 26.5 | 6 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 69012RU | F69012RU | 2886 | 1446 | 31 | 36 |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 68022RU | F68022RU | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 |
| 15 | 24 | 26 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 638022RU | F638022RU | 2073 | 1253 | 28 | 33 |
| 15 | 28 | 30.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 69022RU | F69022RU | 4321 | 2259 | 26 | 30 |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 5 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 68032RU | F68032RU | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 |
| 17 | 26 | 28 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 638032RU | F638032RU | 2233 | 1456 | 26 | 30 |
| 17 | 30 | 32.5 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 69032RU | F69032RU | 4588 | 2565 | 23 | 38 |
| 20 | 27 | 28.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 67042RU | F67042RU | 1402 | 729 | 8.5 | 10 |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68042RU | F68042RU | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 |
| 20 | 32 | 35 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 638042RU | F638042RU | 4015 | 2462 | 21 | 25 |
| 20 | 37 | 40 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 69042RU | F69042RU | 6381 | 3682 | 19 | 23 |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68052RU | F68052RU | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 |
| 25 | 37 | 40 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 638052RU | F638052RU | 4303 | 2932 | 18 | 21 |
| 25 | 42 | 45 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 69052RU | F69052RU | 7001 | 4540 | 16 | 19 |
| 30 | 37 | 39 | 4 | 1 | 0.2 | 67062RU | F67062RU | 1143 | 947 | 5.5 | 7 |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68062RU | F68062RU | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 |
| 30 | 42 | 45 | 10 | 2 | 0.3 | 638062RU | F638062RU | 4538 | 3402 | 15 | 18 |
| 30 | 47 | 50 | 9 | 2 | 0.3 | 69062RU | F69062RU | 7242 | 5003 | 14 | 17 |
| 35 | 47 | 50 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68072RU | F68072RU | 4729 | 3821 | 13 | 16 |
| 35 | 55 | 58 | 10 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 69072RU | F69072RU | 10900 | 7818 | 12 | 14 |
| 40 | 52 | 55 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68082RU | F68082RU | 4923 | 4178 | 12 | 14 |
| 40 | 62 | 65 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 69082RU | F69082RU | 13678 | 9968 | 11 | 13 |
| 45 | 58 | 61 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68092RU | F68092RU | 6187 | 5381 | 11 | 13 |
| 45 | 68 | 71 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 69092RU | F69092RU | 14100 | 10830 | 9.7 | 11 |
| 50 | 65 | 68 | 7 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 68102RU | F68102RU | 6610 | 6090 | 9.6 | 11 |
| 50 | 72 | 75 | 12 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 69102RU | F69102RU | 14540 | 11710 | 9 | 11 |
| 55 | 72 | 9 | 0.3 | 68112RU | 8800 | 8100 | 8.7 | 10 | |||
| 80 | 100 | 10 | 0.6 | 68162RU | 12700 | 13300 | 12.7 | 13.3 |
Notes
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Carbon Chrome bearings use RJ type retainer, stainless steel bearings use J type retainer
LARGE SIZE STAINLESS STEEL 2RU BALL BEARINGS 6000H 6200H 6300H
Metric series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Radius (rs – min) | 2RU Seal Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 6000H2RU* | 3860 | 1570 | 31 | 36 | J |
| 10 | 30 | 9 | 0.6 | 6200H2RU* | 4340 | 1920 | 24 | 29 | RJ/TW |
| 10 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 6300H2RU | 6870 | 2750 | 22 | 27 | RJ |
| 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 6001H2RU* | 4340 | 1910 | 27 | 32 | J/TW |
| 12 | 32 | 10 | 0.6 | 6201H2RU | 5770 | 2450 | 22 | 27 | RJ/TW |
| 12 | 37 | 12 | 1 | 6301H2RU | 8240 | 3360 | 20 | 25 | RJ |
| 15 | 32 | 9 | 0.3 | 6002H2RU* | 4750 | 2270 | 23 | 27 | RJ/TW |
| 15 | 35 | 11 | 0.6 | 6202H2RU | 6490 | 3000 | 20 | 24 | RJ/TW |
| 15 | 42 | 13 | 1 | 6302H2RU | 9710 | 4370 | 17 | 20 | RJ |
| 17 | 35 | 10 | 0.3 | 6003H2RU | 5090 | 2630 | 21 | 25 | RJ/TW |
| 17 | 40 | 12 | 0.6 | 6203H2RU | 8130 | 3850 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
| 17 | 47 | 14 | 1 | 6303H2RU | 11550 | 5330 | 15 | 18 | RJ |
| 20 | 42 | 12 | 0.6 | 6004H2RU | 7960 | 4050 | 17 | 21 | RJ/TW |
| 20 | 47 | 14 | 1 | 6204H2RU | 10910 | 5360 | 15 | 17 | RJ/TW |
| 20 | 52 | 15 | 1.1 | 6304H2RU | 13490 | 6310 | 14 | 17 | RJ |
| 25 | 47 | 12 | 0.6 | 6005H2RU | 8550 | 4690 | 15 | 18 | RJ/TW |
| 25 | 52 | 15 | 1 | 6205H2RU | 11900 | 7390 | 13 | 15 | RJ/TW |
| 25 | 62 | 17 | 1.1 | 6305H2RU | 17490 | 9060 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 30 | 55 | 13 | 1 | 6006H2RU | 11240 | 6610 | 13 | 15 | RJ/TW |
| 30 | 62 | 16 | 1 | 6206H2RU | 16530 | 9080 | 11 | 13 | RJ/TW |
| 30 | 72 | 19 | 1.1 | 6306H2RU | 22630 | 12080 | 9.6 | 12 | RJ |
| 35 | 62 | 14 | 1 | 6007H2RU | 13560 | 8250 | 11 | 13 | RJ |
| 35 | 72 | 17 | 1.1 | 6207H2RU | 21810 | 12360 | 9.2 | 11 | RJ |
| 35 | 80 | 21 | 1.5 | 6307H2RU | 28290 | 15270 | 8.5 | 10 | RJ |
| 40 | 68 | 15 | 1 | 6008H2RU | 14250 | 9220 | 10 | 12 | RJ |
| 40 | 80 | 18 | 1.1 | 6208H2RU | 24730 | 14330 | 8.3 | 10 | RJ |
| 45 | 75 | 16 | 1 | 6009H2RU | 15150 | 9660 | 9.2 | 11 | RJ |
| 45 | 85 | 19 | 1.1 | 6209H2RU | 27790 | 16300 | 7.7 | 9.2 | RJ |
| 50 | 80 | 16 | 1 | 6010H2RU | 18510 | 13260 | 8.4 | 9.9 | RJ |
| 50 | 90 | 20 | 1.1 | 6210H2RU | 29800 | 18610 | 7.1 | 8.5 | RJ |
THRUST SERIES F WITHOUT RACEWAY BALL BEARINGS
Metric series

| Bearing Ref | Inner Ring Bore Ø | Outer Ring Bore Ø | Inner Ring Bore Ø | Inner Ring Bore Ø | Radius | Height | Load Rating | Cage Type | |
| d | D | d1 | D1 | rs (min) | H | ||||
| mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | Ca(N) | Coa(N) | ||
| F2-6 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 0.10 | 3 | 117 | 83 | TD |
| F2X-7 | 2.5 | 7 | 2.5 | 7 | 0.10 | 3.5 | 156 | 117 | TD |
| F3-8 | 3 | 8 | 3 | 8 | 0.10 | 3.5 | 166 | 137 | TD |
| F4-9 | 4 | 9 | 4 | 9 | 0.15 | 4 | 166 | 156 | TD |
| F4-10 | 4 | 10 | 4 | 10 | 0.15 | 4.5 | 274 | 245 | TD |
| F5-11 | 5 | 11 | 5 | 11 | 0.15 | 4.5 | 284 | 284 | TD |
| F6-12 | 6 | 12 | 6 | 12 | 0.15 | 4.5 | 274 | 284 | TD |
| F7-15 | 7 | 15 | 7 | 15 | 0.20 | 5 | 558 | 548 | TD |
| F8-16 | 8 | 16 | 8 | 16 | 0.20 | 5 | 597 | 627 | TD |
| F9-17 | 9 | 17 | 9 | 17 | 0.20 | 5 | 437 | 542 | TD |
| F10-18* | 10 | 18 | 10 | 18 | 0.20 | 5.5 | 617 | 705 | TD |
ABIS TTS Seal Ball Bearings
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Radius (rs – min) | TTS Seal Part No | Flange TTS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Shield Flange Width (Bf1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 2 | 6 | 7.5 | 0.15 | 692TTS | F692TTS | 3 | 0.8 | 330 | 99 | 75 | 90 | W/J/TW |
| 2 | 7 | 8.2 | 0.15 | MR72TTS | MF72TTS | 3 | 0.6 | 386 | 129 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 2 | 7 | 8.5 | 0.15 | 602TTS | F602TTS | 3.5 | 0.9 | 386 | 129 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 2.5 | 7 | 8.5 | 0.15 | 692TTS | F692TTS | 3.5 | 0.9 | 386 | 129 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 3 | 7 | 8.1 | 0.1 | 683TTS | F683TTS | 3 | 0.8 | 311 | 112 | 63 | 75 | W |
| 4 | 9 | 10.3 | 0.1 | 684TTS | F684TTS | 4 | 1 | 641 | 227 | 53 | 63 | W/J/TW |
| 4 | 16 | 18 | 0.3 | 634TTS | F634TTS | 5 | 1 | 1340 | 523 | 36 | 43 | J |
| 5 | 8 | 9.2 | 0.1 | MF85TTS | MR85TTS | 2.5 | 0.6 | 218 | 90 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 5 | 9 | 10.2 | 0.15 | MR95TTZ | MF95TTS | 3 | 0.6 | 431 | 169 | 50 | 60 | W |
| 5 | 13 | 15 | 0.2 | 695TTS(4) | F695TTS(4) | 4 | 1 | 1077 | 432 | 43 | 50 | J |
| 5 | 16 | 18 | 0.3 | 625TTS | F625TTS | 5 | 1 | 1729 | 675 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 6 | 10 | 11.2 | 0.15 | MR106TTS(4) | MF106TTS(4) | |||||||
| 6 | 12 | 13.2* | 0.2 | MR126TTS(4) | MF126TTS(4) | 4 | 0.8 | 716 | 295 | 43 | 50 | W/J/TW |
| 6 | 13 | 15 | 0.15 | 686TTS | F686TTS | 5 | 1.1 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J/TW |
| 6 | 15 | 17 | 0.2 | 696TTS | F696TTS | 5 | 1.2 | 1340 | 523 | 40 | 45 | J |
| 6 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 626TTS(4) | F626TTS(4) | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 32 | 40 | J/TW |
| 7 | 11 | 12.2 | 0.15 | MR117TTS | MF117TTS | 3 | 0.6 | 455 | 202 | 43 | 50 | W |
| 7 | 13 | 14.2* | 0.2 | MF137TTS | MF137TTZ | 4 | 0.8 | 541 | 276 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 7 | 14 | 16 | 0.15 | 687TTS | F687TTS | 5 | 1.1 | 1173 | 513 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 7 | 19 | 22 | 0.3 | 607TTS(4) | F607TTS(4) | 6 | 1.5 | 2336 | 896 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 7 | 22 | 25 | 0.3 | 627TTS | F627TTS | 7 | 1.5 | 3287 | 1379 | 30 | 36 | J/TW |
| 7 | 26 | 0.3 | 637TTS | 9 | 4563 | 1983 | 28 | 34 | J | |||
| 8 | 12 | 13.2* | 0.15 | MR128TTS | MF128TTS | 3.5 | 0.8 | 543 | 274 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 8 | 16 | 18 | 0.2 | 688TTS | F688TTS | 5 | 1.1 | 1252 | 592 | 36 | 43 | J/TW |
| 8 | 22 | 25 | 0.3 | 608TTS | F608TTS | 7 | 1.5 | 3293 | 1379 | 34 | 40 | J/TW |
| 9 | 14 | 15.5 | 0.1 | 679TTS | F679TTS | 4.5 | 0.8 | 919 | 468 | 36 | 42 | J |
Notes
*This dimension is increased by 0.4mm for shielded or seal version
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix S or H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
TTS(4) uses smaller ball, load rating is lower than standard
Value(5) is not based up upon JIS B 1521
TTS SEAL ball bearings
Inch series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Radius (rs – min) | TTS Seal Part No | Flange TTS Seal Part No | Shield Width (B1) | Shield Flange Width (Bf1) | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 0.0781 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0039 | R1-4TTS* | FR1-4TTS* | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 284 | 96 | 67 | 80 | W |
| 0.0937 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.0059 | R1-5TTS* | FR1-5TTS* | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 552 | 176 | 60 | 71 | W |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0039 | R144JTTS* | FR144TTS* | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 311 | 110 | 67 | 80 | J |
| 0.125 | 0.25 | 0.296 | 0.0039 | R144TTS* | FR144TTS* | 0.1094 | 0.031 | 284 | 96 | 67 | 80 | W |
| 0.125 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.0039 | R2-5TTS* | FR2-5TTS* | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 558 | 180 | 60 | 67 | W/J |
| 0.125 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.0059 | R2-6TTS* | FR2-6TTS* | 0.1406 | 0.031 | 640 | 227 | 53 | 63 | J |
| 0.1875 | 0.3125 | 0.359 | 0.0039 | R156TTS* | FR156TTS* | 0.125 | 0.036 | 359 | 150 | 53 | 63 | W |
| 0.1875 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.0039 | R166TTS* | FR166TTS* | 0.125 | 0.031 | 709 | 272 | 50 | 60 | J |
| 0.1875 | 0.5 | 0.565 | 0.0118 | R2TTS* | 0.196 | 0.042 | 1301 | 488 | 43 | 53 | J | |
| 0.25 | 0.375 | 0.422 | 0.0039 | R168TTS* | FR168TTS* | 0.125 | 0.036 | 373 | 172 | 48 | 56 | W |
| 0.25 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.0059 | R188TTS* | FR188TTS* | 0.1875 | 0.045 | 1082 | 442 | 40 | 50 | J |
| 0.25 | 0.625 | 0.69 | 0.0118 | R4TTS* | FR4TTS* | 0.196 | 0.0633 | 1480 | 621 | 38 | 45 | J |
| 0.3125 | 0.5 | 0.547 | 0.0059 | R1810TTS* | FR1810TTS* | 0.1562 | 0.031 | 542 | 276 | 40 | 48 | W |
| 0.375 | 0.875 | 0.969 | 0.0157 | R6TTS | FR6TTS** | 0.2812 | 0.062 | 3332 | 1411 | 32 | 38 | J |
| 0.5 | 1.125 | 1.2252 | 0.0157 | R8TTS | FR8TTS** | 0.3125 | 0.062 | 5108 | 2413 | 27 | 32 | J |
Notes
*Available with inner ring width extended by 0.0156″ (0.3962mm) each side
Bearings also available with stainless materials: prefix S
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Extra Thin TTS Ball Bearings - 6700 6800 6900
Metric Series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Flange Ø (Df) | Open Width (B) | Open Flange Width (Bf) | Radius (rs – min) | TTS Seal Part No | Flange TTS Seal Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) |
| 10 | 15 | 16.5 | 3 | 0.8 | 0.15 | 6700TTS | 855 | 435 | 15 | 17 | |
| 12 | 18 | 19.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6701TTS | F6701TTS | 926 | 530 | 13 | 15 |
| 15 | 21 | 22.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6702TTS | F6702TTS | 937 | 582 | 11 | 13 |
| 17 | 23 | 24.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6702TTS | F6703TTS | 1000 | 658 | 9.5 | 11 |
| 20 | 27 | 28.5 | 4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 6704TTS | F6704TTS | 1402 | 729 | 8.5 | 10 |
Notes
Bearings also available with stainless materials: suffix H
Bearing also available with single shield or seal: suffix Z, RS, RU or TS
Carbon Chrome bearings use RJ type retainer, stainless steel bearings use J type retainer
Large Size Stainless Steel TTS Seal Ball Bearings 6000H 6200H 6300H
Metric series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Radius (rs – min) | TTS Seal Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 10 | 26 | 8 | 0.3 | 6000HTTS* | 3860 | 1570 | 31 | 36 | J |
| 12 | 28 | 8 | 0.3 | 6001HTTS* | 4340 | 1910 | 27 | 32 | J/TW |
Extra Thin TTS Seal Ball Bearings - ET
Metric series

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Shield/ Seal Width (B1) | Radius (rs – min) | TTS Seal Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 16 | 23 | 4.5 | 4.5 | 0.15 | ET2316TTS | 968 | 619 | 20 | 24 | W |
| 20 | 25 | 4 | 4 | 0.15 | ET2520TTS | 1011 | 691 | 17 | 20 | W |
Extra Thin TTS Seal Ball Bearings - ER
Inch

| Bore Ø (d) | Outer Ø (D) | Open Width (B) | Shield/ Seal Width (B1) | Radius (rs – min) | ZZ Shield Part No | Load Rating Cr(N) | Load Rating Cor(N) | Max Speed Grease (x1000 rpm) | Max Speed Oil (x1000 rpm) | Cage Type |
| 0.3750 | 0.6250 | 0.1562 | 0.1562 | 0.0098 | ER1038 | 856 | 435 | 30 | 35 | W |
| 0.5000 | 0.7500 | 0.1562 | 0.1562 | 0.0098 | ER1212 | 918 | 542 | 24 | 28 | W |
| 0.6250 | 0.8750 | 0.1562 | 0.1562 | 0.0098 | ER1458 | 968 | 619 | 20 | 24 | W |
| 0.7500 | 1.0000 | 0.1562 | 0.1562 | 0.0098 | ER1634 | 1011 | 691 | 17 | 20 | W |
Notes
Bearings also available with single shield or seal: suffix ZS or TS
Bearings also available with stainless material: suffix S